Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disease that causes damage to the optic nerve, which transfers information from the eye to the primary visual cortex section of the brain. In most cases, this condition is related to ocular hypertension, which causes elevated pressure within the eye. The detection and monitoring of glaucoma involve various diagnostic techniques, including optic nerve head evaluation, visual field testing and intraocular pressure measurements.
Furthermore, intraocular pressure has been identified as a risk factor for developing glaucomatous optic neuropathy (progressive loss of retinal ganglion cells). Lowering intraocular pressure delays the progression of degenerative retinal changes. Moreover, intraocular pressure values do not correlate to the extent of damage to the optic nerve head.
Nevertheless, the visualisation of the optic nerve head in glaucoma by ophthalmoscopic examination is subjective to the healthcare professional. Visual field analysis is experienced through Goldmann kinetic perimetry and threshold static automated perimetry. These techniques are used to evaluate glaucomatous neuropathy and monitor disease progression.
However, automated perimetry has several disadvantages, such as the lack of flexibility in the procedure, examining only certain variables, and patients over fifty who require a reasonable cognitive function to perform automated perimetry.
Another technique for evaluating glaucoma involves a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, which uses real-time imaging to produce 3-D images of the optic nerve head. The Heidelberg Retina Tomograph is a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (CSLO) device that provides reproducible measurements of the parapapillary retina and optic disc.
The Heidelberg Retina Tomograph uses a diode laser beam (wavelength, 670 nm) and captures 32 sequential 2-D scans in a total acquisition time of 1.6 seconds. The Heidelberg Retina Tomograph registers and aligns the 32 consecutive scans, correcting for eye movements that may occur during image acquisition.
home » glaucoma
Medical Imaging Modalities
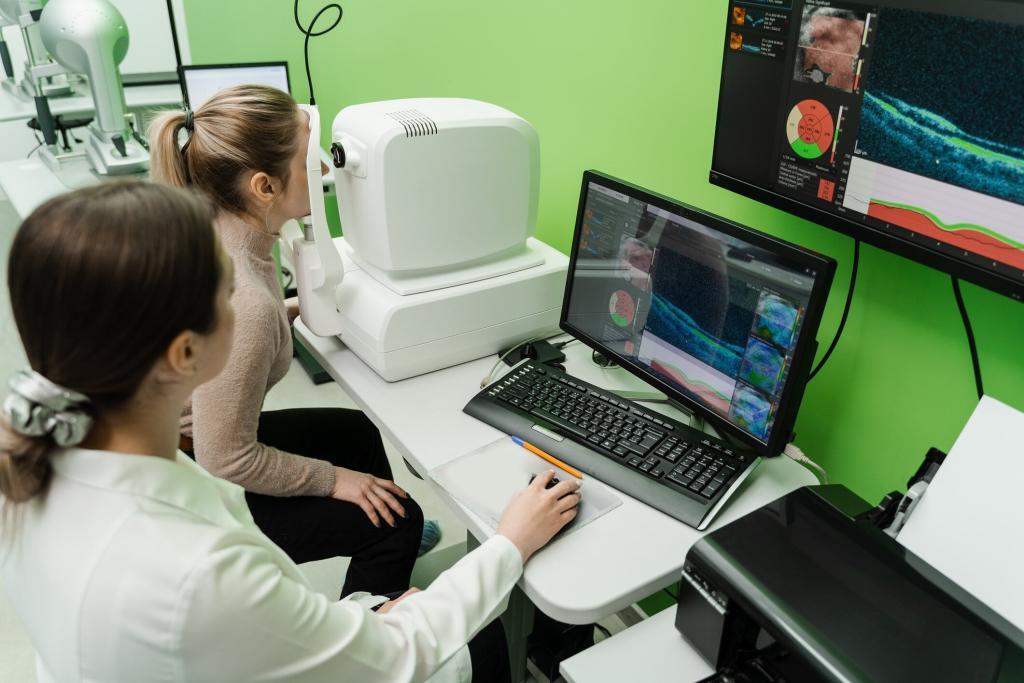
Optical Coherence Tomography revolutionises medical diagnostics by providing high-resolution, non-invasive imaging of tissue microstructures across diverse medical specialities. Image for illustration only. People depicted are models.
Optical Imaging
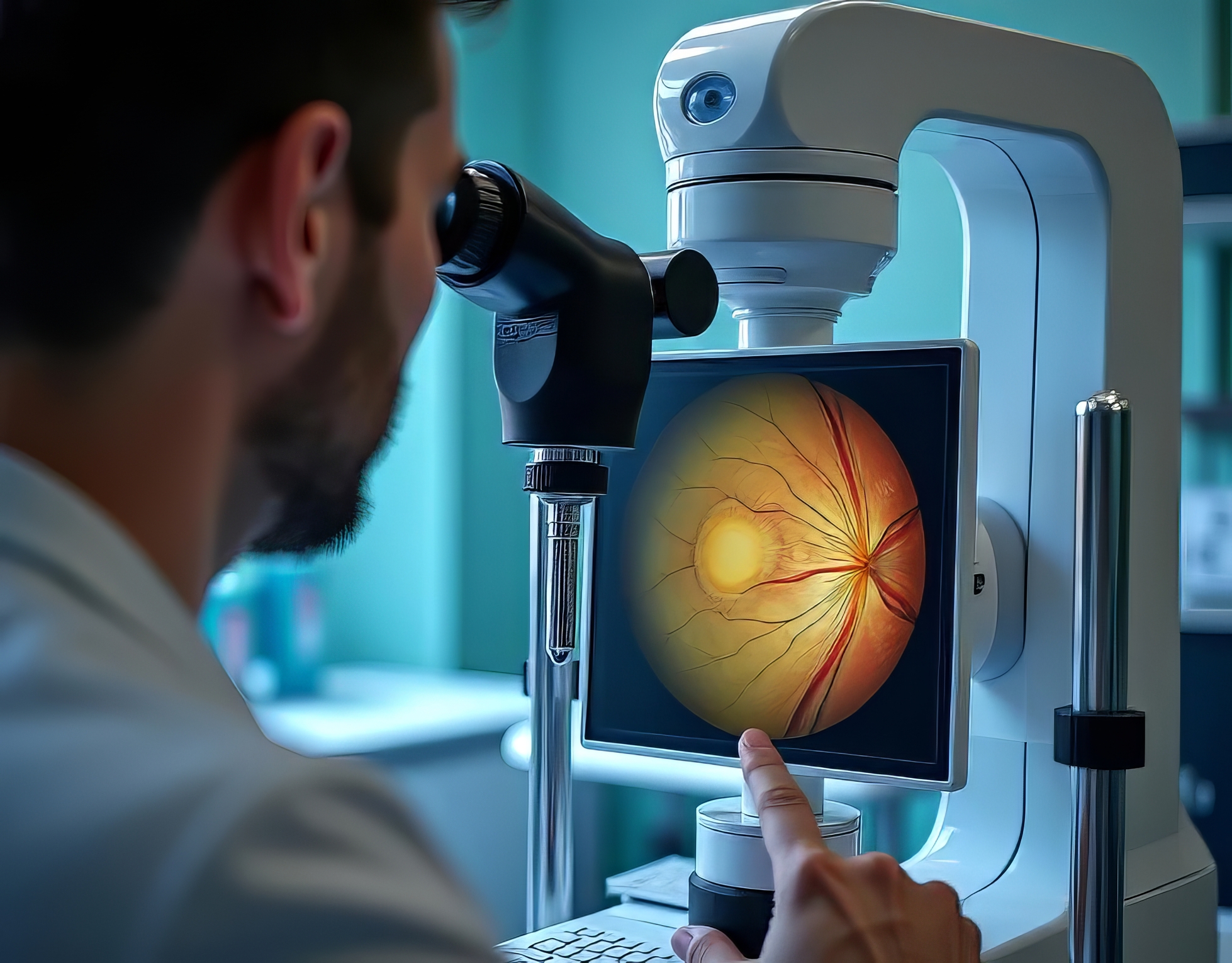
Since the 1800s, optic disc photography has been considered the gold standard for optic nerve evaluation. Image for illustration only. Person depicted is a model.