Brain Imaging
Brain imaging techniques, or neuroimaging, are non-invasive methods for studying brain activity and anatomy. These techniques allow researchers and clinicians to visualize the brain and detect abnormalities or changes in brain function without invasive neurosurgery.
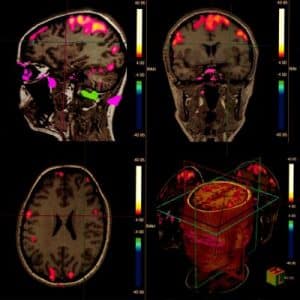
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is one of the most commonly used brain imaging techniques. It measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen supply in response to neural activity. This technique has high spatial resolution and can identify specific active brain regions during certain tasks or experiences. It is used to study neurological and psychiatric conditions, including depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
Computed tomography (CT) scanning is another brain imaging technique that uses X-rays to create 2D and 3D images of the brain. CT scans can reveal significant brain features, such as tumours, haemorrhages, and other structural abnormalities. However, CT scans are less effective in resolving the brain’s structure and are not typically used for studying brain function.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a brain imaging technique that uses short-lived radiotracers to map functional processes in the brain. Regions of high radioactivity are associated with brain activity. PET is used to study brain function and metabolism and is often used to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurological disorders.
Electroencephalography (EEG) measures the brain’s electrical activity by recording from electrodes placed on the scalp. The electroencephalogram (EEG) represents an electrical signal from many neurons. EEG is commonly used to diagnose and monitor seizure disorders and to study sleep, memory, and other cognitive functions.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a brain imaging technique that measures the magnetic fields generated by electrical activity in the brain. This technique uses susceptible devices known as SQUIDs (Superconducting QUantum Interference Devices) to detect the magnetic fields. MEG has high temporal resolution and is used to study brain function in healthy individuals and patients with neurological disorders.
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is an optical brain imaging technique that measures changes in blood oxygenation in the brain. fNIRS has high temporal resolution and can be used to study brain function in infants and young children. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is another optical technique that provides high-resolution images of the brain and can be used to study retinal diseases.
In conclusion, brain imaging techniques have revolutionized our understanding of the brain and its functions. These non-invasive techniques are used in research and clinical settings to diagnose and monitor neurological and psychiatric disorders, study brain function, and guide treatment decisions. Each technique has advantages and disadvantages, and researchers and clinicians often use a combination of techniques to understand brain function and anatomy.
You are here:
home » brain imaging