Da Vinci Surgical System
The Da Vinci Surgical System, a groundbreaking robotic-assisted surgical platform, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2000, revolutionizing minimally invasive surgery. This state-of-the-art system was named after Leonardo da Vinci, the renowned artist and scientist who was also an avid student of human anatomy. The system’s primary objective is to enhance surgical precision, dexterity, and control, allowing surgeons to perform intricate procedures through tiny incisions of just 1-2 centimetres.
The Da Vinci Surgical System is widely used in various surgical disciplines, including urology, cardiology, and gynaecology. The system’s advanced capabilities have transformed prostatectomies, cardiac valve repair, and gynaecological operations. Nearly 5,000 Da Vinci Surgical Systems are being utilized in clinical settings worldwide, costing approximately $1.5 million for each unit.
The surgical robot has many applications, including pyeloplasty, cystectomy, radical prostatectomy, nephrectomy, and ureteral reimplantation. Additionally, it has been employed in sacrocolpopexy, myomectomy, hysterectomy, hiatal hernia repair, and transoral robotic surgery (TORS) for head and neck cancer treatment. The versatility and precision offered by the Da Vinci System have made it an indispensable tool in the modern surgical landscape.
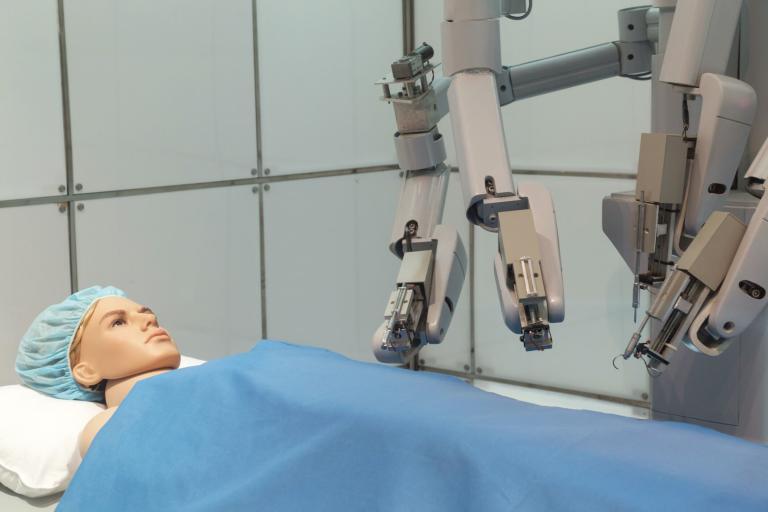
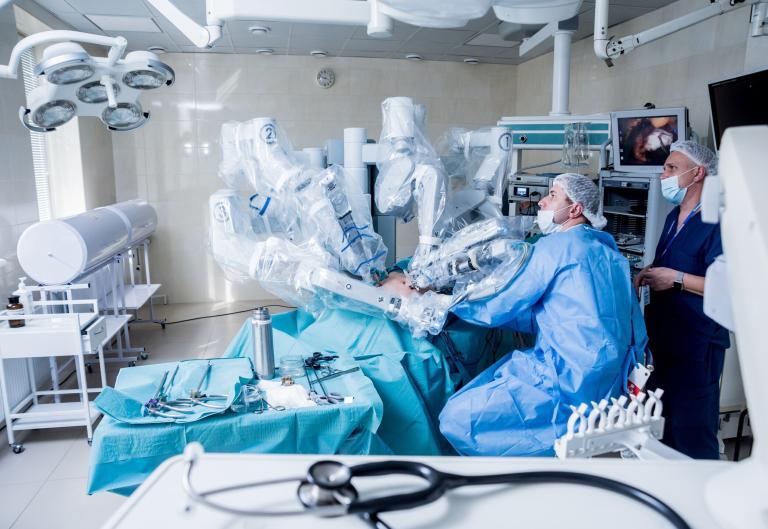
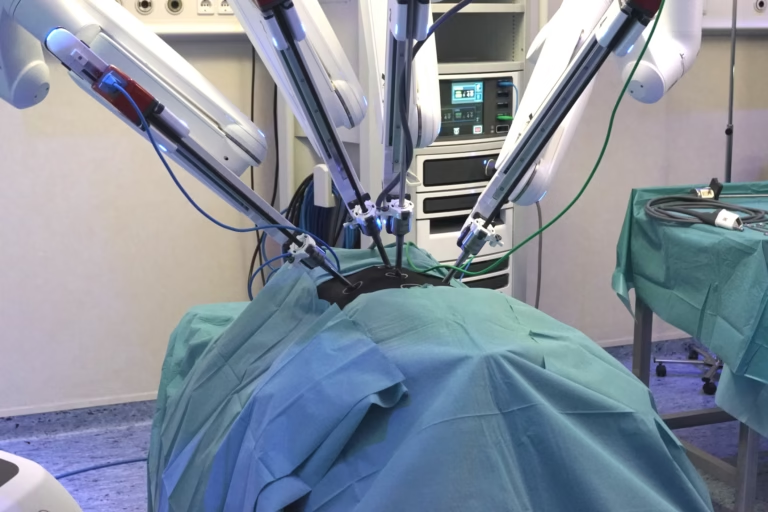
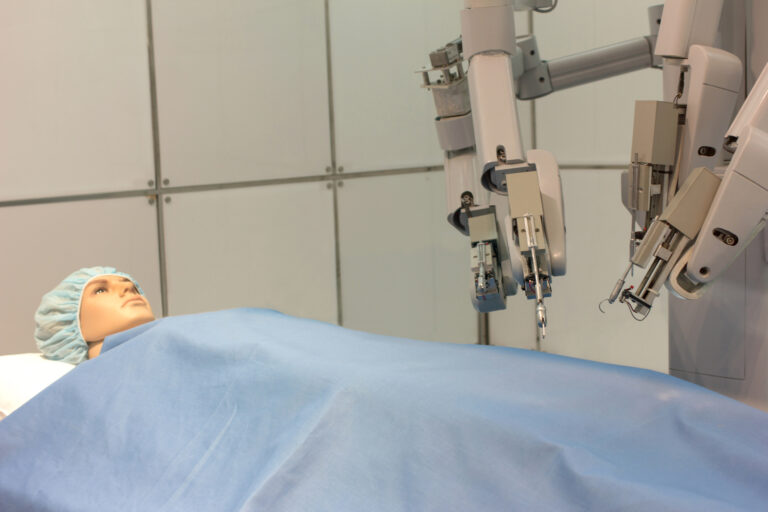
The surgical system comprises two main components: the surgeon’s console and the patient-side cart, featuring four interactive robotic arms. Three arms are designed to hold and manipulate various surgical instruments, such as scissors, graspers, and scalpels. The fourth arm controls the 3-D high-definition cameras, which provide the surgeon with a detailed, immersive view of the surgical site.
Sitting at the console, the surgeon manipulates the robotic arms to perform the surgery on the patient. The system translates the surgeon’s hand movements into precise, scaled-down motions, offering unparalleled control and reducing the likelihood of human error. By using the Da Vinci Surgical System, surgeons can achieve better patient outcomes and reduce complications associated with traditional surgical methods.
One prime example is the use of the robotic system for performing hysterectomies in benign conditions. This minimally invasive approach has been shown to reduce blood loss, postoperative pain, and recovery time while lowering the risk of complications compared to conventional surgery.
home » da Vinci Surgical System