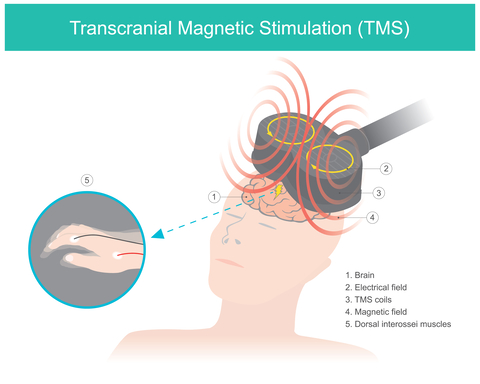
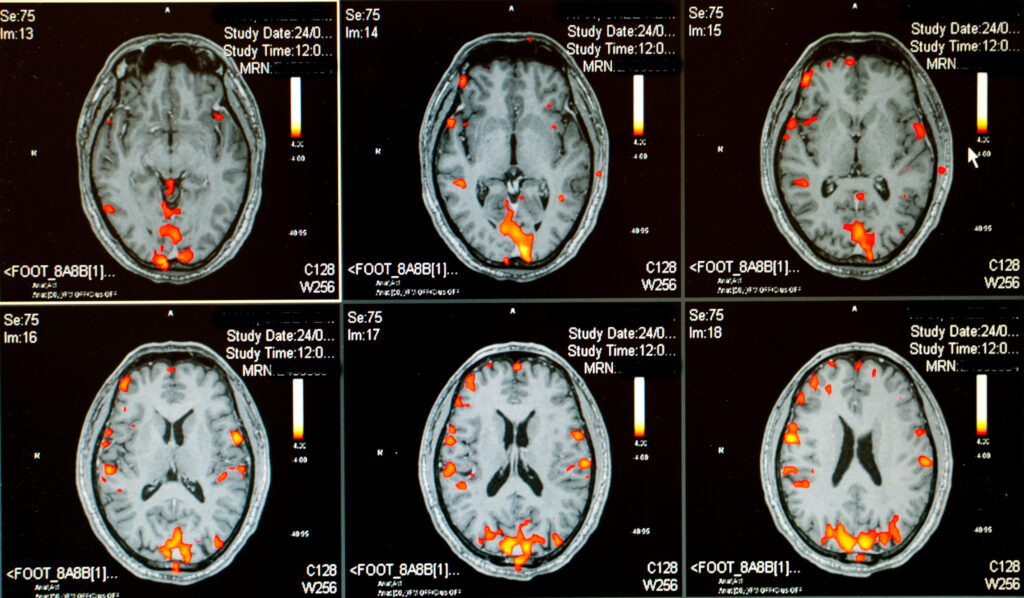
Medical Technologies
Medical technologies encompass a wide array of tools, equipment, and techniques used to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases and injuries. These technologies have revolutionised healthcare delivery and improved patient outcomes.
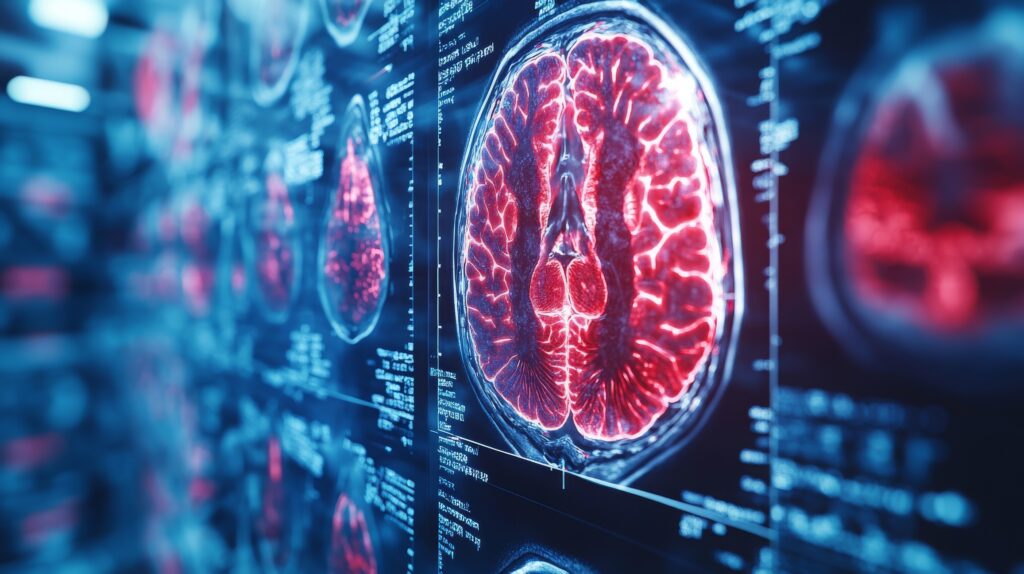
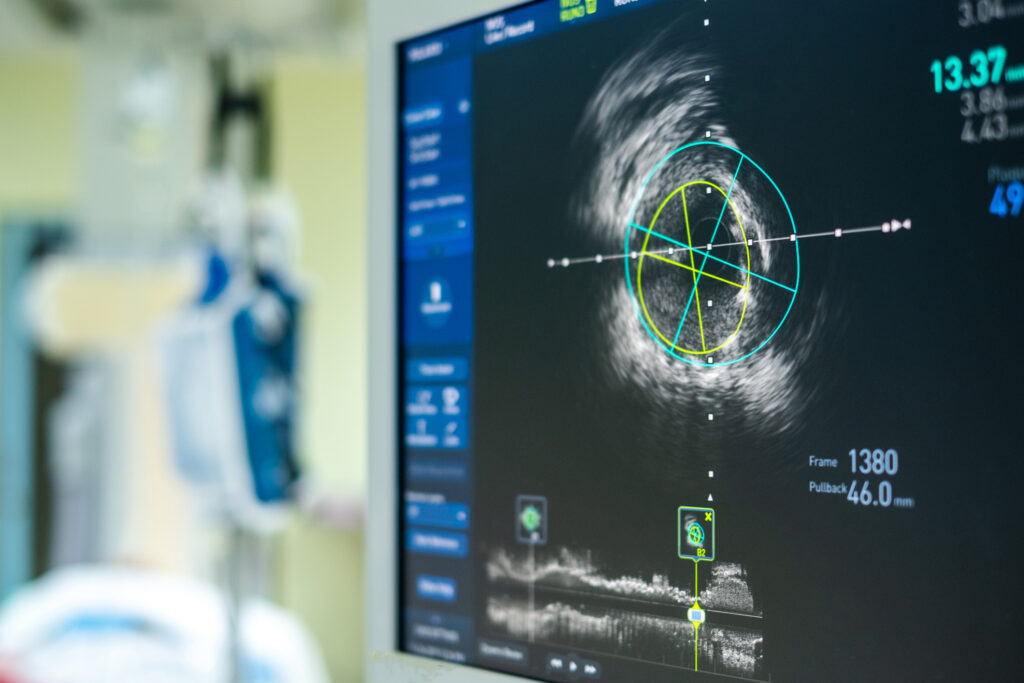
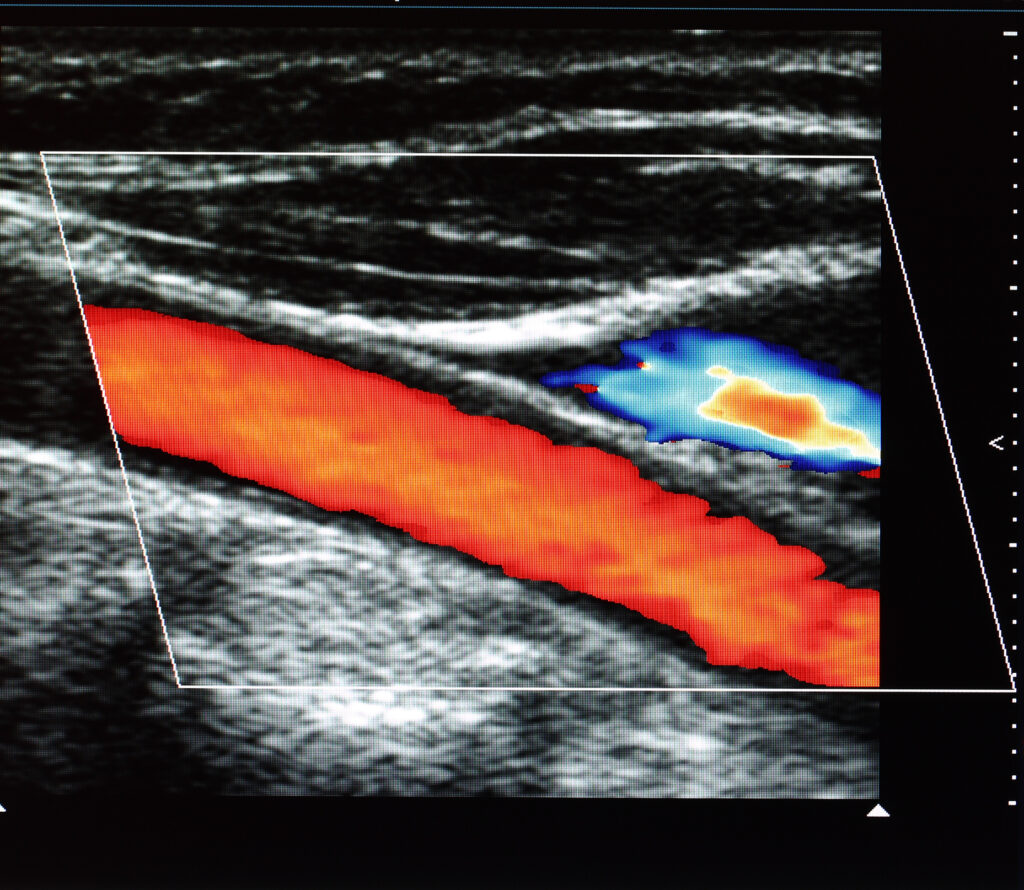
One of the most significant medical technologies is medical imaging. These diagnostic tools, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, allow doctors to visualise the body’s internal structures and detect abnormalities that may not be visible otherwise.
This has led to earlier and more accurate diagnoses of cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. Another critical medical technology is telemedicine. This refers to using communication and information technologies to provide healthcare services remotely.
Telemedicine has become increasingly important in recent years, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, as it allows doctors to consult with and treat patients without needing in-person visits. This technology can potentially improve access to healthcare, particularly in rural or underserved areas where there may be a shortage of medical professionals.
In addition to diagnostic and telemedicine technologies, numerous medical devices are used to treat various conditions. For example, implantable devices such as pacemakers and artificial joints can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with heart conditions or joint problems. Other medical devices, such as insulin pumps and blood glucose monitors, are used to manage chronic conditions such as diabetes.
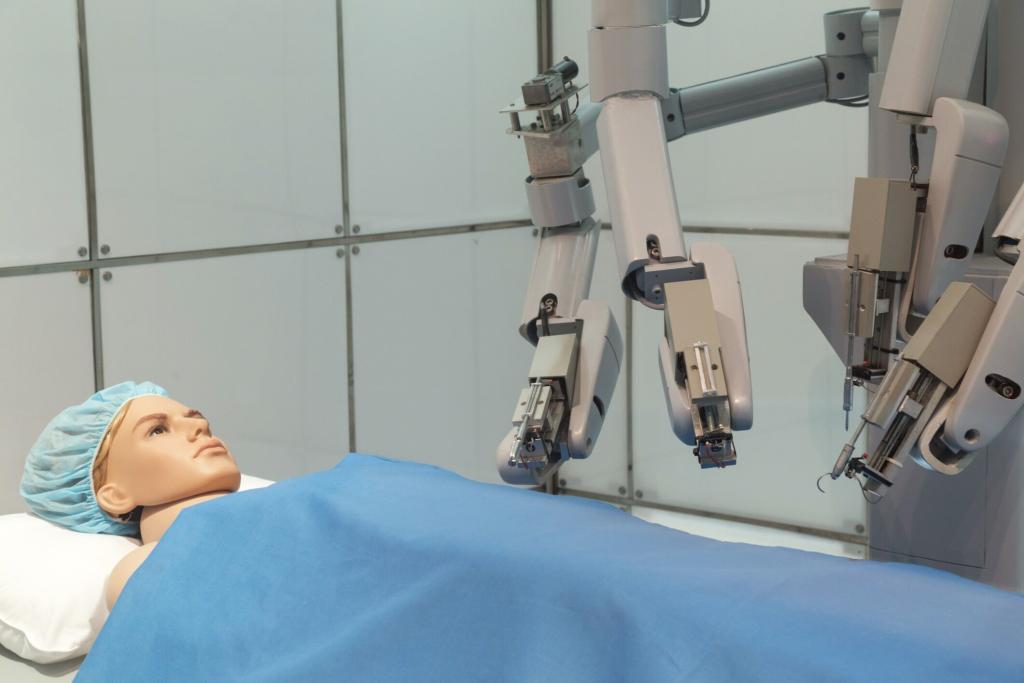
Medical technologies also play a significant role in surgery. For example, minimally invasive procedures, such as laparoscopy, use small incisions and specialised instruments to perform surgeries with less pain, scarring, and recovery than traditional open surgeries. Robotics and other advanced technologies are also used to assist surgeons in conducting complex procedures with greater precision and control.
While medical technologies offer tremendous benefits, they also pose some challenges. For example, the high cost of many medical technologies can make them inaccessible to some patients, particularly in low-income countries. There are also concerns about the possible overuse or misuse of specific technologies, which can lead to unnecessary procedures, increased costs, and risks to patient safety.
You are here:
home » medical technologies