Table of Contents
Exploring Medical Imaging: Techniques and Applications in Modern Healthcare
X-rays in medical imaging, together with CT scanners, MRI scans, and hybrid scanners such as PET-CT and SPECT-CT, are pivotal in producing detailed images of the human body for diagnostic purposes. These technologies allow healthcare professionals to generate and scrutinise images to evaluate and diagnose various medical conditions. This critical process facilitates the development of personalised treatment plans for individual patients. Furthermore, medical imaging is crucial for the ongoing monitoring of potential health issues, making it an essential component of continuous health screening programmes.
Since the discovery of X-rays, radiologists have been able to depict the human body in intricate detail using a variety of medical imaging scanners. These include computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and ultrasound, among other techniques. Examples of hybrid scanners include PET-CT, which combines PET’s functional imaging with CT’s anatomical detail, and SPECT-CT, which integrates single photon emission computed tomography with CT for enhanced diagnostic accuracy.
Healthcare organisations utilise screening programmes, such as advanced positron emission mammography (PEM), to detect breast cancer. Ultrasound remains the most prevalent and extensively used imaging method, suitable for examining the liver, kidneys, muscles, and joints.
Medical imaging is crucial in evaluating various heart conditions through cardiac imaging. This article concisely overviews the different medical imaging modalities employed in hospitals and healthcare settings, highlighting the integration of traditional and hybrid technologies for comprehensive diagnostics.

What is an X-ray?
In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Röentgen was working in his laboratory at Würzburg University in Germany when he observed crystals near a high-voltage cathode-ray tube beginning to glow. He concluded that a form of energy was being generated by the cathode-ray tube -which was able to penetrate the nearby paper – causing the crystals to glow. Röentgen named the unknown energy ‘X-radiation’.
X-rays in medical imaging are now a general diagnostic procedure used to obtain images inside the human body. The procedure only takes a few minutes. The significant advantage of this imaging technique is that the X-ray machine does not enclose the human body, which can, therefore, limit anxiety in people suffering from claustrophobia.
X-ray in medical imaging is commonly used to check for damaged or broken bones in the human skeleton. In the field of dentistry, X-rays prove crucial for assessing the health of teeth and deciding if treatment is needed. Generally, X-rays are also utilized to guide surgeons during surgical procedures, such as in the detection of bone tumours.
What is a CT scan?
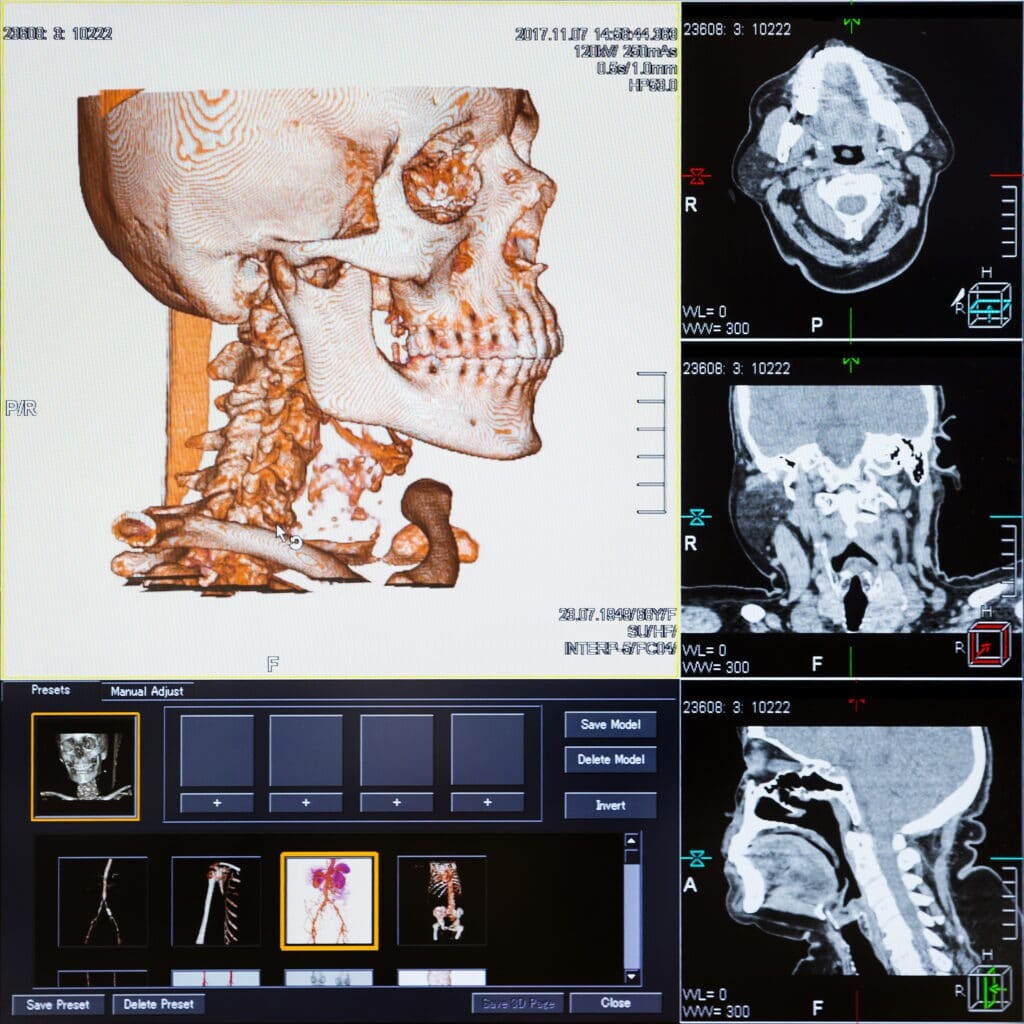
The CT scanner is able to create an internal image of the human body by using a combination of X-rays and computers. Ultimately, the CT scanner is an advanced X-ray machine that can produce 3-D images of soft tissue inside the body. This is in contrast to planer X-ray machines, which only generate 2-D images and can be used to detect pneumonia and certain cancers.
Furthermore, the CT scanner can visualise several parts of the human body, including the skeleton, internal organs, and blood vessels. CT scanning is mostly used on the brain, neck, spine, and chest. Another important use of the CT scanner is to locate tumours and broken bones within the patient.
However, an X-ray scan can sometimes be inconclusive; in such cases, a CT scanner is used to aid further diagnosis. During the CT scanning process, the patient lies on a movable horizontal bed that enters the scanner. The gantry, which houses the X-ray units, rotates around the patient’s body in cross-sections. It is crucial for the patient to remain still during this stage to ensure the clarity of the CT images.
During the scanning procedure, the radiologist will be in an adjoining room to operate the scanner and be shielded from the radiation. The CT scan can take up to 20 minutes – depending on the condition of the patient – and a computer subsequently analyses the scans. Also, CT scanning is a non-invasive, pain-free technique.
What is an MRI scan?
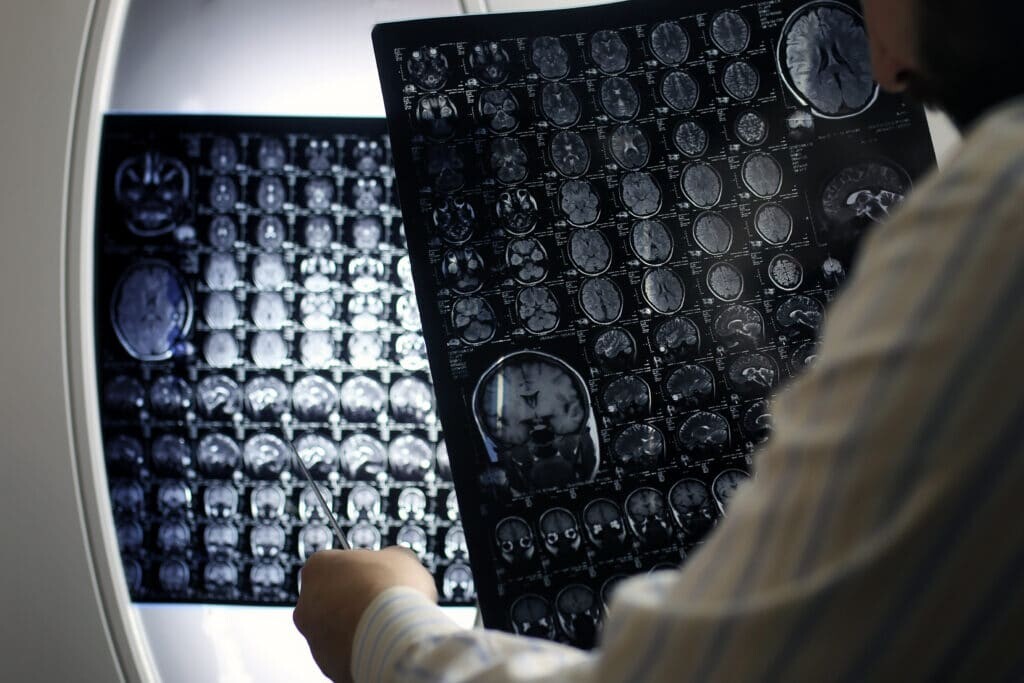
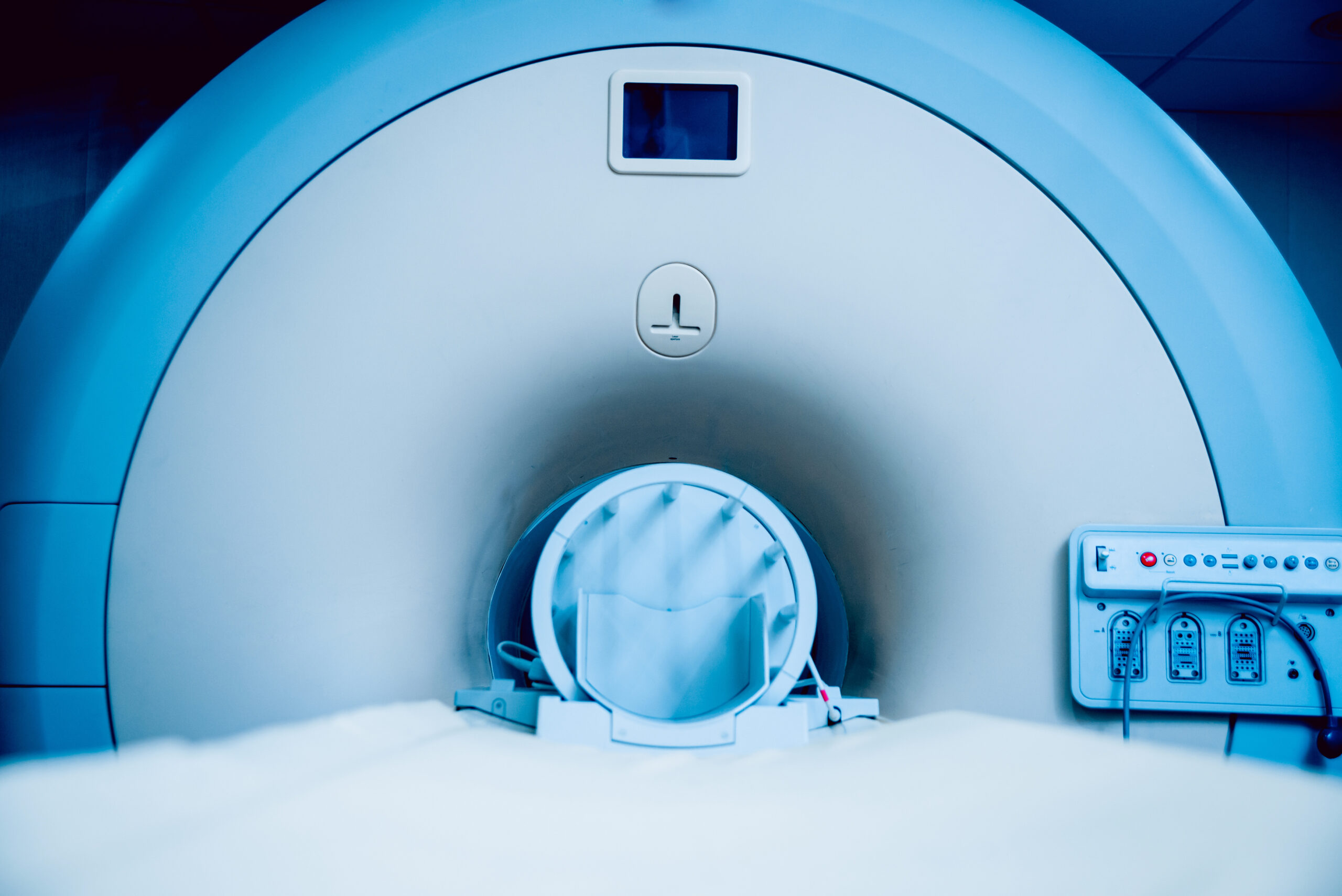
Magnetic resonance imaging, known as an MRI scan, is a technique to produce cross-sectional images of the human body. CT and MRI produce high-quality images that enable healthcare professionals to evaluate the disease state in the patient.
MRI is used to scan the brain and spinal cord, for example, in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and other neurological conditions. It also scans the skeleton, heart, blood vessels, and internal organs. In contrast to the CT scanner, the MRI scanner surrounds the whole body. The process involves the patient lying on a movable bed, which slowly transports into a ‘cylinder’ with a patient-friendly entry diameter of at least 60 cm.
The patient will then be subjected to a strong magnetic field and a sequence of radio waves to create the images. While the patient is in the MRI scanner, the radiographer will be in an adjacent viewing room and in contact with the patient. The MRI scan can take up to 90 minutes and is a much noisier machine than the CT scanner. Hence, the patient will be given ear protection.
There are several advantages of having an MRI scan – as opposed to a CT scan – primarily because X-ray radiation is not involved. Therefore, it remains a safe procedure that is suitable for use on pregnant women. Since MRI uses strong magnetic fields, it is essential for the patient to notify healthcare professionals about shunts, pacemakers and any metal objects within the body.
In some cases, patients will be offered an open MRI scanning procedure instead of a closed system. These open scanners will still provide high-quality imaging but are unsuitable for cardiac and breast imaging. The main benefit of the open MRI scanner is for patients who experience anxiety or claustrophobia. The patient in the open MRI scanner will be more comfortable, relaxed, and able to remain still, allowing the radiographer to obtain high-quality scans.
What is a PET scan?
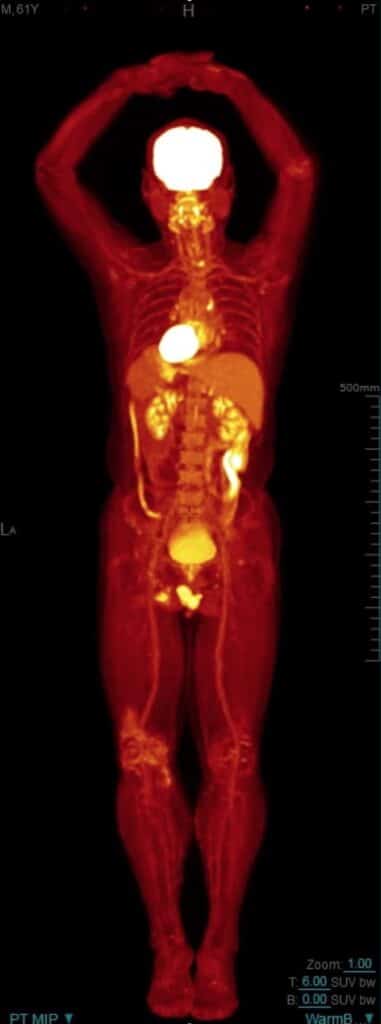
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) creates 3-D images of the human body. These scanners are mostly located in the Nuclear Medicine Departments of hospitals and healthcare providers. The PET scanner can be combined with CT to produce images of the body’s internal workings.
A whole-body PET scan is used on cancer patients to detect the disease’s progression and evaluate the patient’s response to chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatment. These PET scans are also used in the planning of certain types of surgery, such as brain or heart operations. Furthermore, PET imaging can help diagnose dementia by evaluating brain function.
When a patient is scheduled for a PET scan, they are injected with a radiotracer, typically FDG (18F-fluorodeoxyglucose). This substance is administered into the arm and emits radiation over a defined period.
The PET scanner detects the radiation emitted, creates the images, and indicates the level of radiation accumulating inside the body. Accordingly, if no FDG levels are indicated, that would specify normal body function within that particular region of the body.FDG is similar to glucose; cancer cells will take this radiotracer up faster than normal cells.
Therefore, by analysing the PET scans for FDG accumulation, the type of cancer can be identified and tracked throughout the human body. A typical PET scan can take up to 30 minutes to complete. Furthermore, the PET scanner can be used to investigate metabolic changes at the cellular level in various organs or tissues, which would be more of a challenge with CT or MRI scanners.
What is an ultrasound scan?
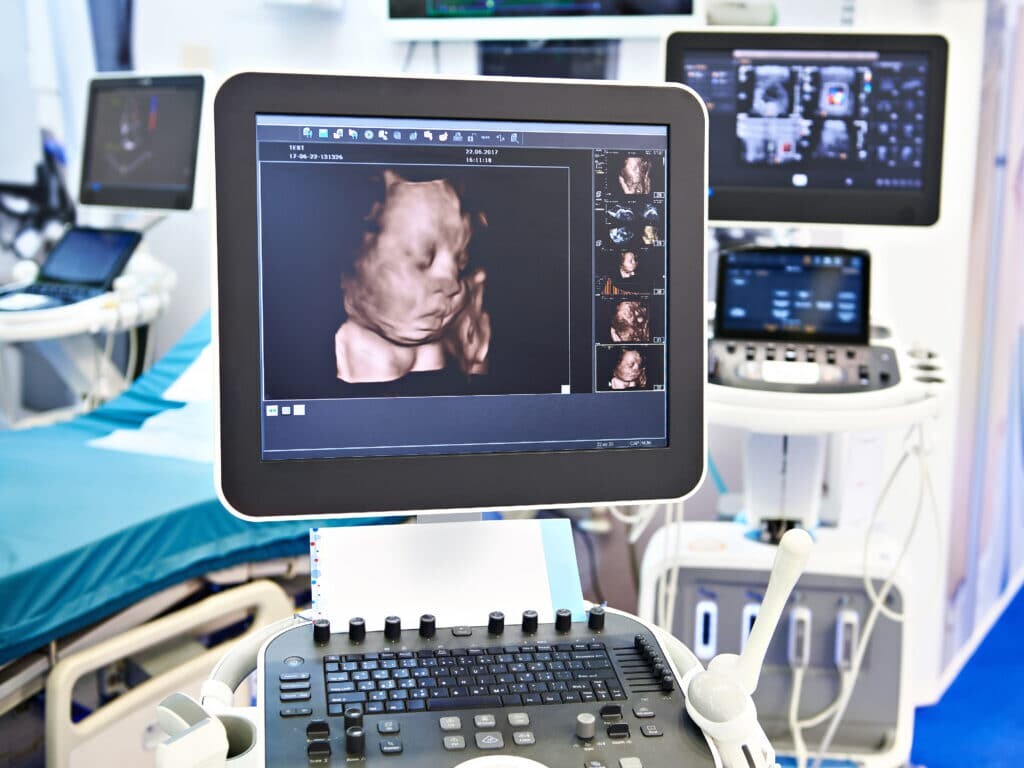
An ultrasound scanner produces images by passing high-frequency waves into the human body. Ultrasound is widely used to obtain images of unborn children in real-time. They are also used by surgeons – for specific procedures – to help them in the diagnosis of the patient. Ultrasound systems work by using a probe capable of emitting high-frequency sound waves. The sound waves reflect off various organs and surrounding tissues to create echoes, which bounce back to the probe to form 2-D or 3-D images in real-time. The scanning process can last up to 45 minutes and is performed externally and internally.
Accordingly, endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is an invasive procedure to investigate gastrointestinal and lung diseases. The EUS imaging technique can be used to find the causes of abdominal or chest pain. EUS can be used with other diagnostic tests, such as CT and MRI scans, to evaluate colon, oesophagus, lung, pancreas, stomach and rectum cancers. The main advantage of ultrasound is that there are no patient after-effects, and normal activities can be resumed.
Mobile Scanners
It is important to address the rising demand for medical imaging and provide the advanced technologies that patients require. Accordingly, there is an increase in demand from the private sector and the NHS for mobile scanning. These portable scanners aim to improve diagnosis and deliver quality patient care. Essentially, these units help reduce hospital waiting lists and patient waiting times. Unfortunately, some hospitals do not provide a broad range of medical imaging services. Nevertheless, there is a need for everybody in society to access high-quality diagnostic services in order to improve patient treatment care plans. Mobile imaging services can help meet the hospitals’ short- and long-term requirements. These facilities can incorporate CT, MRI, Cardiac Cath Labs, X-ray, DEXA scanning, and PET-CT imaging, amongst others.
You Are Here: Home »
Tags: Computed Tomography, DEXA, Human Body, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Medical Imaging