Proton Therapy: An Examination of Challenges and Future Directions
Challenges of proton therapy include high costs, technical complexities, limited evidence, and accessibility issues for patients worldwide.
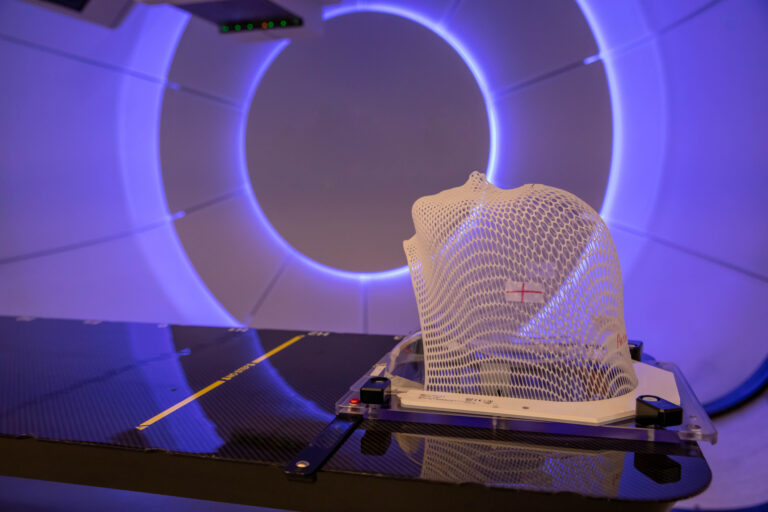
Image-guided therapy (IGT) represents a significant advancement in the field of medical interventions, offering enhanced accuracy and reduced invasiveness. This technology uses medical imaging techniques to direct therapeutic procedures, ensuring precision and improving patient outcomes. Particularly prevalent in the United Kingdom, IGT is transforming various medical specialities, including oncology, neurosurgery, and cardiovascular interventions.
The cornerstone of image-guided therapy is the use of real-time imaging modalities such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET). These imaging techniques provide clinicians with detailed internal views of the patient’s body, which are crucial for precise diagnosis and treatment planning. For instance, in cancer treatment, IGT enables the accurate delivery of radiation therapy, minimising exposure to healthy tissues and maximising the dose to tumour cells.
One of the primary advantages of IGT is its minimally invasive nature. Traditional surgical procedures, which often require large incisions and have significant recovery times, can be replaced with techniques that make smaller incisions or use body orifices as natural entry points. This approach significantly reduces recovery times, minimises surgical risks, and lowers the overall cost of healthcare by shortening hospital stays and reducing the need for postoperative care.
In the context of neurosurgery, image-guided systems are indispensable for procedures such as the removal of brain tumours or the treatment of vascular abnormalities. Surgeons rely on 3D images generated from patient scans to navigate complex anatomical structures safely. This precision is crucial in avoiding critical areas of the brain responsible for vital functions.
The UK has been at the forefront of adopting and developing IGT technologies. British institutions and hospitals are actively involved in research and clinical trials aimed at furthering the capabilities of image-guided interventions. For example, the National Health Service (NHS) has invested in state-of-the-art IGT facilities to improve treatment protocols and patient outcomes across various specialities.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with IGT is opening new avenues for even more refined and personalised treatment options. AI algorithms can process imaging data in real time, offering surgeons enhanced decision-making support during procedures. This synergy between advanced imaging technologies and AI holds the potential to revolutionise patient care by enabling even more precise and effective treatments.
As image-guided therapy continues to evolve, its impact on patient care within the UK is expected to grow significantly. By enhancing the precision of medical interventions and reducing their invasiveness, IGT improves clinical outcomes and enhances patient quality of life. This aligns well with the ongoing efforts in British healthcare to incorporate innovative technologies that cater to the needs of a diverse patient population while maintaining cost-effectiveness and high standards of care.
home » Image-Guided Therapy
Challenges of proton therapy include high costs, technical complexities, limited evidence, and accessibility issues for patients worldwide.
Advancements in Proton Beam Therapy have led to better cancer treatments with fewer side effects.