Treatment Personalisation through Imaging
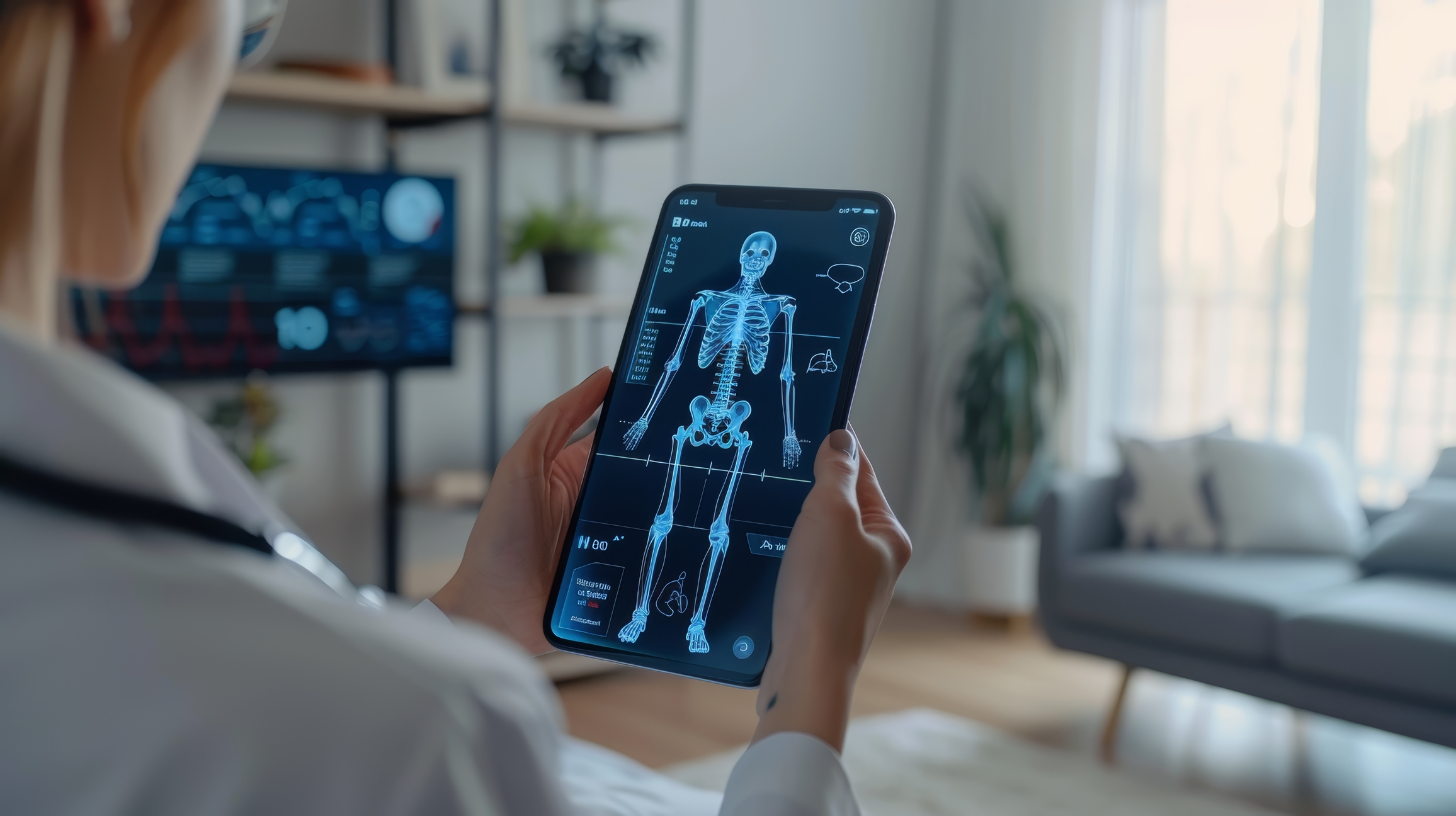
Medical imaging advances have revolutionised the healthcare approach, ushering in an era of personalised treatment. Treatment Personalisation through Imaging tailors therapeutic strategies to the unique characteristics of an individual, and imaging plays a pivotal role in achieving this precision. By providing detailed, real-time insights into the human body, imaging techniques such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Positron Emission Tomography (PET), Computed Tomography (CT), and functional imaging are redefining diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment.
At the heart of treatment personalisation lies the ability to stratify patients based on their disease profile. Imaging enables clinicians to differentiate between subtypes of conditions that may appear similar but respond differently to therapies. For instance, in oncology, PET scans can reveal the metabolic activity of tumours, helping to identify aggressive cancers that may require intensive treatment. Similarly, molecular imaging can detect specific biomarkers, enabling oncologists to predict whether a patient will likely benefit from targeted therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies or tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Moreover, imaging facilitates real-time monitoring of treatment efficacy. Functional MRI (fMRI) is increasingly used in neurological conditions to track changes in brain activity following interventions. This capability enables clinicians to adapt treatment regimens dynamically, ensuring that patients receive therapies that continue to be effective while minimising unnecessary side effects. Such adaptive approaches can significantly enhance outcomes in conditions like epilepsy, stroke rehabilitation, and mental health disorders.
Cardiology is another domain benefiting immensely from personalised imaging. Echocardiography and cardiac MRI allow clinicians to assess heart function with precision, enabling tailored interventions for conditions such as heart failure or congenital abnormalities. Imaging also underpins advances in interventional procedures, such as transcatheter valve replacements, by guiding the placement of devices in real time.
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with imaging further accelerates the shift towards personalisation. AI algorithms can analyse vast datasets from imaging studies, identifying patterns and anomalies that might elude human observers. These insights empower clinicians to make more accurate diagnoses and optimise treatment strategies. For example, AI-enhanced radiology tools can assess tumour margins or predict recurrence risks, supporting personalised decision-making.
In addition to improving therapeutic outcomes, imaging-based personalisation holds economic benefits. Identifying the most suitable treatment pathways reduces trial-and-error prescribing and prevents complications, ultimately lowering healthcare costs. It also enhances patient satisfaction by offering a more precise and practical approach to their care.
Despite its transformative potential, challenges remain in adopting treatment personalisation through imaging. High costs, the need for specialised training, and ethical considerations related to data privacy must be addressed. However, with continued advancements, imaging will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of personalised medicine, paving the way for a future where every patient receives care tailored precisely to their needs.
home » Treatment Personalisation through Imaging