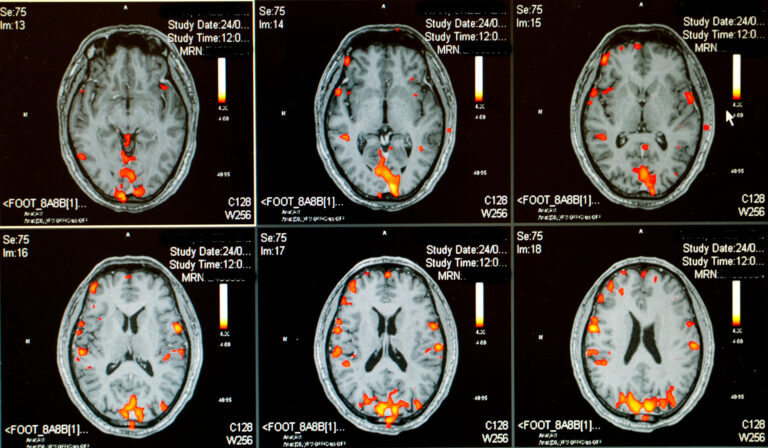
Neuroradiology
Neuroradiology, a specialised branch of radiology, focuses on diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the nervous system, spine, head, and neck using advanced imaging techniques. This field plays a crucial role in medical diagnostics, particularly in understanding and managing neurological disorders.
The core of neuroradiology is the sophisticated imaging technology that allows clinicians to view detailed images of the brain, spinal cord, and surrounding structures. These technologies include Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT), and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). MRI is particularly valuable because it produces high-resolution images of brain structures without exposing patients to radiation. It is instrumental in detecting and monitoring diseases such as multiple sclerosis, brain tumours, and strokes.
CT scans, on the other hand, are often used in emergency settings to quickly assess injuries from accidents or acute neurological events like haemorrhages. They provide rapid, valuable insights that can be pivotal in life-threatening situations. PET scans add another layer of functionality by measuring metabolic activity within brain tissues, helping to identify metabolic disorders and malignancies accurately.
Neuroradiologists require extensive training not only in the use of these imaging modalities but also in understanding the complex anatomy and pathology of the nervous system. Their expertise allows them to interpret subtle changes in imaging that could signify the early stages of the disease, making their role critical in both diagnosis and subsequent management plans.
Moreover, neuroradiology is integral to interventional procedures such as treating aneurysms and delivering medication directly into the cerebrospinal fluid. These procedures often rely on real-time imaging guidance to ensure accuracy and safety.
As technology advances, neuroradiology continues to evolve. Artificial intelligence and machine learning developments are beginning to enhance image interpretation, potentially speeding up diagnosis and refining accuracy. This progress promises to amplify neuroradiology’s impact on patient care.
In conclusion, neuroradiology is a vital medical field that combines advanced imaging techniques with expert knowledge of neuroanatomy to diagnose and treat nervous system disorders. As technologies develop, neuroradiology’s capabilities and contributions will expand, further solidifying its role in modern medicine.
home » Neuroradiology