Along with serious degenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, cancer remains one of the last remaining frontiers that modern medicine has yet to really conquer. Anyone familiar with the big C, through working in healthcare or through MSN programs, knows that cancer has an undeniable hold on our collective psyche.
In the range of treatment protocols developed over the years, chemotherapy remains a key weapon in the fight against cancer. This article provides an overview of chemotherapy, exploring what it is, why it’s used, how it works, its side effects, and what patients can expect during treatment.
What is Chemotherapy?
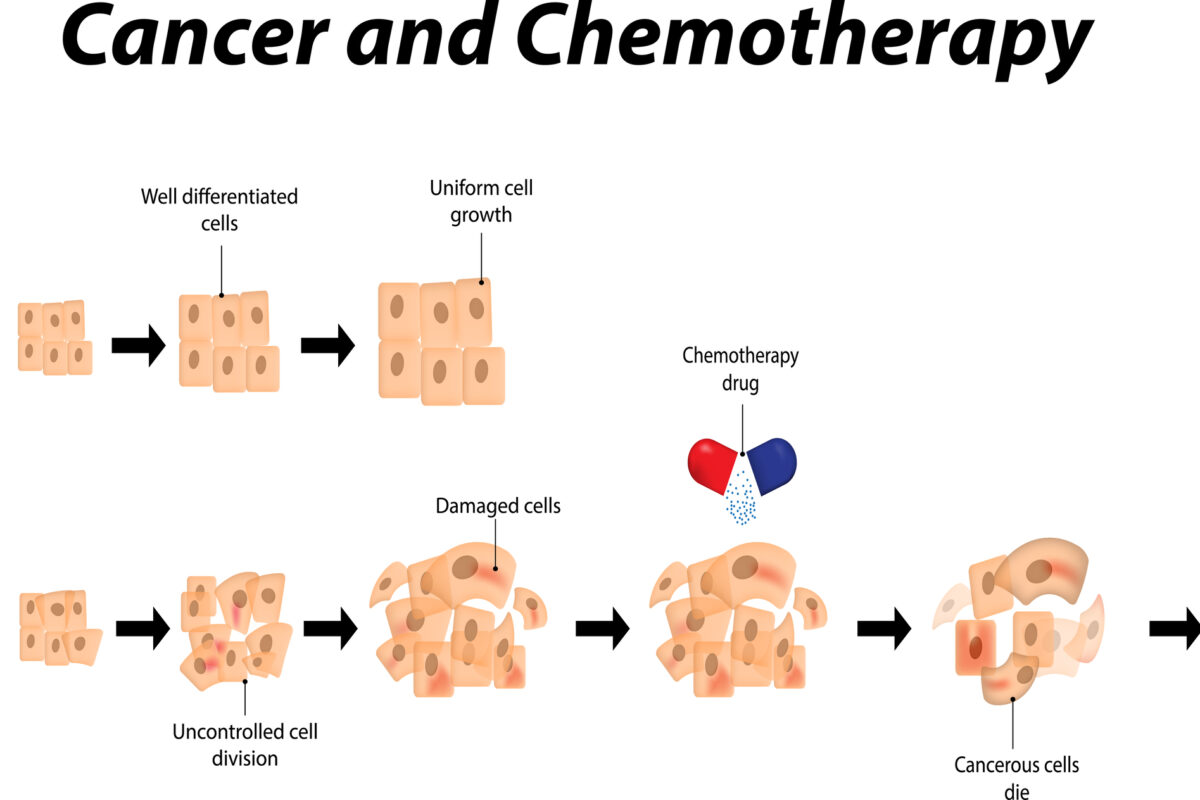
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses powerful (often toxic) chemicals to kill fast-growing cells in the body. It is most commonly used to treat cancer, as cancer cells grow and multiply much more quickly than most cells in the body. While there are many different types of chemotherapy drugs available, they all share the common goal of targeting and destroying cancer cells.
Why is Chemotherapy Used?
Chemotherapy is used in a few ways depending on the treatment protocol. The specifics of the treatment is determined based on the type of cancer and on a case-to-case basis. Unlike many other conditions, no two cancers are ever the same, and for the same reason, treatment often has to be modular and customized based on the specific requirements of the patient.
As a primary treatment
In some cases, chemotherapy can be used as the sole treatment to completely kill cancer cells. Chemo as a primary mode of treatment is especially effective against testicular cancer and Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
As supplementary treatment
After other treatments like surgery, chemotherapy can be used to kill any remaining cancer cells, reducing the risk of recurrence. This protocol, named adjuvant chemotherapy, is commonly deployed in more advanced cases where the cancer has metastasized to multiple systems.
Chemotherapy may also be used to shrink tumours before other treatments, such as radiation or surgery.
In advanced stages of cancer, chemotherapy can help relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
How Does Chemotherapy Work?
According to the American Cancer Society, chemotherapy works by interfering with the cell cycle, the process by which cells grow and divide. Cancer cells tend to form new cells more quickly than normal cells, making them more susceptible to chemotherapy drugs. These drugs target cells at different phases of the cell cycle, effectively killing cancer cells and preventing them from multiplying.
However, chemotherapy drugs cannot differentiate between healthy cells and cancer cells. This lack of specificity is what leads to many of the side effects associated with treatment. The good news is that most normal cells can recover from the effects of chemotherapy over time, while cancer cells typically cannot.
Common Side Effects of Chemotherapy
While chemotherapy is effective at killing cancer cells, it can also affect healthy cells in the body, leading to various side effects. Some common side effects include:
Fatigue: This is one of the most common side effects, often described as a persistent feeling of tiredness.
Hair loss: Many chemotherapy drugs can cause hair loss, which is usually temporary.
Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms can often be managed with anti-nausea medications.
Decreased blood cell counts: This can lead to an increased risk of infection, anaemia, and easy bruising or bleeding.
Mouth sores: Some patients experience painful sores in the mouth and throat.
Changes in appetite: Chemotherapy can affect taste and appetite, leading to weight changes.
Skin and nail changes: Some patients may experience dry skin, rashes, or changes in nail colour or texture.
Cognitive changes: Often referred to as “chemo brain,” some patients experience difficulty with memory and concentration.
It’s important to note that not everyone experiences all of these side effects, and their severity can vary from person to person.
Managing Side Effects
While side effects can be challenging, there are many ways to manage them:
- Medications: Doctors can prescribe medications to help manage nausea, pain, and other symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Eating a balanced diet, getting adequate rest, and engaging in light exercise (when approved by a doctor) can help manage fatigue and improve overall well-being.
- Complementary therapies: Some patients find relief through complementary therapies like acupuncture or massage, though it’s important to discuss these with a healthcare provider first.
- Mental health support: Counseling or support groups can be beneficial for managing the emotional impact of cancer treatment.
What to Expect During Chemotherapy Treatment
Preparing for chemotherapy can help patients feel more in control of their treatment. Here’s what to expect:
Pre-treatment evaluation: Before starting chemotherapy, patients undergo a series of tests to assess their overall health and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment schedule: Chemotherapy is typically given in cycles, with periods of treatment followed by rest periods. The schedule varies depending on the type of cancer and the drugs used.
Administration: Chemotherapy can be given in various ways, including orally, intravenously, or by injection. The most common method is intravenous (IV) infusion.
Monitoring: Throughout treatment, patients are closely monitored for side effects and treatment effectiveness. Regular blood tests and imaging studies may be performed.
Support: Many cancer centres offer support services to help patients manage side effects and cope with the emotional aspects of treatment.
Remember, every patient’s experience with chemotherapy is unique. It’s essential to maintain open communication with your healthcare team throughout the treatment process. They can provide personalized advice and support to help you navigate your cancer journey.
Disclaimer:
The content provided in this article, “Chemotherapy to Treat Cancer: How Does It Work?” by Open Medscience, is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. Open Medscience does not endorse any specific treatment, product, or service mentioned in this article. Information is accurate as of the publication date but may be subject to change.