Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy (radiotherapy) is a crucial component in comprehensive cancer treatment. This noninvasive treatment method employs high-energy radiation beams to eradicate malignant cells, disrupt their DNA, and halt tumour growth. Since its inception in the early 20th century, radiotherapy has significantly advanced, evolving into a highly targeted and effective cancer treatment option. Estimates suggest that almost half of all cancer patients will receive radiation treatments at some point during their treatment journey.
Types of Radiation Therapy:
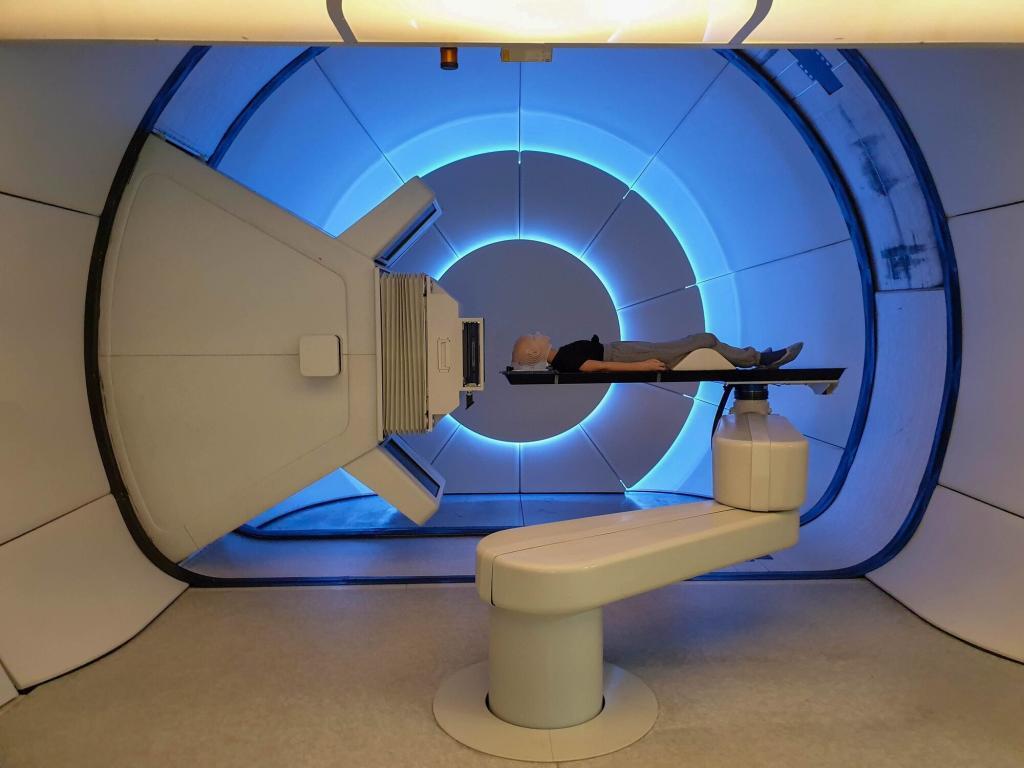
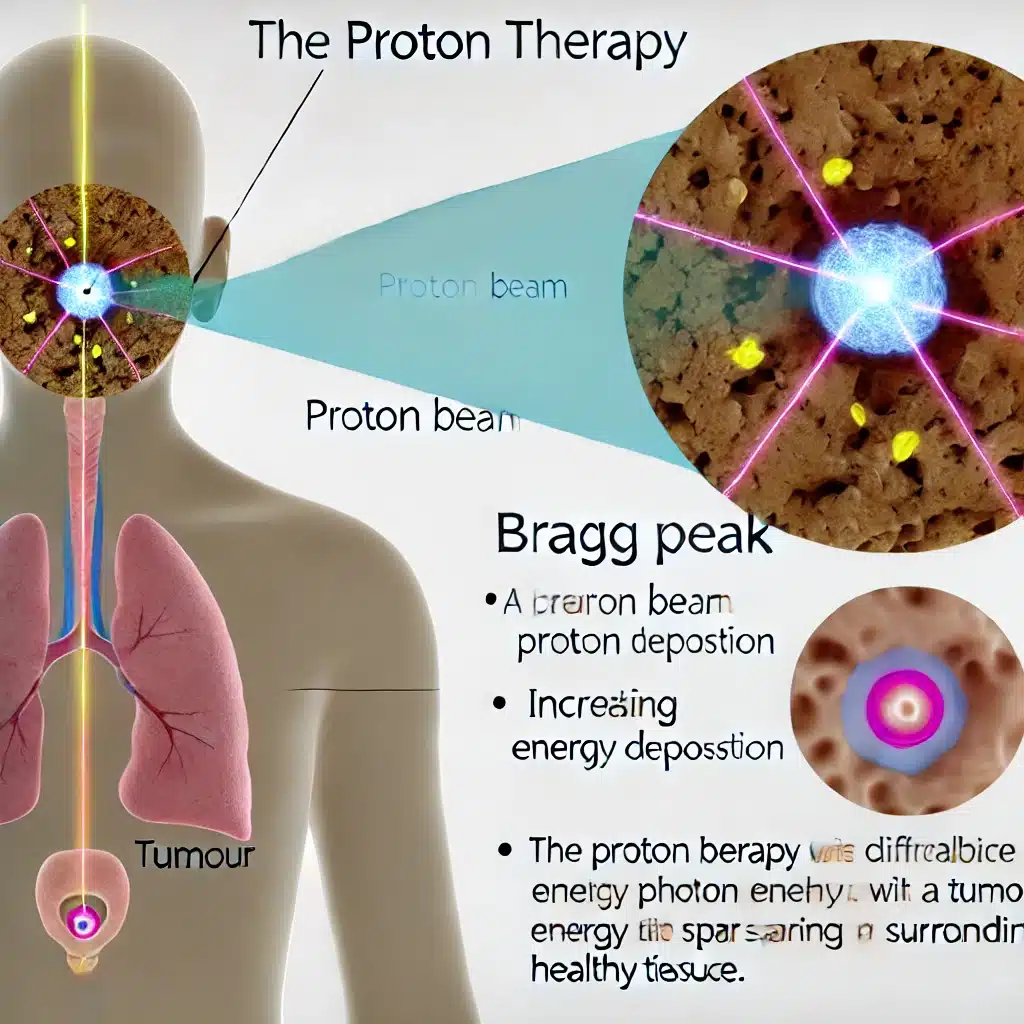
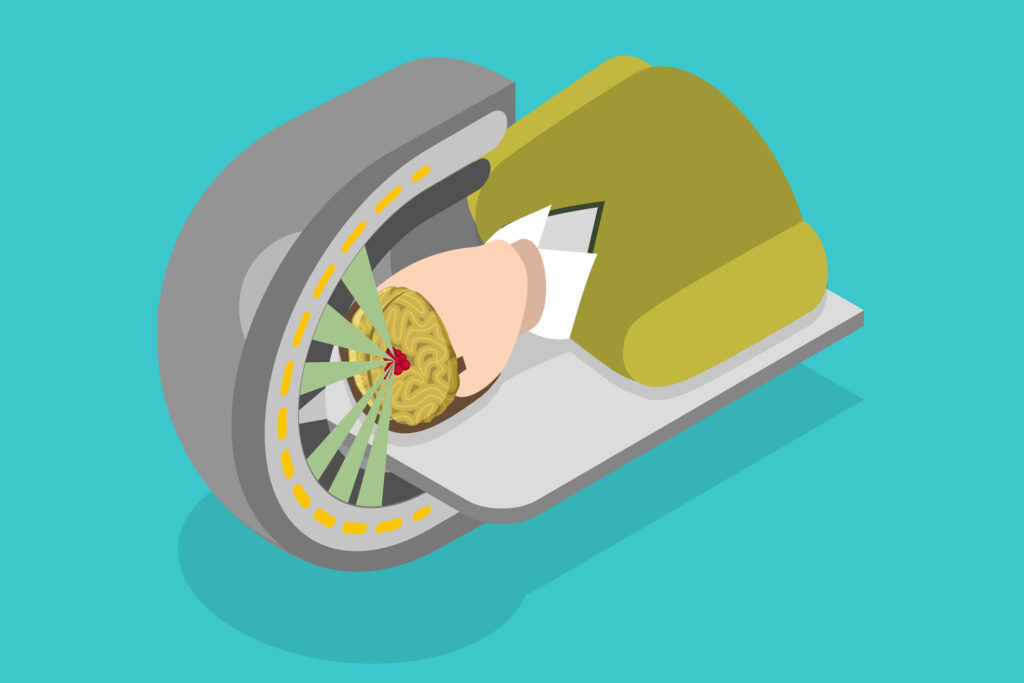
- External Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This is the most common type of radiotherapy, where high-energy beams are directed from outside the patient’s body towards the tumour. Advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), enable precise targeting and reduce damage to surrounding healthy tissue. EBRT can be further subdivided into several types, including 3d-conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT), Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT), Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS), Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) and Proton Therapy
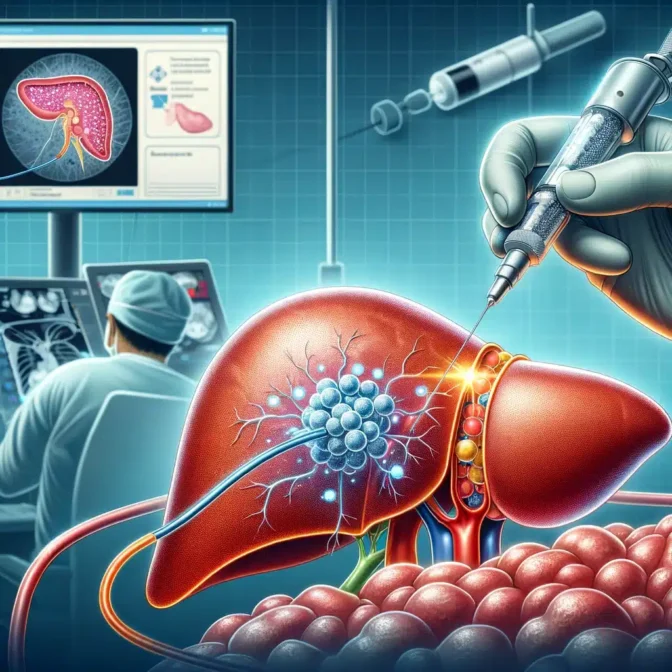
- Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy) involves placing radioactive sources directly into or near the tumour. This allows for the delivery of higher radiation doses to the cancerous cells while minimizing exposure to healthy tissue.
- Systemic radiotherapy uses either injected or ingested radioactive drugs to deliver radiation throughout the patient’s body. It is most commonly used to treat cancers that have spread to multiple locations.
Radiation therapy can be used in various clinical settings, either as a standalone treatment or in combination with other modalities such as surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Treatment choice depends on the cancer type, stage, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Adjuvant therapy is often employed as an adjuvant treatment following surgery to eliminate any remaining tumour cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Palliative therapy is where the cancer is too advanced or cannot be entirely removed; radiotherapy can relieve symptoms such as pain and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Radiotherapy is generally well-tolerated but may have side effects like any medical treatment. These can range from mild skin irritation and fatigue to more severe complications such as tissue damage or secondary malignancies. However, technological advances and treatment planning have significantly reduced these risks, making radiotherapy a safer and more effective option for many cancer patients.
You are here:
home » radiation therapy