Gamma Radiation: Its Discovery, Applications, and Safety Considerations
Gamma radiation is essential for medical imaging, cancer treatment, industrial testing, yet requires stringent safety measures due to risks
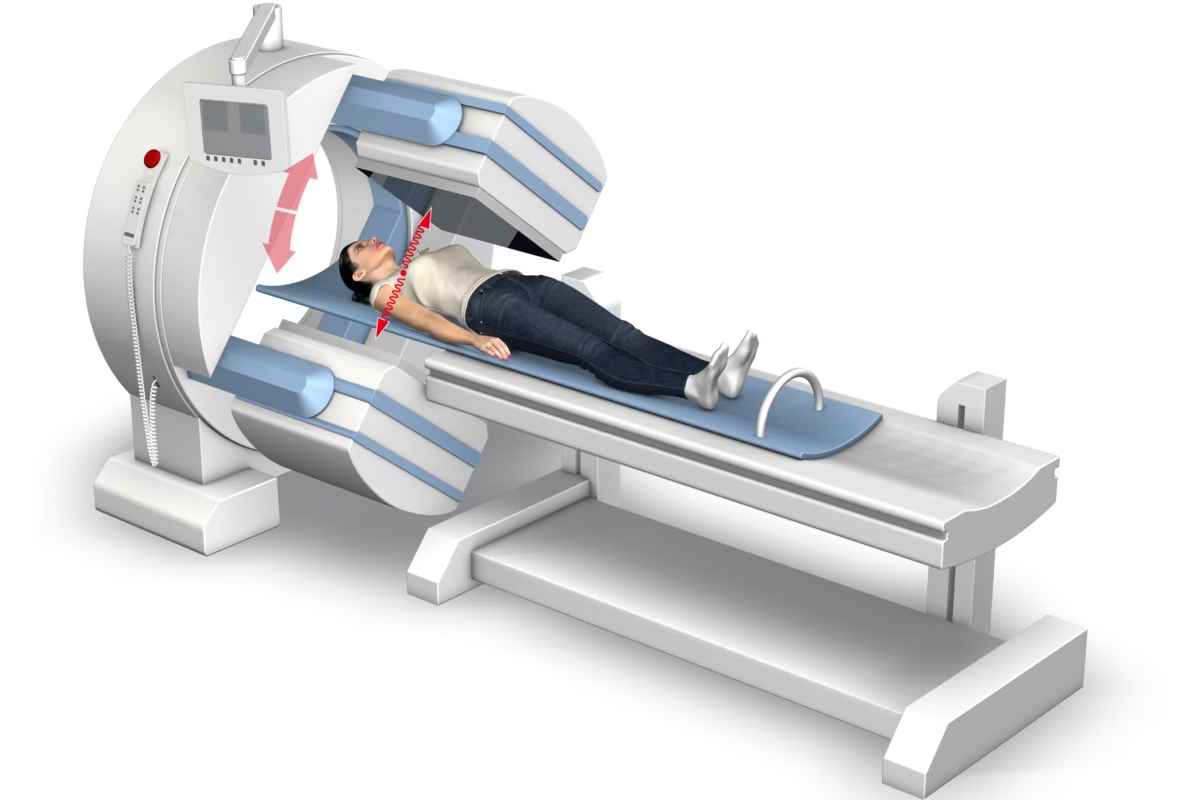
Gamma radiation therapy, also known as gamma knife surgery, represents a significant advancement in the field of medical treatment for various brain disorders, particularly brain tumours, vascular malformations, and functional disorders such as trigeminal neuralgia. This form of therapy is a type of radiosurgery. This non-invasive technique utilises highly focused beams of gamma rays to treat small to medium-sized lesions, usually in the brain. It is known for its precision and ability to reach deep-seated brain abnormalities without the need for actual surgery.
Gamma radiation therapy harnesses beams of gamma rays emitted from multiple sources of cobalt-60. These beams converge on a single point, delivering a high dose of radiation with extreme accuracy. The convergence of beams ensures that a high dose of radiation can be administered to the target area while minimising exposure to the surrounding healthy tissue. This pinpoint accuracy is critical in the brain, where the avoidance of damage to healthy tissue is paramount due to the risk of serious neurological deficits.
Gamma knife surgery is meticulous. It begins with detailed imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, to determine the lesion’s exact size, location, and shape. Based on these images, a specialised team of neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, and medical physicists collaboratively develops a treatment plan. Patients wear a stereotactic head frame, which is fixed to the skull to prevent head movement during the procedure, ensuring that the gamma rays are delivered precisely.
One of the most compelling advantages of gamma radiation therapy is that it is typically done in a single session, known as an outpatient procedure. The patient can usually return home on the same day, a stark contrast to traditional surgery, which might require a prolonged hospital stay and carries the risks associated with open surgery, such as infection and bleeding. The therapy is also associated with fewer complications and side effects compared to traditional surgery, making it a favourable option for patients who are elderly or in conditions where conventional surgery poses too high a risk.
Even though it has many benefits, gamma radiation therapy is not suitable for all types of brain tumours or patients. The nature, size, and location of the tumour influence its effectiveness. Moreover, as it is a relatively new technique, long-term data on outcomes and potential late side effects are still being gathered.
In conclusion, gamma radiation therapy is a revolutionary approach to the treatment of certain brain disorders. It offers a noninvasive alternative with precision, efficacy, and reduced recovery time compared to traditional surgical methods. As medical technology advances, the scope of its applicability may expand, offering hope to patients with complex neurological conditions.
home » Gamma Radiation Therapy
Gamma radiation is essential for medical imaging, cancer treatment, industrial testing, yet requires stringent safety measures due to risks