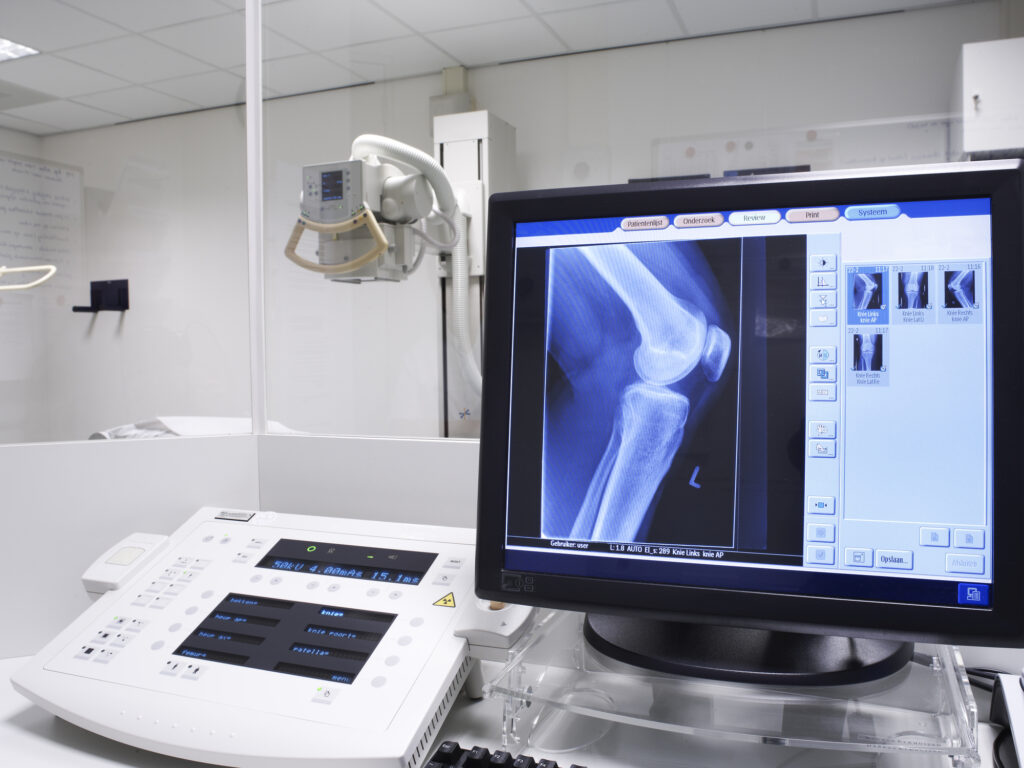
X-ray Radiography
X-ray radiography is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses X-rays to produce images of the body’s internal structures. It helps detect fractures, infections, and abnormalities in bones and soft tissues.
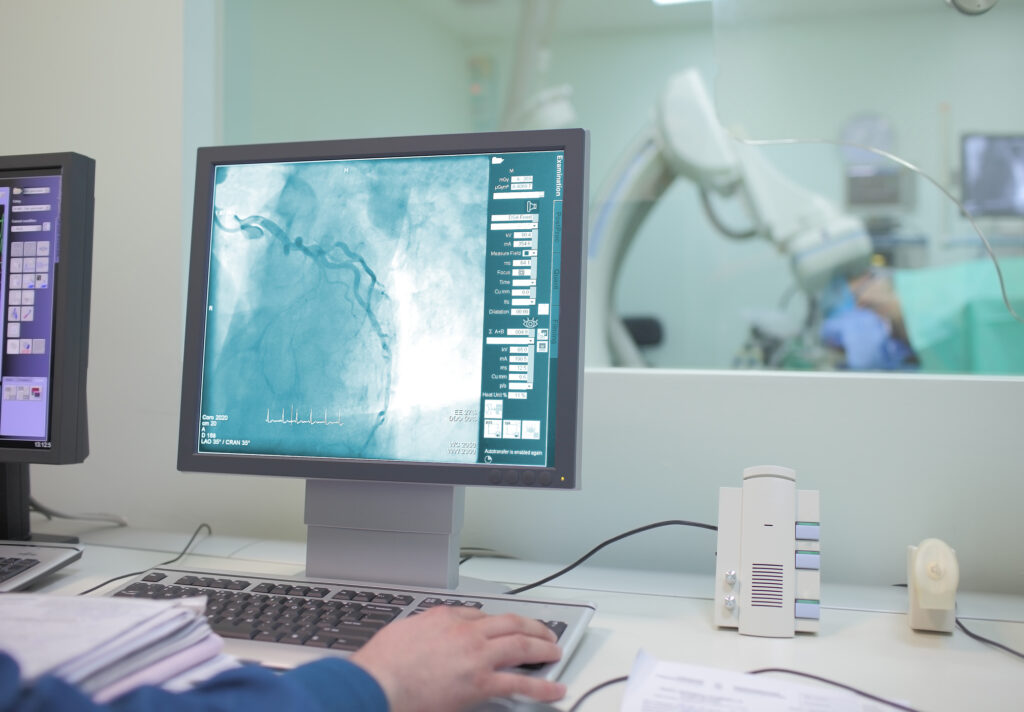
Angiography
Heart angiography is a medical procedure that uses contrast dye and X-rays to visualise the heart’s blood vessels. It helps diagnose blockages, assess heart function, and guide interventional treatments such as stenting.
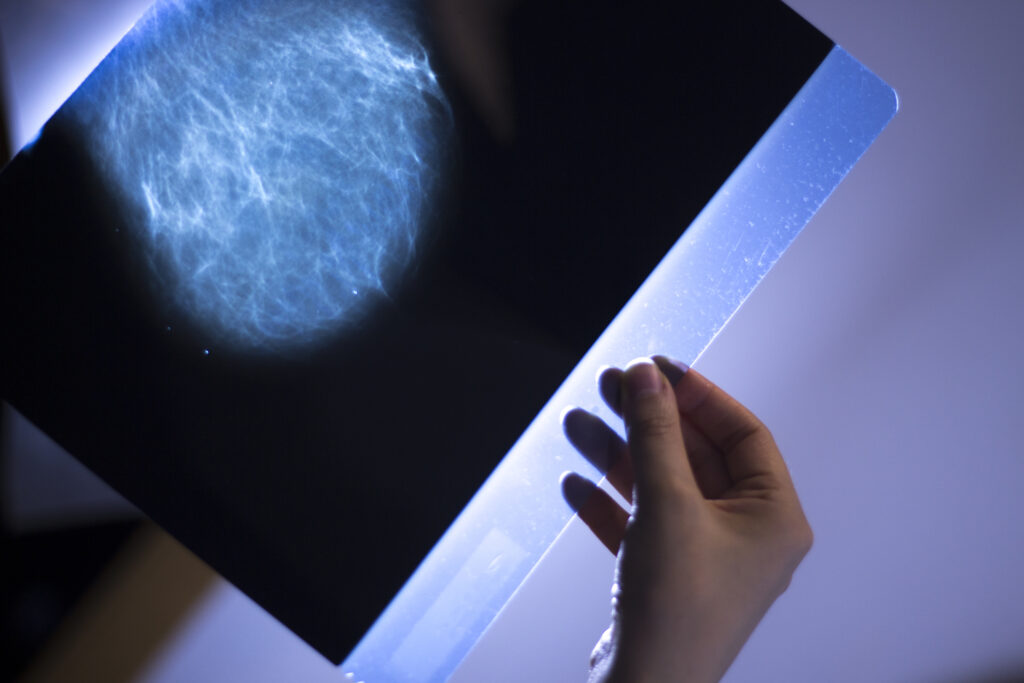
Mammography
Mammography is a specialised medical imaging technique that uses low-dose X-rays to examine breast tissue. It is essential for early detection of breast cancer and helps in assessing lumps and other abnormalities.
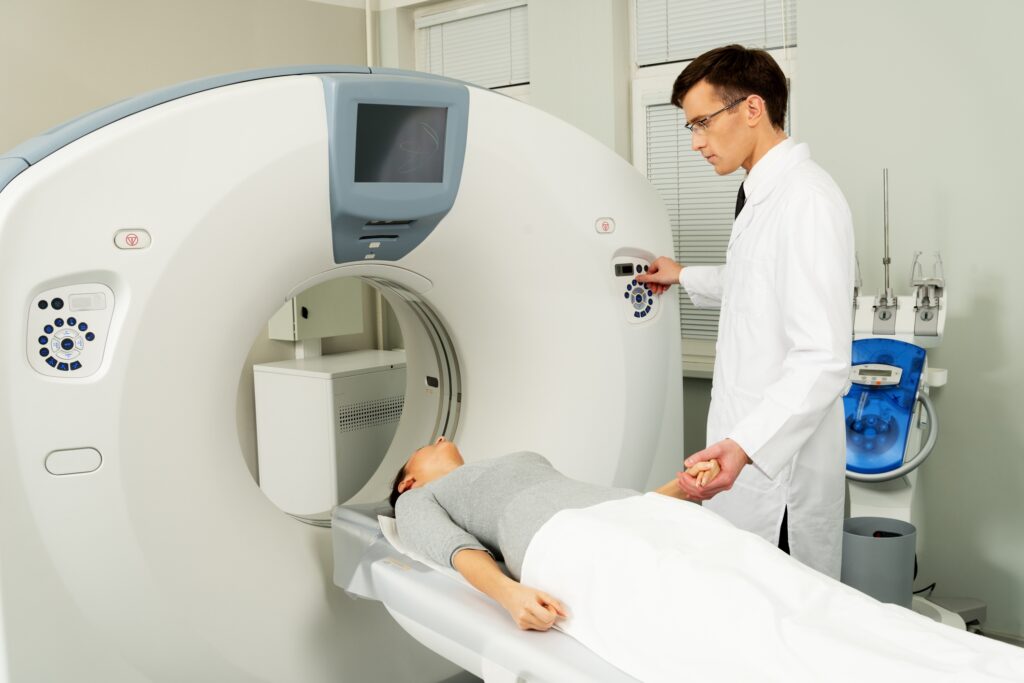
Computed Tomography
Computed Tomography (CT) is a diagnostic tool that combines X-rays with computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of internal organs, bones, and tissues. This facilitates precise medical analysis and treatment planning. Image for illustration only. People depicted are models.
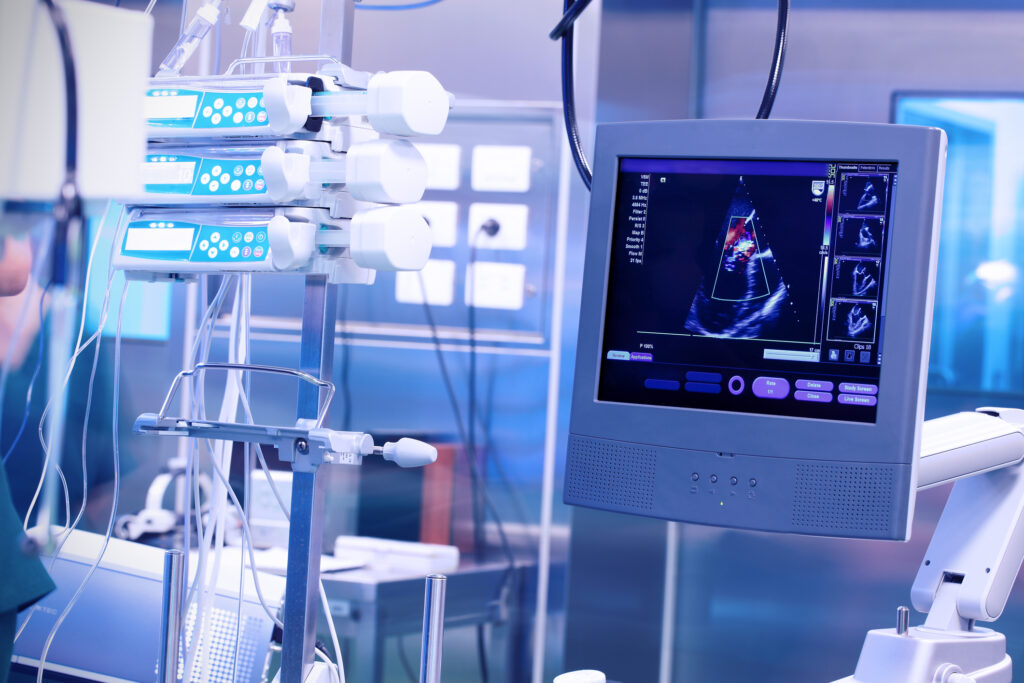
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues. It is safe, non-invasive, and widely used for prenatal screenings and diagnosing conditions.
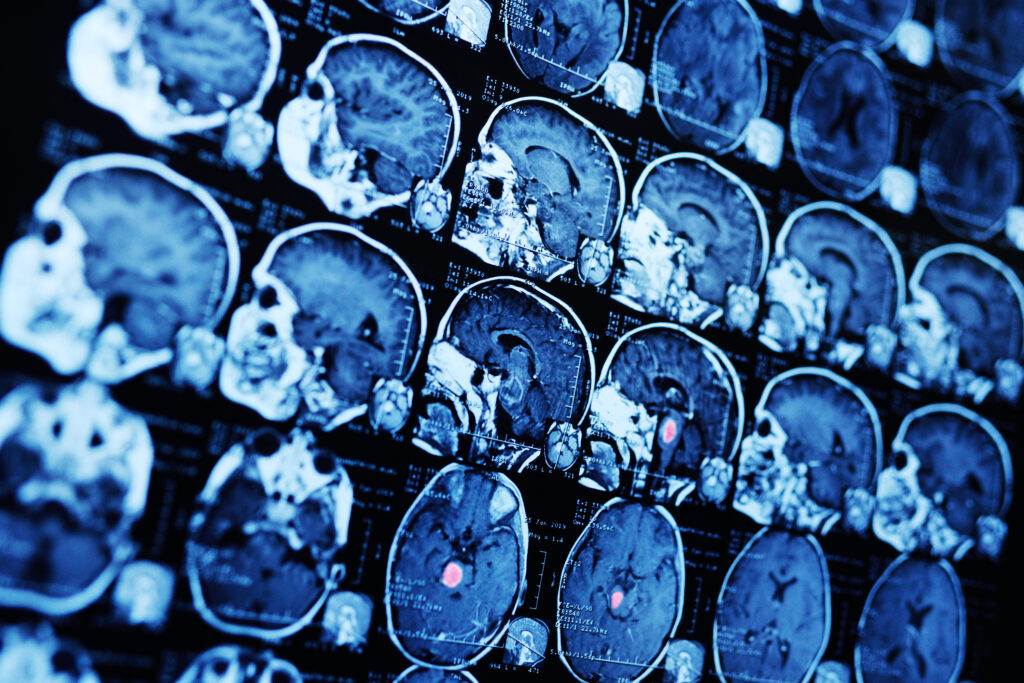
MR Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues. This aids in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
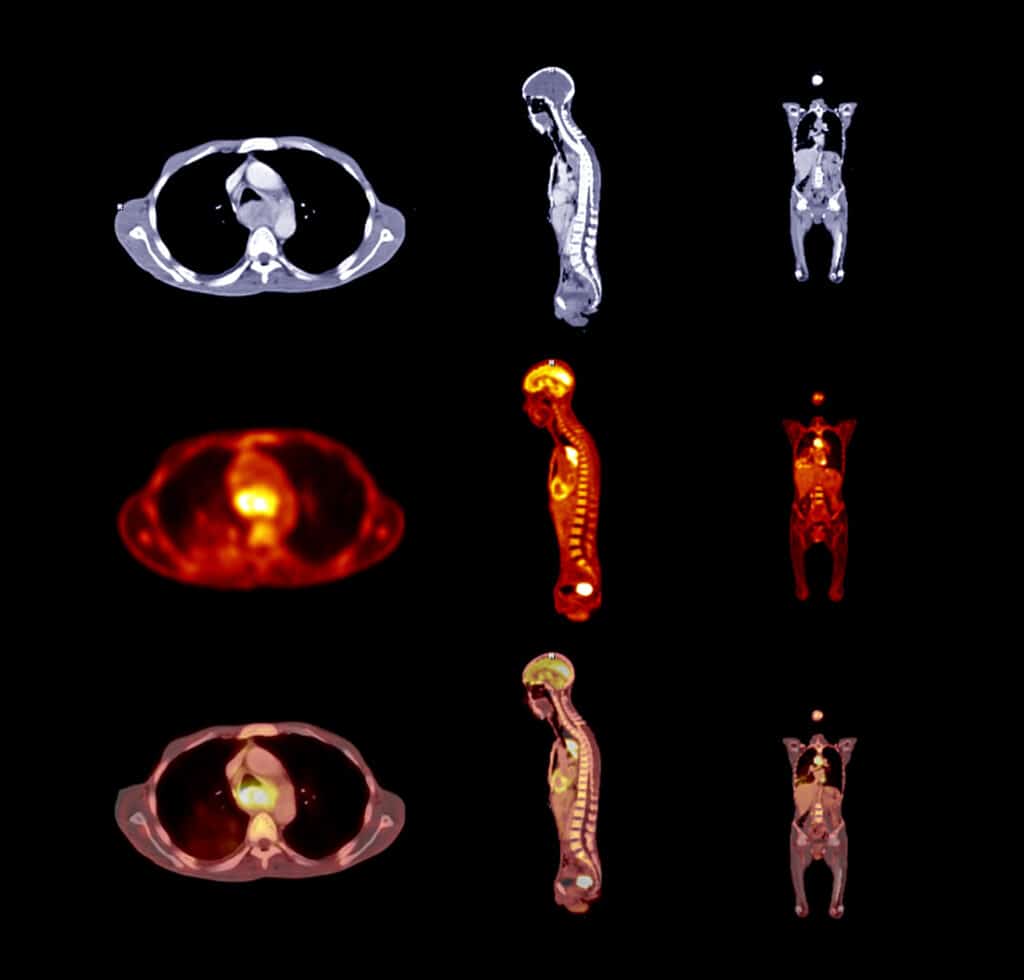
PET Imaging
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging is a sophisticated diagnostic technique that uses radioactive tracers to visualise and measure metabolic processes in tissues. It aids in detecting and managing diseases like cancer.
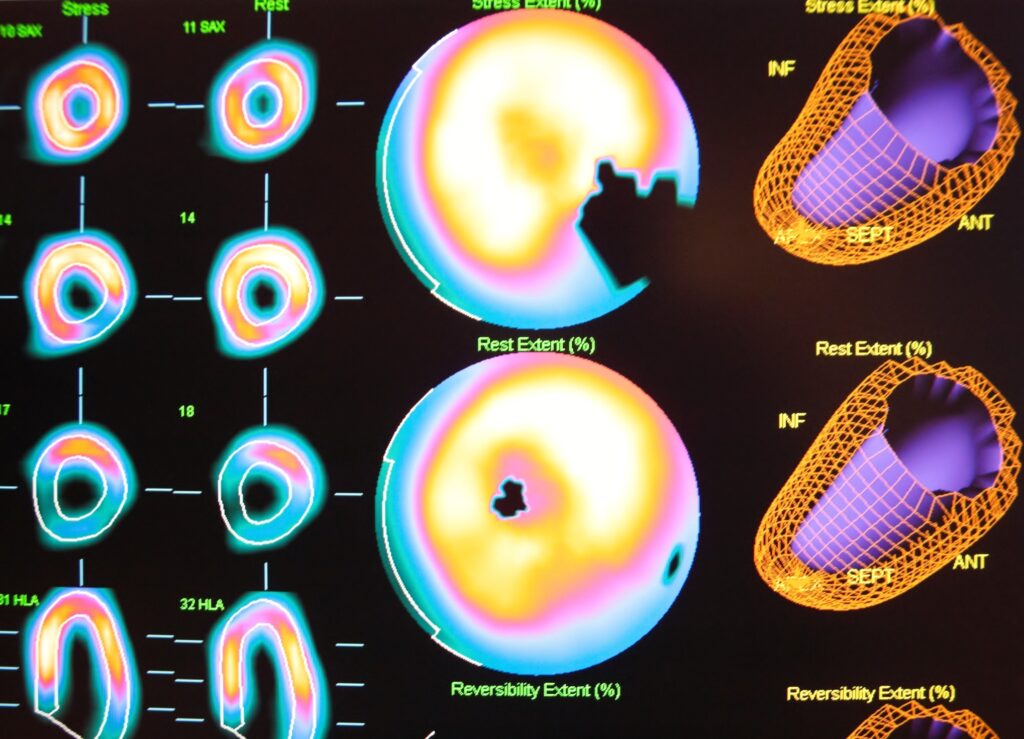
SPECT Imaging
Myoview, a radiopharmaceutical used in SPECT imaging, contains technetium Tc-99m tetrofosmin. It’s particularly effective for cardiac studies, helping to visualise and assess myocardial perfusion and identify coronary artery disease.
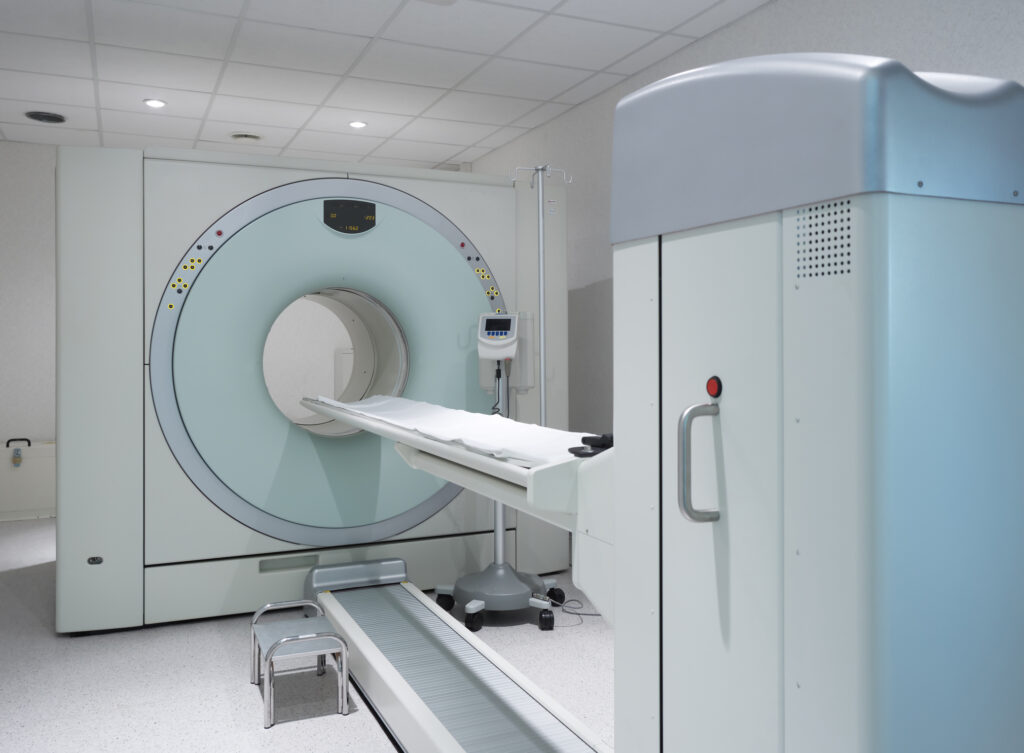
Hybrid Scanners
Hybrid scanners such as PET-CT and PET-MRI combine technologies to provide detailed images, blending metabolic and anatomical data. This integration enhances diagnostic accuracy for various diseases, including cancer, by providing comprehensive insights into body functions.
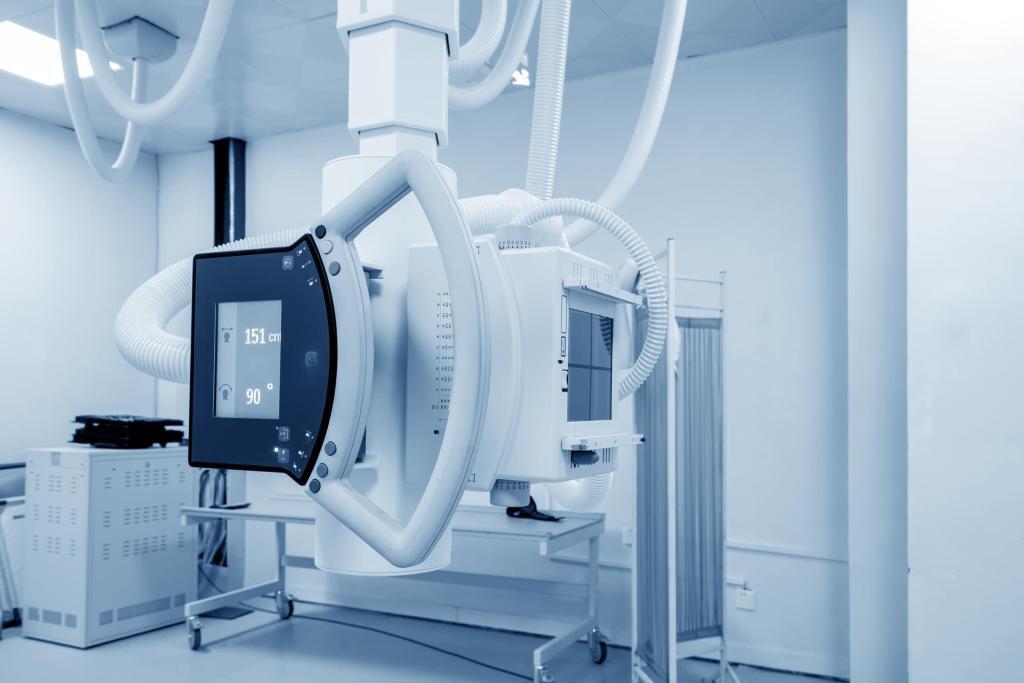
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of the body. It helps doctors diagnose and guide treatments by visualising organs, bones, and other structures.
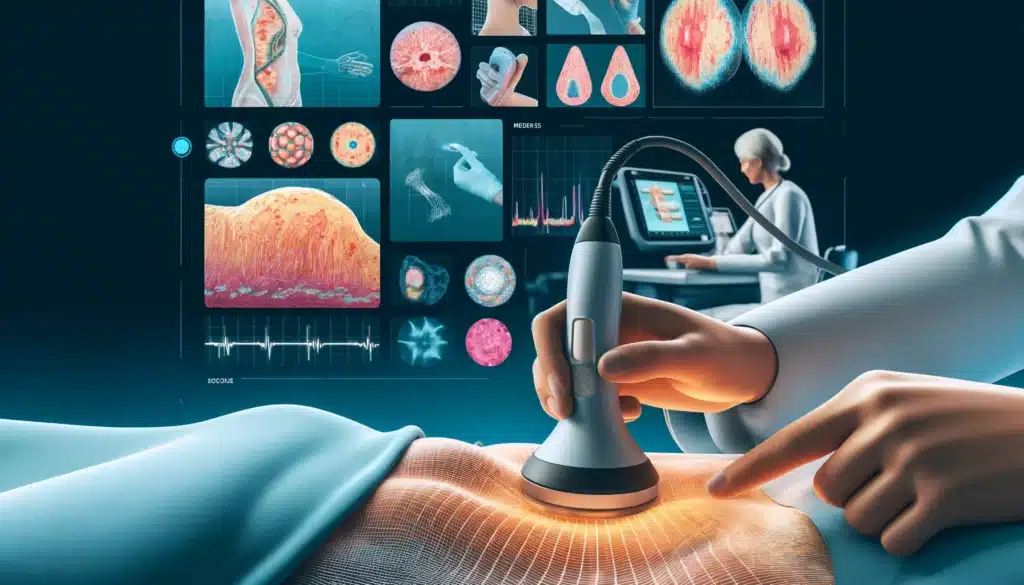
Tactile Imaging
Tactile imaging is a diagnostic technique that converts the sense of touch into a digital image. It allows clinicians to detect abnormalities in soft tissues, such as lumps, by mapping pressure patterns and providing detailed visual information.
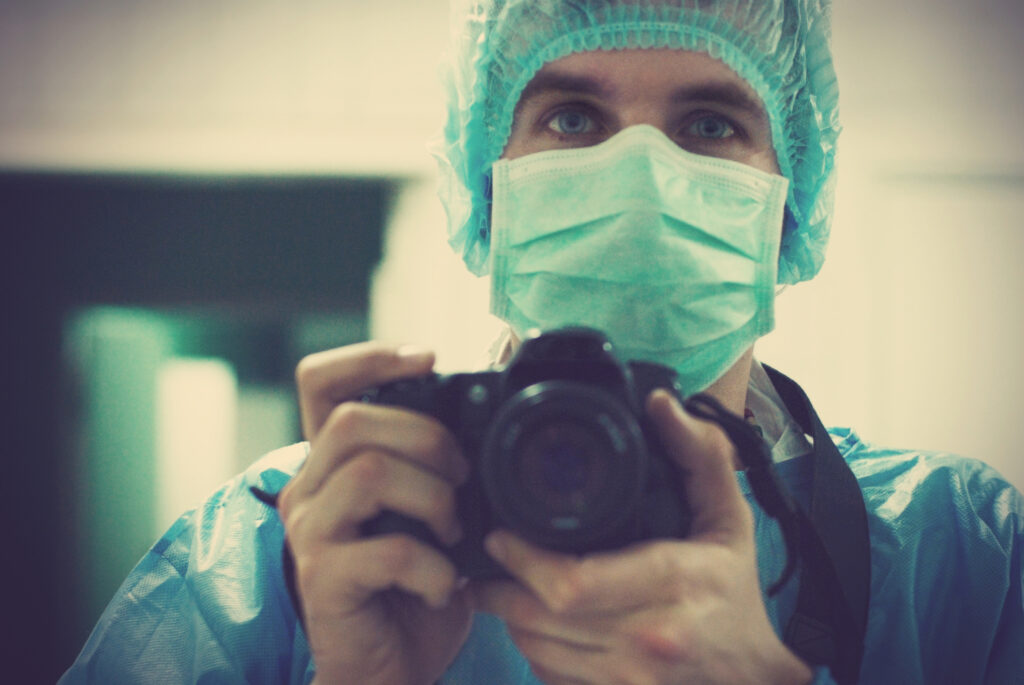

Medical Photography
Medical photography involves capturing detailed images of patients’ conditions, procedures, and treatments. These images document medical progress, aid diagnosis, and support medical education and research, providing essential visual records for accurate patient care and professional training. Image for illustration only. Person depicted is a model.
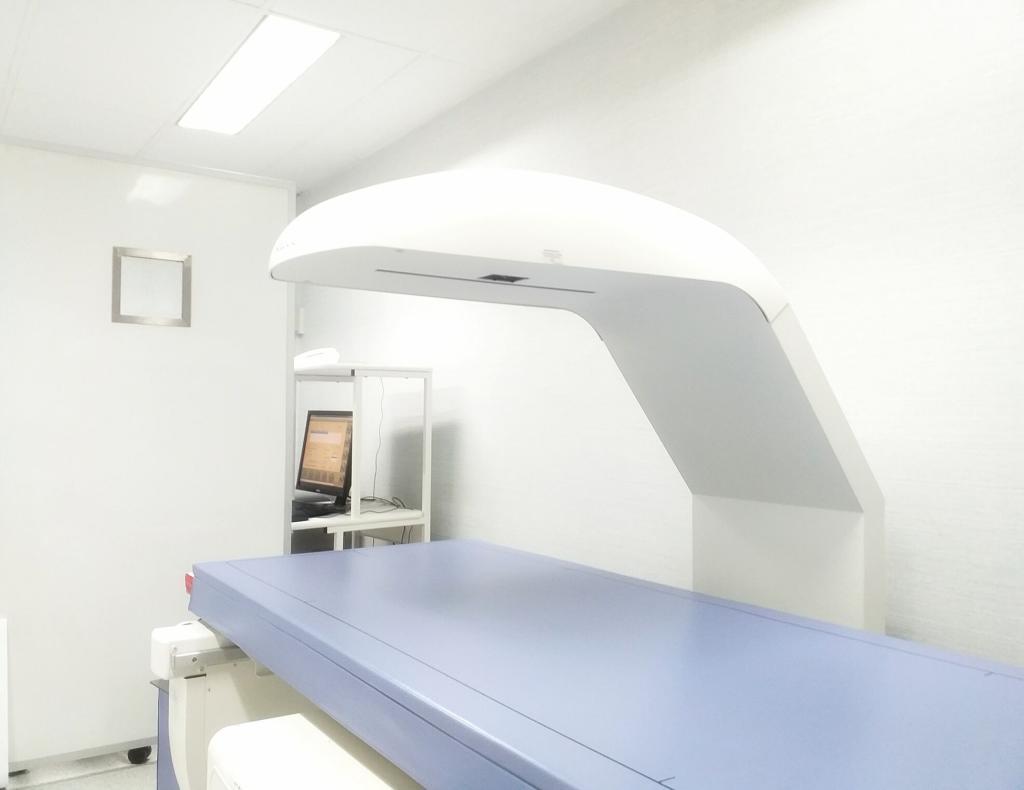
Bone Densitometry
Bone densitometry, also known as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), is a non-invasive technique for measuring bone mineral density. It helps diagnose osteoporosis and assess fracture risk, guiding treatment decisions for bone health.
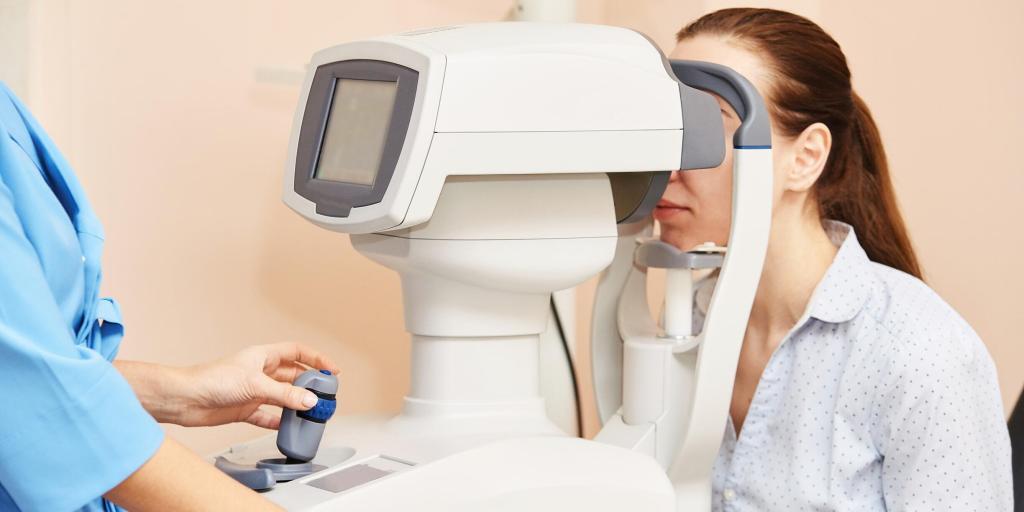
Optical Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides high-resolution, cross-sectional images of biological tissues. Widely used in ophthalmology, it aids in diagnosing and monitoring eye diseases by revealing detailed retinal structures. Image for illustration only. Person depicted is a model.
Photoacoustic Imaging
Photoacoustic imaging combines laser-induced ultrasound and optical imaging to create detailed images of biological tissues. It provides high-resolution, real-time insights into tissue composition and vascular structures, aiding in early cancer detection and other medical diagnostics.
