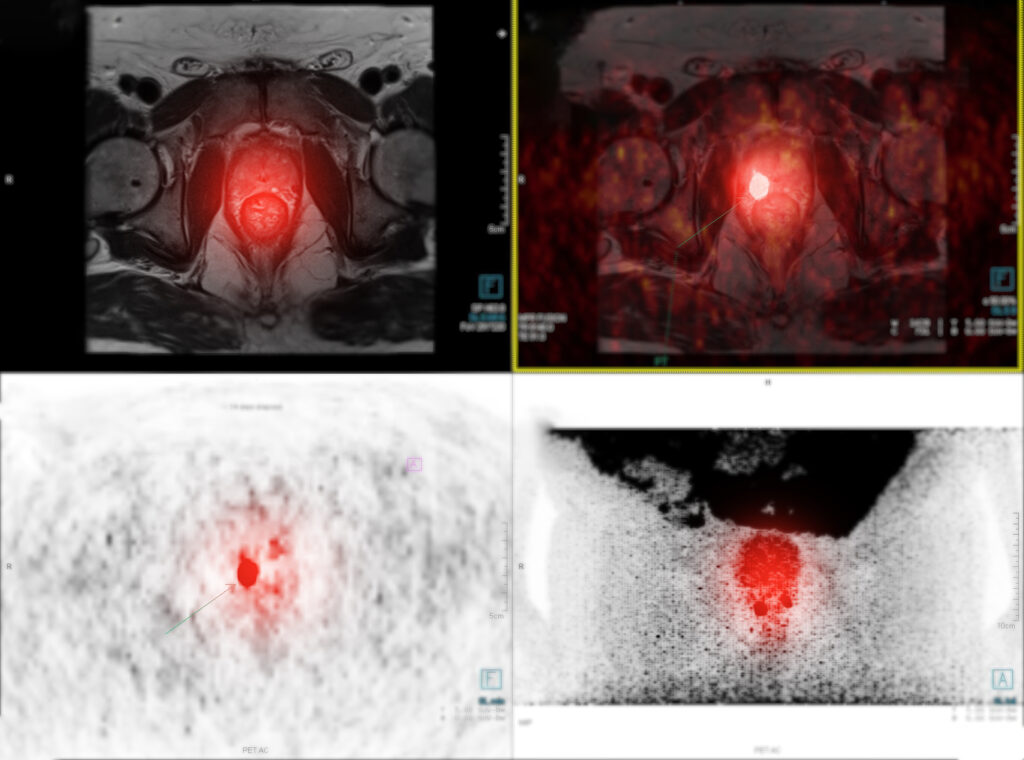
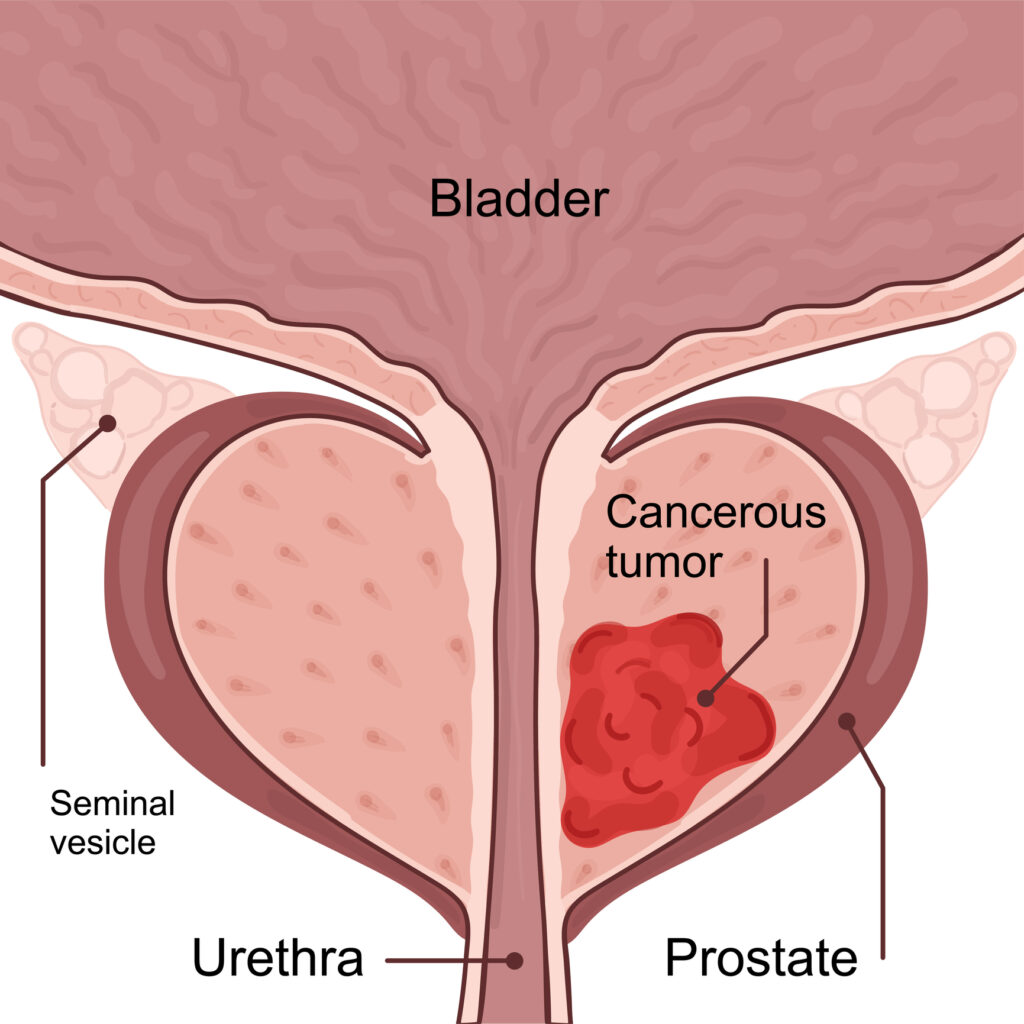
Modern Approaches to Prostate Cancer Treatment: From Early Detection to Recovery
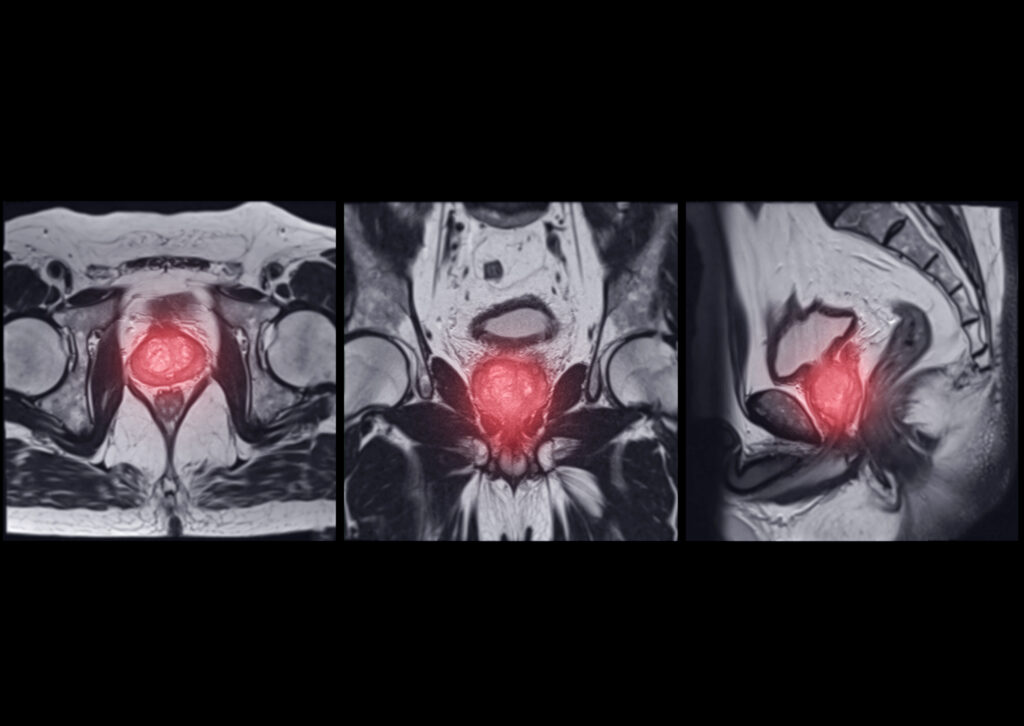
Modern prostate cancer treatment includes early detection, targeted therapies, and personalised care for improved patient outcomes and recovery.
Modern Approaches to Prostate Cancer Treatment: From Early Detection to Recovery Read Article »