In recent years, GLP-1 therapy has become a transformative treatment option for individuals managing Type 2 diabetes and obesity. Standing for glucagon-like peptide-1, GLP-1 is a naturally occurring hormone that plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels, appetite, and even the body’s ability to metabolise fat.
With the advent of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1s), these medications mimic the effects of GLP-1, providing powerful benefits for those struggling with metabolic disorders. With digital health innovations, tools like a GLP-1 app are making it easier for patients to track doses, monitor progress, and stay on top of their therapy. In this article, we’ll explore what GLP-1 therapy is, its health benefits, and what patients can expect from this innovative treatment.
What is a GLP-1?
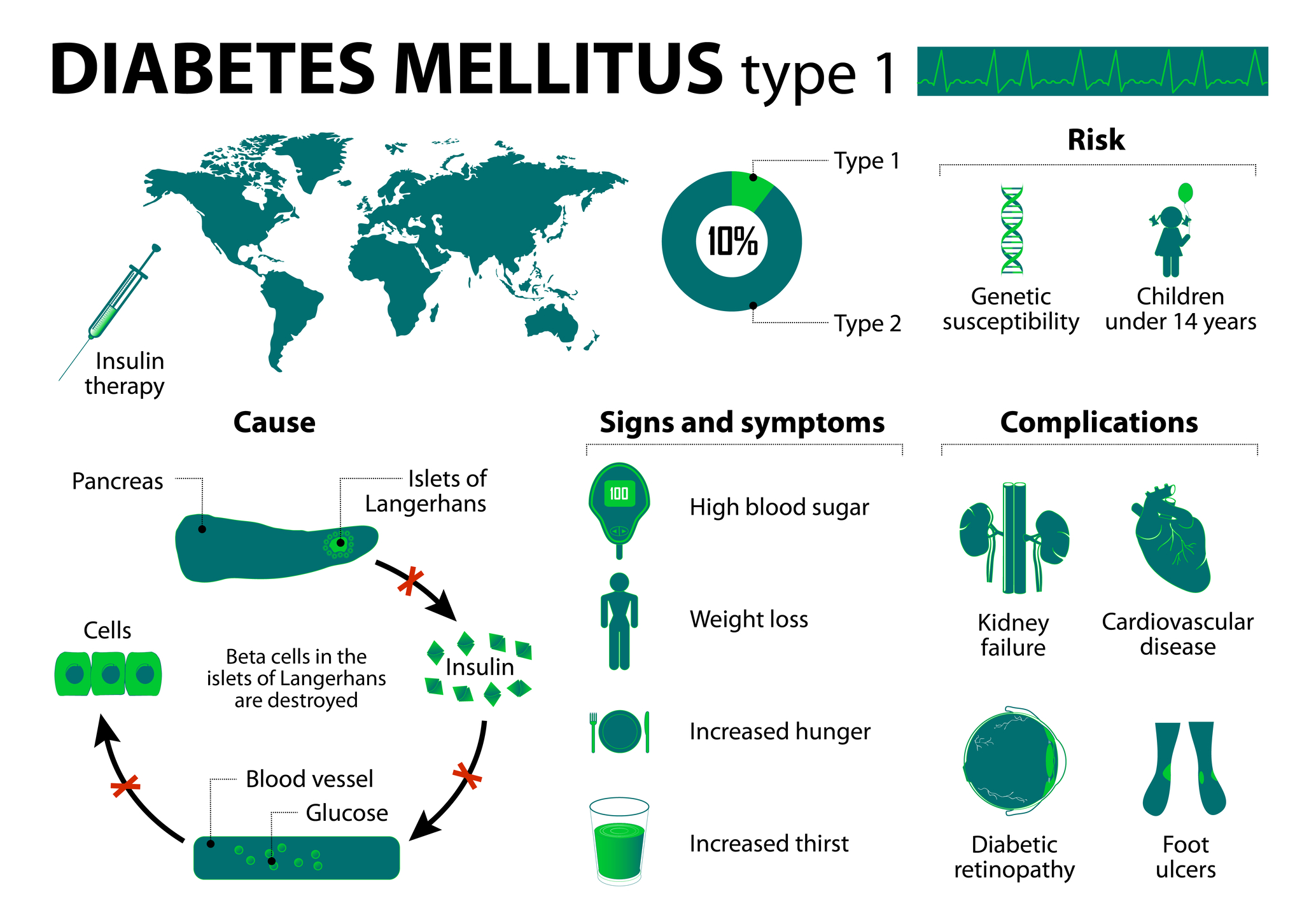
GLP-1 is a hormone secreted by the intestines in response to food intake. It plays a crucial role in regulating several physiological processes:
- Insulin Secretion: GLP-1 helps stimulate the pancreas to release insulin, a hormone essential for lowering blood glucose (sugar) levels after eating.
- Glucagon Inhibition: GLP-1 suppresses glucagon, another hormone produced by the pancreas that signals the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. This ensures that blood sugar levels don’t spike after meals.
- Appetite Regulation: GLP-1 acts on the brain to help regulate appetite and promote a feeling of fullness, which can reduce overall calorie consumption.
- Gastric Emptying: It slows the rate at which food leaves the stomach, contributing to feelings of fullness after eating and helping to manage blood sugar levels.
These functions of GLP-1 make it a key player in regulating glucose metabolism and controlling appetite, both of which are crucial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes and obesity.
How Does GLP-1 Therapy Work?
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1s) are a class of medications designed to mimic the action of the natural GLP-1 hormone. These drugs bind to GLP-1 receptors in the body, activating the same beneficial effects that GLP-1 would under normal circumstances.
The main benefits of GLP-1 therapy include:
- Enhanced insulin secretion in response to meals
- Reduced glucagon release, preventing high blood sugar levels
- Slowed gastric emptying, leading to prolonged satiety
- Decreased appetite, which may help with weight loss
Currently available GLP-1 receptor agonists include drugs like liraglutide (Victoza), semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy), exenatide (Byetta), and dulaglutide (Trulicity). These medications are typically administered via injection, although oral forms, like Rybelsus (semaglutide), are also available.
Benefits of GLP-1 Therapy
The benefits of GLP-1 therapy extend beyond just controlling blood sugar. Here are some of the primary advantages:
- Blood Sugar Control: For people with Type 2 diabetes, GLP-1 therapy offers a reliable and effective way to regulate blood glucose levels. By enhancing insulin secretion when blood sugar levels are high and reducing glucagon production, GLP-1 receptor agonists help lower fasting and post-meal glucose levels. This can be especially beneficial for those who struggle with managing blood sugar through diet and oral medications alone.
- Weight Loss: One of the most compelling benefits of GLP-1 therapy is its ability to promote weight loss. GLP-1s can slow gastric emptying, helping patients feel fuller for longer periods, which can reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, these drugs help to regulate appetite by acting on the brain, further contributing to reduced food consumption. Clinical trials have shown that semaglutide and liraglutide, in particular, can lead to significant weight loss, making them attractive options for individuals with obesity, even if they don’t have diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Recent studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists may provide cardiovascular benefits. For individuals with Type 2 diabetes, who are at an increased risk for heart disease, GLP-1 therapy has been shown to lower the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events. Semaglutide, in particular, has demonstrated a reduction in major cardiovascular events in clinical trials.
- Improved Beta-Cell Function: GLP-1 therapy may also help improve beta-cell function in the pancreas, the cells responsible for insulin production. This effect can help people with Type 2 diabetes better regulate their blood sugar over time, potentially reducing their reliance on other medications.
- Lower Blood Pressure: Some GLP-1 receptor agonists, like semaglutide and liraglutide, have also been shown to reduce blood pressure, offering an added benefit for individuals managing both high blood pressure and diabetes.
What to Expect During GLP-1 Therapy
When starting GLP-1 therapy, patients typically undergo an initial consultation with their healthcare provider to determine if this treatment is appropriate. The doctor will evaluate factors such as overall health, diabetes management, and weight loss goals before prescribing a GLP-1 receptor agonist.
Administration of GLP-1
Most GLP-1 therapies are injected subcutaneously, under the skin. The frequency of injections varies depending on the medication:
- Semaglutide (Ozempic): Once a week
- Liraglutide (Victoza): Once daily
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity): Once a week
Patients are usually instructed on how to inject the medication, and many find the process easy to manage with a pre-filled pen. For those who prefer oral medication, Rybelsus (oral semaglutide) is an option, though it is taken daily, unlike the injectable versions.
Managing Side Effects
Like any medication, GLP-1 therapy can cause side effects. The most common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
These symptoms typically occur during the early stages of treatment and may subside as the body adjusts to the medication. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimise these effects. If symptoms ramp up or feel hard to manage, having urgent care in San Clemente, CA as a same-day option can support timely evaluation. It’s important for patients to communicate with their healthcare provider if side effects persist or become bothersome.
In rare cases, GLP-1 receptor agonists can lead to more serious side effects, such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), thyroid tumours, or kidney problems. Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor for any adverse effects.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
While GLP-1 therapy can be highly effective in managing blood sugar and promoting weight loss, it is not a substitute for healthy lifestyle choices. Patients should continue to follow a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and maintain a healthy weight. The combination of GLP-1 therapy and lifestyle changes can have a profound impact on managing diabetes and improving overall health.
Cost and Accessibility
The cost of GLP-1 receptor agonists can be a concern for some patients, as these medications are often more expensive than traditional oral diabetes medications. However, many insurance plans cover these treatments, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes or obesity. Additionally, patient assistance programs may help reduce out-of-pocket costs.
GLP-1 Therapy: Advanced Healthcare
GLP-1 therapy represents a significant advancement in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes and obesity. By mimicking the natural hormone GLP-1, these medications offer a multifaceted approach to managing blood sugar, reducing appetite, promoting weight loss, and even improving cardiovascular health. With growing evidence supporting their effectiveness, GLP-1 receptor agonists are fast becoming a cornerstone of treatment for many patients.
If you are considering GLP-1 therapy, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if this treatment is appropriate. With the right guidance and lifestyle adjustments, GLP-1 therapy can provide meaningful benefits and help patients achieve better control over their health.
Disclaimer
The content provided in this article is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. GLP-1 receptor agonists and other treatments discussed are prescription medications that should only be used under the guidance and supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Individual responses to treatment may vary, and not all patients are suitable candidates for GLP-1 therapy. Always consult your doctor or another qualified medical provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment options. Open MedScience does not endorse or promote any specific brand or product mentioned in this article.
home » blog » health and wellbeing »