Summary: Mobile CT scanners represent a transformative advancement in medical imaging, allowing for rapid, on-the-go diagnosis and treatment in settings where traditional, fixed CT scanners are unavailable or impractical. These devices have proven particularly beneficial in emergency care, remote locations, military settings, and in response to pandemic needs. This article looks into the technology behind mobile computed tomography scanners, explores their applications, discusses their benefits and limitations, and considers their future in healthcare.
Introduction to Mobile CT Scanners
Computed Tomography (CT) has long been a staple in diagnostic imaging due to its ability to provide detailed, cross-sectional views of the body’s internal structures. Traditionally, CT scanners have been housed in fixed locations within hospitals and clinics. However, advances in technology have led to the development of mobile CT scanners, which can be transported to various settings, providing crucial diagnostic imaging where it is needed most.
Mobile CT scanners have dramatically improved accessibility, ensuring that patients who cannot reach hospital facilities, such as those in rural areas or in military zones, still receive high-quality imaging. They have also proven invaluable in emergency settings and during pandemics, where they can rapidly diagnose patients at the point of care, reducing the need for patient transport and minimising exposure.
Technology Behind Mobile CT Scanners
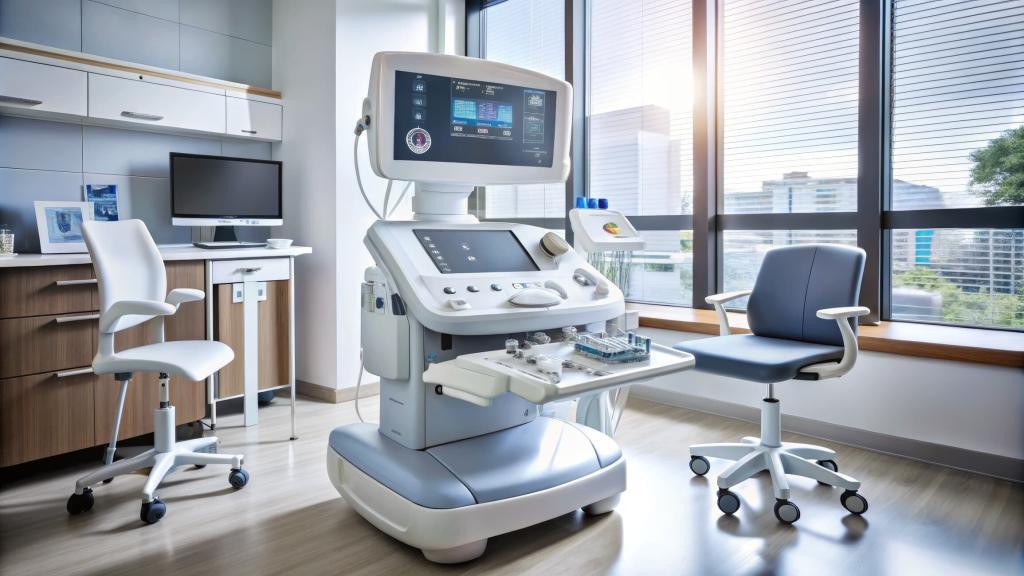
The technology in mobile computed tomography scanners mirrors that of fixed scanners but has been refined for portability and versatility. Traditional CT scanners use rotating X-ray beams and detectors to capture detailed images of body structures, which are then reconstructed by computers. Mobile CT scanners achieve the same diagnostic accuracy but with designs that allow them to be transported and operated in a range of environments.
Key technological advancements that enable mobile CT include:
- Compact and Lightweight Designs: Mobile CT scanners are engineered to be lighter and more compact than their fixed counterparts, allowing for easier transportation.
- Battery and Power Management Systems: Many mobile units are battery-powered or come with adaptable power systems, enabling use in various environments without dedicated power supplies.
- Advanced Image Reconstruction Software: The latest software in mobile CT scanners allows for rapid image processing, making high-resolution images available almost immediately after scanning.
Applications of Mobile CT Scanners
The versatility of mobile CT scanners allows them to be used across diverse healthcare settings:
Emergency and Trauma Care
In emergency and trauma care, time is of the essence. Mobile computed tomography scanners can be deployed in emergency rooms or ambulances, allowing for immediate imaging of patients suspected of serious injuries or internal bleeding. This quick access to imaging is vital for patients with traumatic brain injuries or stroke, where every second counts.
Rural and Remote Healthcare
Access to advanced diagnostic imaging can be limited in rural or remote areas. Mobile CT scanners enable healthcare providers to bring imaging capabilities to these regions, reducing the need for patients to travel long distances. This accessibility ensures that patients in remote locations receive timely diagnosis and treatment, leading to better health outcomes.
Military and Disaster Settings
Mobile CT scanners are invaluable in military and disaster settings, where there may be no access to hospital infrastructure. Deployed alongside field hospitals, they enable military medical teams to assess injuries on-site. Additionally, mobile CT has been instrumental in disaster relief, where it assists in quickly evaluating injuries in the field, allowing for efficient triage and prioritisation of care.
Pandemic and Infectious Disease Response
During the COVID-19 pandemic, mobile CT scanners proved indispensable in assessing patients’ lung health. By positioning mobile scanners in or near isolation areas, healthcare facilities could rapidly evaluate patients without transporting them through hospital corridors, reducing cross-contamination risks. Mobile CT continues to play a role in managing infectious disease outbreaks, ensuring rapid assessment and isolation.
Benefits of Mobile CT Scanners
Mobile CT scanners offer several significant advantages over traditional, fixed units:
Increased Accessibility
One of the main benefits of mobile CT is its ability to provide access to high-quality imaging in a variety of locations, bridging the gap for patients who may otherwise struggle to access such services. This can be life-saving in emergency situations or rural areas where timely access to diagnostics is essential.
Improved Patient Outcomes
The immediacy of imaging provided by mobile computed tomography scanners allows healthcare providers to make faster and more accurate diagnoses, leading to quicker intervention and treatment. This rapid response is especially beneficial in cases like stroke, where early diagnosis can significantly affect recovery outcomes.
Reduction in Patient Transport and Associated Risks
By bringing the scanner to the patient rather than the other way around, mobile CT scanners eliminate the need for patient transportation, which can be risky for critically ill individuals. In emergency rooms, mobile CT units can be moved directly to the patient, reducing movement and minimising potential complications.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Mobile CT scanners are highly adaptable and can be quickly relocated to meet changing needs, such as sudden patient surges or disaster response scenarios. Their flexibility allows healthcare providers to adapt to diverse and unpredictable situations, enhancing the overall resilience of healthcare systems.
Limitations and Challenges of Mobile CT Scanners
While mobile CT scanners offer many benefits, they are not without limitations:
Cost and Maintenance
Mobile CT scanners are often more expensive than fixed units due to the advanced technology and portability features. Additionally, they require regular maintenance to ensure consistent performance, which can be a logistical challenge, especially in remote settings.
Limited Imaging Power
Some mobile CT scanners may offer slightly lower resolution or reduced scanning capabilities compared to fixed units. While they are effective for many diagnostic purposes, they may not be suitable for more complex imaging needs, such as detailed cardiac or neurological scans.
Infrastructure Requirements
Despite their portability, mobile CT scanners still require certain infrastructure, such as stable power sources and appropriate space, which may not be readily available in all settings. This can limit their deployment in certain field situations or extremely remote locations.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
Radiation exposure remains a consideration, particularly for patients requiring multiple scans. Mobile CT scanners, while generally safe, may involve higher radiation doses for certain scans due to the compact design of the equipment. It is essential to balance the diagnostic benefits with safety, following radiation protection principles.
Case Studies Highlighting the Impact of Mobile CT Scanners
Several case studies illustrate the impact of mobile CT technology in different settings:
Stroke Diagnosis in Ambulances
In some countries, mobile CT scanners are being installed in ambulances to enable on-site diagnosis of strokes. With rapid on-the-spot scanning, emergency medical teams can determine whether a patient is experiencing an ischaemic or haemorrhagic stroke, allowing for the correct intervention en route to the hospital. This approach has been shown to improve patient outcomes, reducing the time to treatment significantly.
Disaster Response in Earthquake Zones
In earthquake-affected areas, where hospital infrastructure may be compromised, mobile CT scanners have been deployed to assess injuries. After a major earthquake, mobile units were used to triage patients, quickly identifying those who required urgent care. The scanners helped streamline patient management and ensure that limited resources were allocated efficiently.
Pandemic Preparedness in Asia
During the COVID-19 pandemic, some Asian countries utilised mobile CT scanners in densely populated urban areas. Mobile units were stationed at community centres, allowing rapid assessment of suspected cases and helping to prevent the spread of infection within hospitals. This approach proved to be highly effective in managing patient flow and ensuring timely diagnoses.
The Future of Mobile CT Scanners
The future of mobile CT technology is likely to see further advancements in portability, imaging quality, and integration with other healthcare technologies. Innovations on the horizon include:
Enhanced Portability and Power Efficiency
With continued advancements in lightweight materials and battery technology, future mobile CT scanners will become even more compact and efficient. This will increase their accessibility in areas with limited infrastructure, extending the reach of diagnostic imaging even further.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-powered software is set to play a critical role in mobile CT imaging, offering capabilities like automatic detection of abnormalities and rapid image analysis. AI integration will help improve diagnostic accuracy, streamline workflows, and reduce the burden on healthcare professionals, especially in high-stress emergency settings.
Expansion into New Clinical Applications
As mobile CT technology improves, it may expand into new clinical applications beyond traditional imaging. For example, there may be potential for use in precision-guided surgeries in remote or resource-limited settings, helping doctors perform minimally invasive procedures with real-time imaging guidance.
Increased Focus on Radiation Safety
With ongoing research into low-dose imaging, future mobile CT scanners are expected to offer reduced radiation exposure, balancing diagnostic benefits with patient safety. New shielding materials and optimised scanning protocols are likely to make mobile CT safer and more sustainable.
Conclusion
Mobile CT scanners have revolutionised the field of diagnostic imaging by providing rapid, on-the-spot imaging capabilities in a variety of settings. From emergency rooms to disaster zones and rural clinics, these portable scanners are extending the reach of medical imaging to areas previously underserved. While there are challenges associated with cost, maintenance, and imaging limitations, the benefits of mobile computed tomography scanners in terms of accessibility, patient outcomes, and adaptability are undeniable.
As technology continues to evolve, mobile CT scanners are set to become even more compact, powerful, and integrated with AI, further enhancing their role in modern healthcare. In the coming years, mobile CT is likely to become an essential tool in delivering timely and accurate medical care wherever it is needed.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for general informational and educational purposes only. While Open Medscience aims to present accurate and up-to-date content, we make no guarantees regarding the completeness, accuracy, or reliability of the information discussed.
This article does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment and should not be relied upon as a substitute for consultation with qualified healthcare professionals. Any medical decisions or actions based on the information in this article should be made in consultation with a licensed healthcare provider.
The mention of specific technologies, manufacturers, or products does not imply endorsement or recommendation by Open Medscience. Readers are encouraged to verify details independently and consider local regulatory and clinical guidance when evaluating the use of mobile CT scanners or similar diagnostic equipment.
Open Medscience disclaims any liability for loss or damage resulting from the use of, or reliance on, the information presented in this article.
home » blog » medical imaging modalities »