Hip replacement surgery has evolved significantly over the past two decades, driven largely by advances in medical imaging technology. Today, patients who consult an orthopedic hip surgeon often benefit from highly detailed imaging that enables more accurate diagnosis, planning, and surgical execution. These tools help surgeons understand each patient’s unique anatomy, which is essential for achieving long-lasting results and restoring mobility. As imaging becomes more precise, hip replacement procedures are becoming safer, more predictable, and more personalized.
The Role of Imaging in Pre-Surgical Planning
Advanced imaging is central to understanding the extent and cause of hip joint damage. X-rays remain a foundational tool, offering a clear view of joint space narrowing, bone deformities, and arthritis progression. These images help confirm whether hip replacement is necessary and establish a baseline for further evaluation.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography scans add another layer of detail. These modalities allow surgeons to assess soft-tissue structures, bone density, and three-dimensional joint geometry, which are critical factors in planning implant size and positioning. By combining multiple imaging sources, surgeons can anticipate challenges before surgery and reduce the risk of complications.
Precision Through Three-Dimensional Visualisation
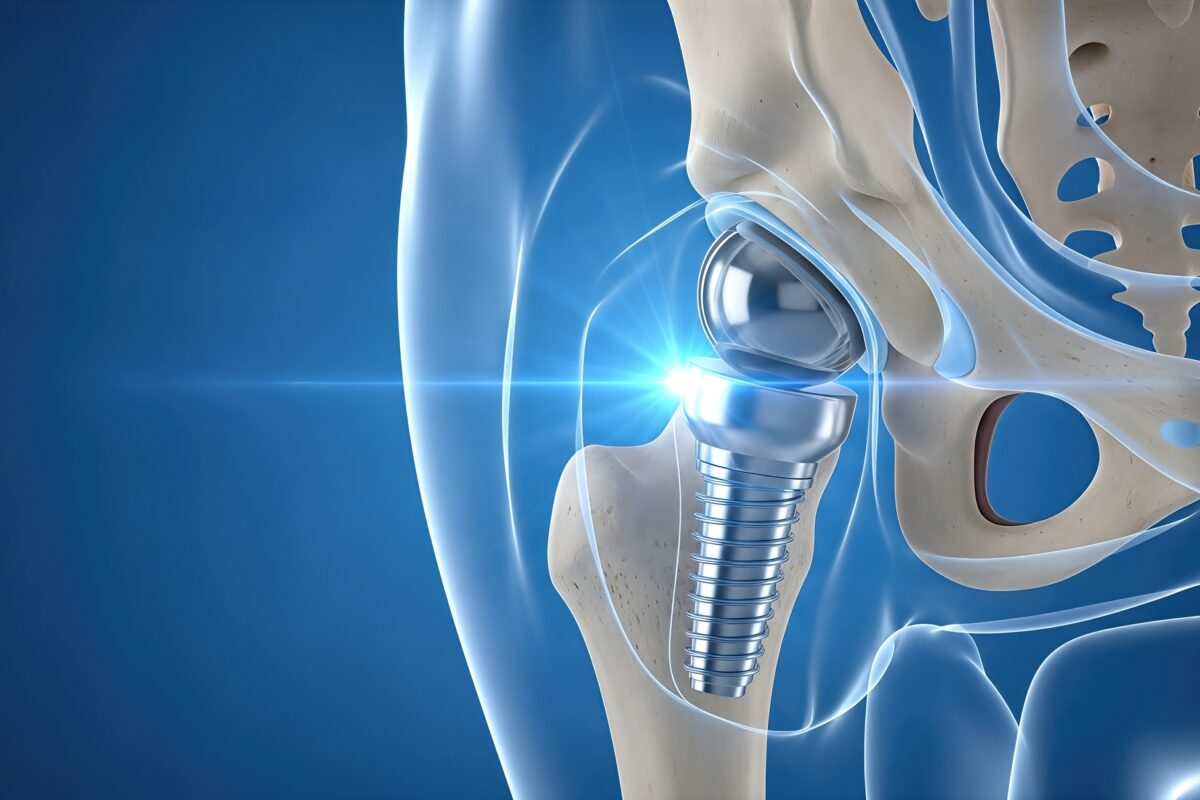
Three-dimensional imaging has reshaped how hip replacement procedures are planned. Using CT-based data, surgeons can generate accurate digital models of the hip joint, allowing them to simulate the procedure before entering the operating room. This approach improves precision by enabling surgeons to select implants that best match the patient’s anatomy.
Virtual surgical planning also supports better alignment and balance of the hip joint. Proper implant positioning is essential for stability, range of motion, and long-term durability. With three-dimensional visualization, surgeons can refine angles and measurements in advance, leading to smoother procedures and more consistent outcomes.
Intraoperative Guidance and Surgical Accuracy
Advanced imaging does not stop at pre-surgical planning. In some cases, imaging data is integrated into navigation systems or robotic-assisted platforms used during surgery. These technologies use real-time feedback to guide implant placement, helping surgeons stay aligned with the preoperative plan.
This level of guidance reduces variability and enhances accuracy, particularly in complex cases. Even small deviations in implant positioning can affect recovery and joint performance. Image-guided systems help minimize these risks, supporting a higher standard of care and improved patient confidence.
Imaging and Minimally Invasive Techniques
Minimally invasive hip replacement techniques rely heavily on precise imaging. Smaller incisions and limited surgical exposure require surgeons to have a clear understanding of internal anatomy before and during the procedure. Advanced imaging provides this clarity, making less invasive approaches more feasible and effective.
Patients often benefit from reduced tissue disruption, less pain, and faster recovery times when minimally invasive techniques are used. Imaging helps ensure that these benefits do not come at the expense of accuracy or safety. Instead, it allows surgeons to balance smaller surgical footprints with precise implant placement.
Post Surgical Imaging and Long-Term Outcomes
Imaging continues to play an important role after hip replacement surgery. Follow-up X-rays and scans help monitor implant position, bone integration, and overall joint health. These images allow surgeons to detect potential issues early, often before symptoms develop.
Long-term outcomes are closely tied to how well the implant integrates with the body. Imaging provides objective data that supports ongoing care and informed decision-making. By tracking changes over time, surgeons can help patients maintain mobility and address concerns proactively.
Conclusion
Advanced imaging has become a cornerstone of modern hip replacement surgery, guiding every stage from diagnosis to long-term follow-up. By offering detailed insight into joint structure and alignment, these technologies enable surgeons to plan and perform procedures with greater precision and confidence. For patients, this means safer surgeries, better-fitting implants, and more reliable outcomes.
As imaging technology continues to advance, its role in hip replacement will only expand. Patients considering hip surgery can feel reassured that modern imaging supports a personalized, data-driven approach to care. Precision-guided by imaging is not just about improving surgical techniques; it is redefining what successful hip replacement looks like for patients in Knoxville, TN, and beyond.
Disclaimer
This article is published for general informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations. The content is not intended to replace consultation with a qualified healthcare professional, including an orthopaedic surgeon, radiologist, or other medical specialist.
Readers should not rely on this information to make decisions about their health or medical care. Individual clinical circumstances vary, and imaging techniques, surgical approaches, and treatment outcomes depend on multiple patient-specific factors. Always seek personalised advice from a licensed healthcare provider regarding symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, or surgical procedures.
Open MedScience makes no guarantees regarding the accuracy, completeness, or applicability of the information presented and accepts no liability for any loss, injury, or damage arising from the use or interpretation of this content. References to technologies, procedures, or geographic locations are provided for contextual understanding only and do not represent endorsements or professional recommendations.
By reading this article, you acknowledge that responsibility for healthcare decisions rests solely with you and your qualified medical professionals.
home » blog » medical technologies »