Radiology
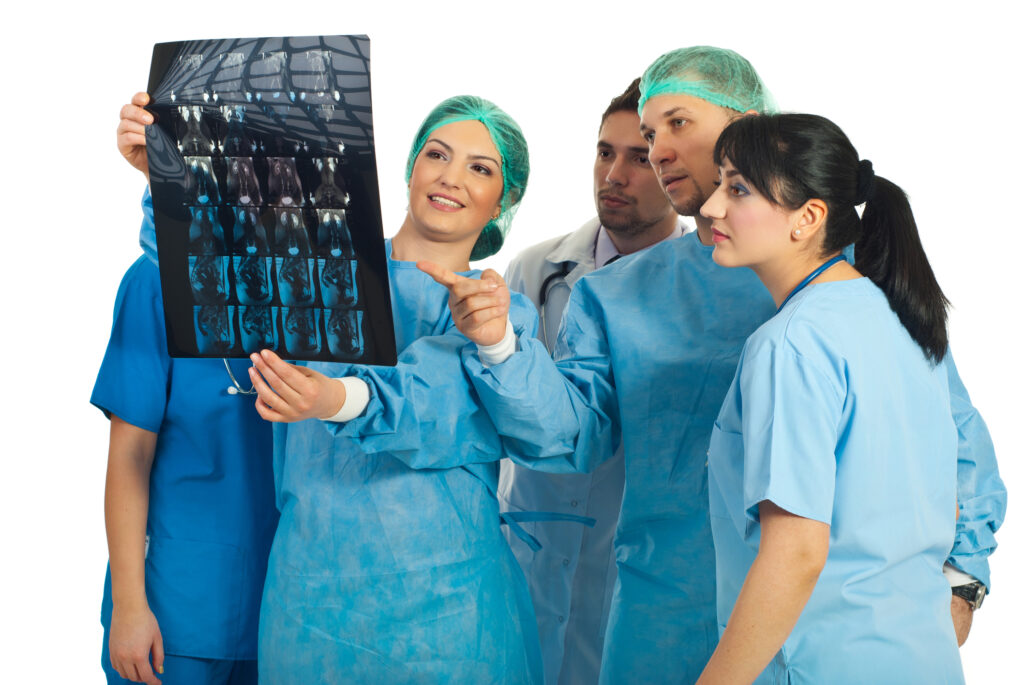
Radiology is a medical branch that uses medical imaging technology to diagnose and treat diseases. Radiology has been a critical tool in medical practice for over a century, and with the advent of new technology and techniques, it continues to evolve and improve.
Radiology refers to using radiation to create images of the body’s internal structures. These images can be used to diagnose a wide variety of medical conditions and to guide treatment. Radiology had come a long way since its beginnings in the late 19th century when X-rays were first discovered.
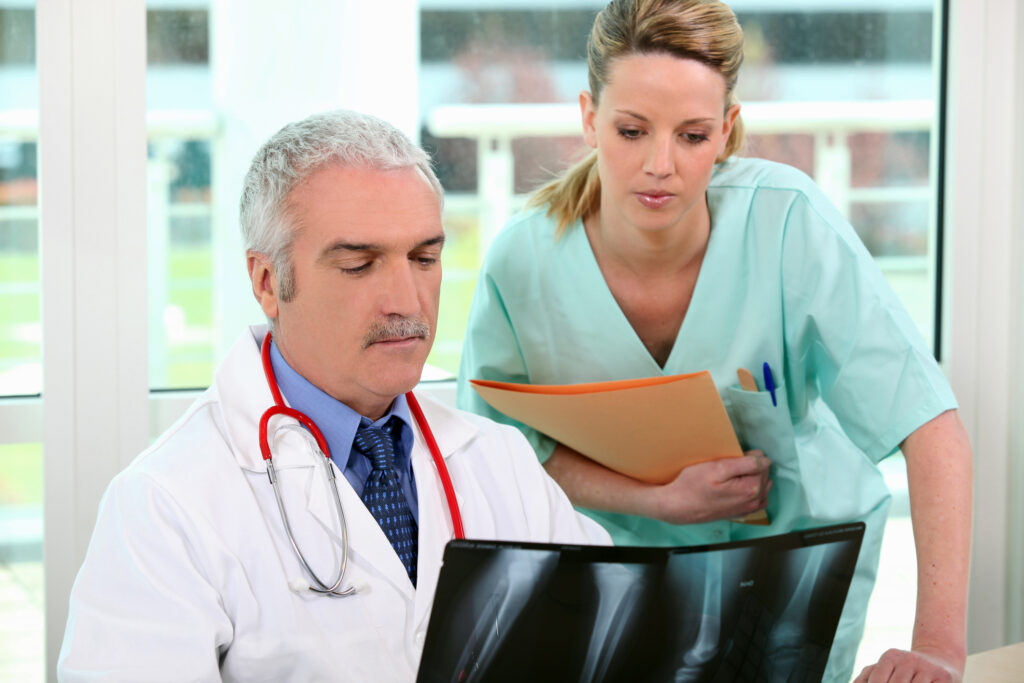
Today, various medical imaging technologies are used in radiology, including X-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, and nuclear medicine. X-rays are the oldest and most commonly used form of medical imaging. They work by passing a beam of radiation through the body, which is absorbed differently by different tissues, allowing doctors to see images of the body’s internal structures. CT scans use X-rays to produce cross-sectional images of the body.
Unlike traditional X-rays, CT scans provide much more detailed images, making it easier to diagnose certain conditions. MRI uses radio waves and powerful magnetic fields to create detailed body images. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use radiation. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body. It examines organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys. Nuclear medicine uses radioactive substances to image the body’s internal structures. It is often used to diagnose and treat cancer. Radiology is crucial in modern medicine, helping doctors diagnose and treat various conditions.
You are here:
home » radiology