Radiation Dose Optimisation
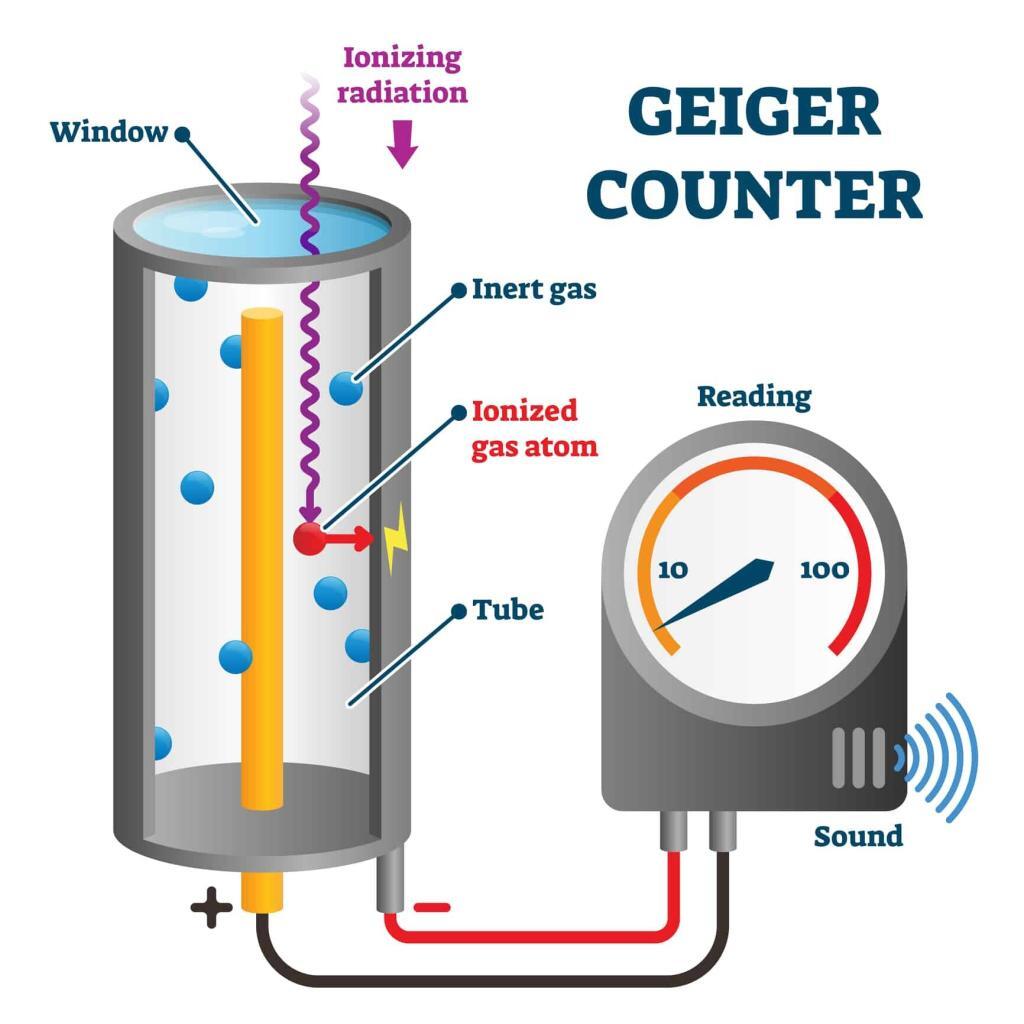
Radiation dose optimisation plays a crucial role in the medical field, particularly in radiology and nuclear medicine. The principle behind this concept is to manage and reduce the amount of radiation patients are exposed to during diagnostic procedures while ensuring that the quality of the imaging is sufficient to achieve accurate diagnoses. This balance is vital for patient safety and advancing the effectiveness of medical imaging practices.
The framework for radiation dose optimisation is often encapsulated in the concept of “As Low As Reasonably Achievable” (ALARA). ALARA is a safety principle designed to minimise radiation doses and radioactive material releases by employing all reasonable methods. It is a critical guideline in the medical imaging field, ensuring that every precaution is taken to reduce exposure without compromising diagnostic integrity.
One of the primary strategies for optimisation is the selection of appropriate imaging protocols tailored to the patient’s specific medical needs. For instance, adjusting the exposure parameters based on the patient’s size and the area of interest can significantly reduce unnecessary radiation while obtaining the necessary diagnostic information. Moreover, advancements in technology play a pivotal role. Modern devices come equipped with features like automatic exposure control and dose-modulation techniques, which adjust the amount of radiation used during a scan based on the density of the body part being imaged.
Training and education of radiological staff are equally important in dose optimisation. Radiologists, technologists, and medical physicists need to be well-versed in the latest protocols and technological advancements. Regular workshops and seminars are essential to keep them updated with the best practices and innovations in radiation safety and imaging techniques.
Furthermore, developing and implementing international and national guidelines and standards for radiation safety are vital. Regulatory bodies such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and national health and safety organisations provide frameworks and regulations that guide practices around radiation use. These standards are pivotal for patient safety and ensure uniformity of care quality across different regions and institutions.
In conclusion, radiation dose optimisation is a multifaceted approach involving careful planning of imaging protocols, leveraging technological advancements, continuous professional development, and adherence to stringent regulatory standards. As medical imaging technologies evolve, so must our dose reduction strategies. By maintaining the delicate balance between minimising radiation exposure and ensuring diagnostic accuracy, healthcare providers can protect patient health while delivering the highest standards of care.
You are here:
home » Radiation Dose Optimisation