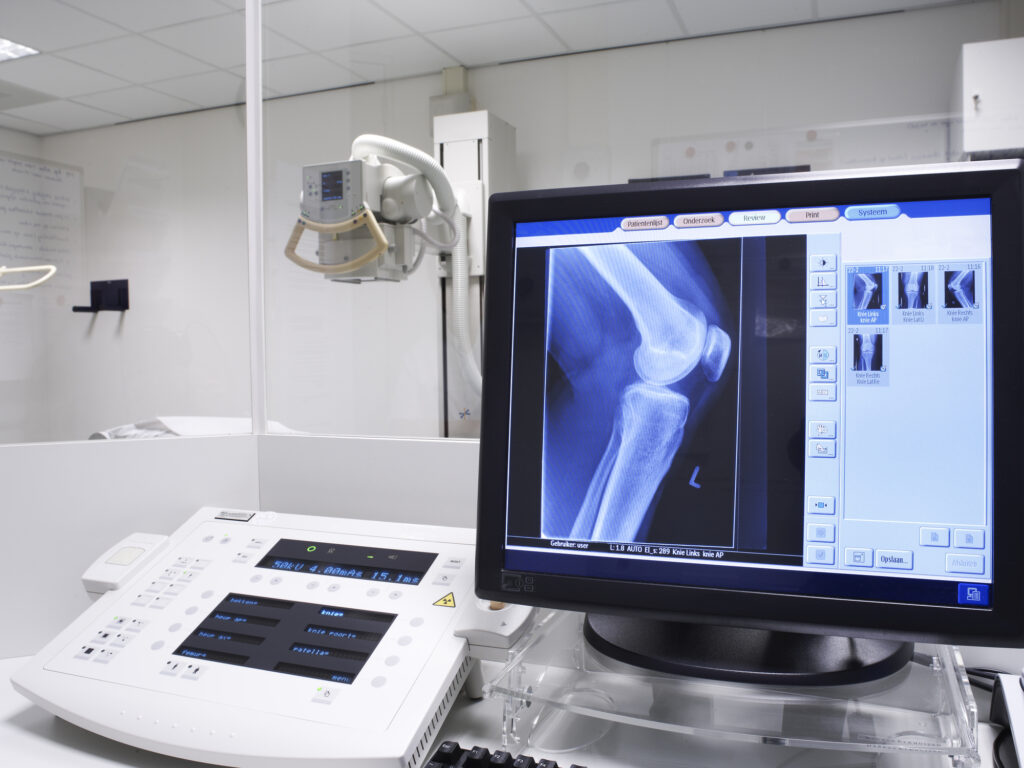
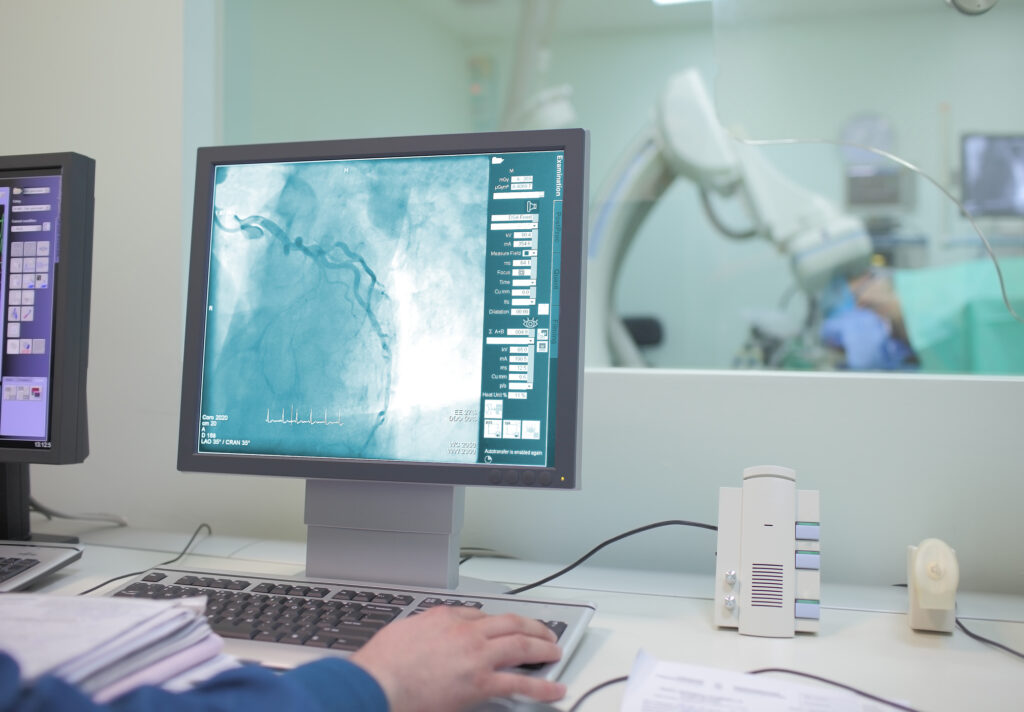
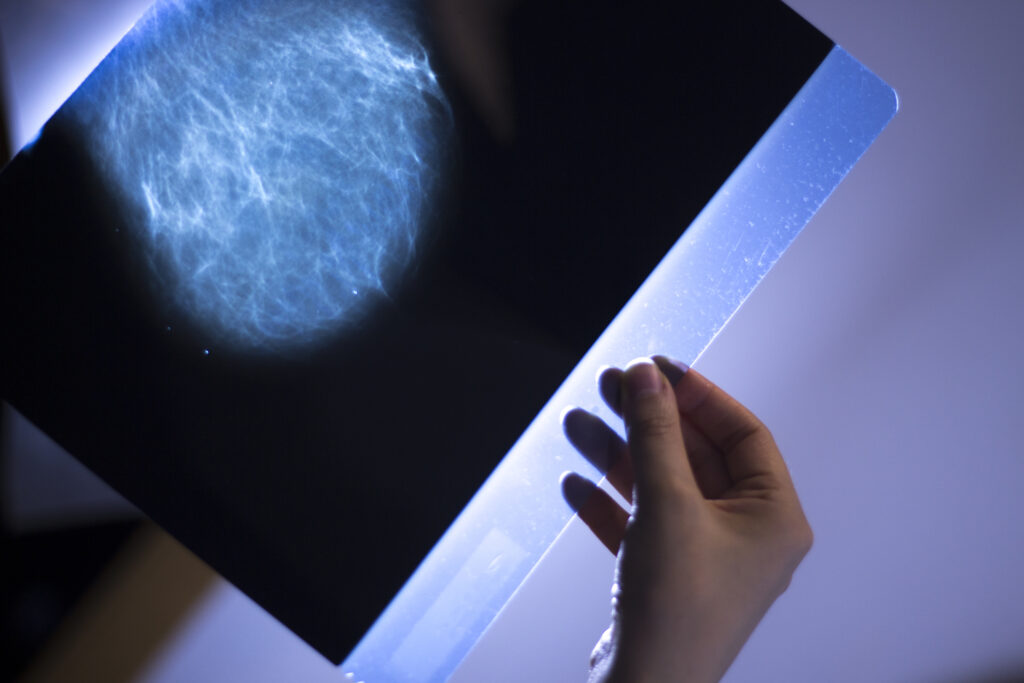
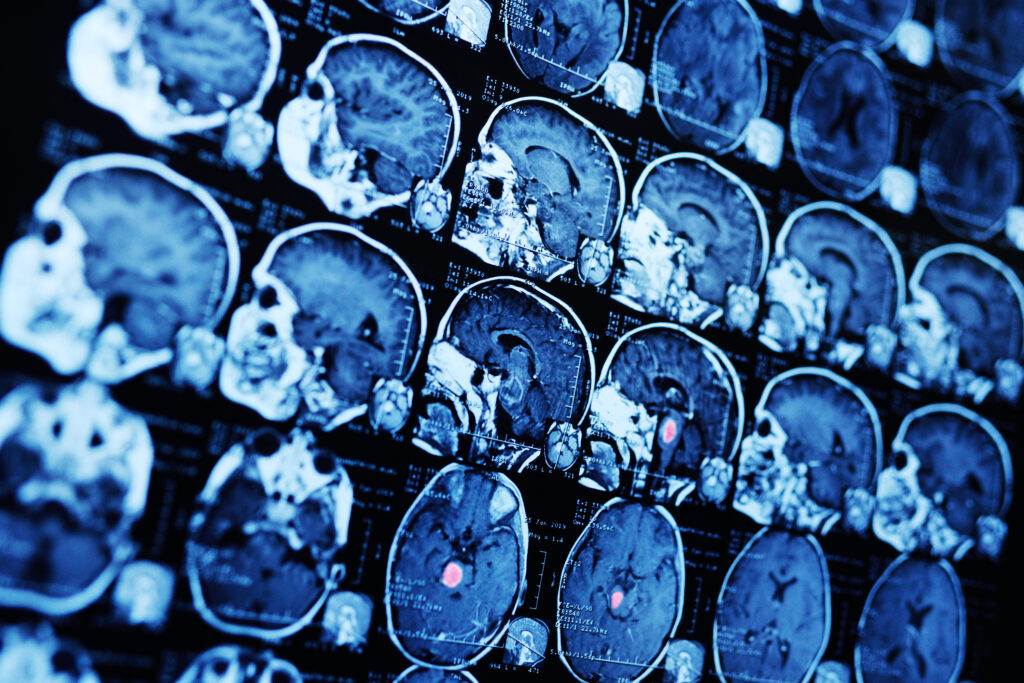
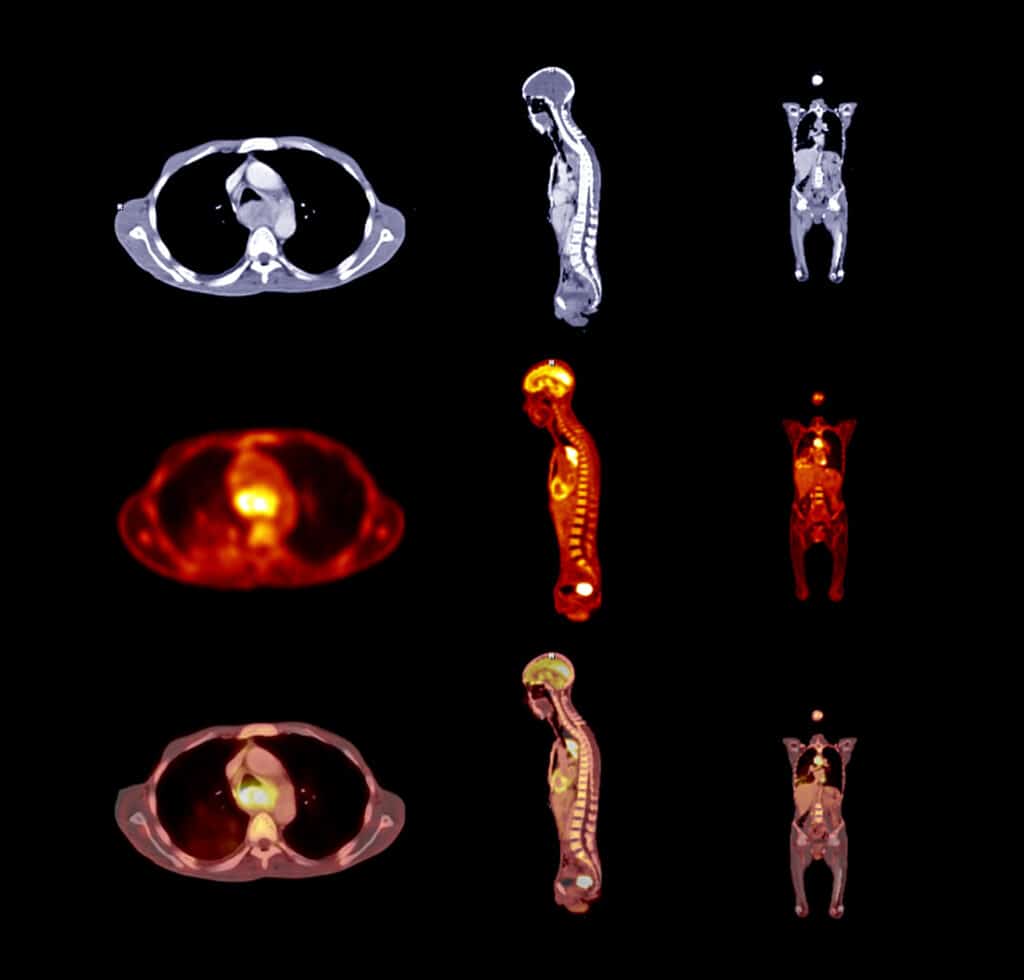
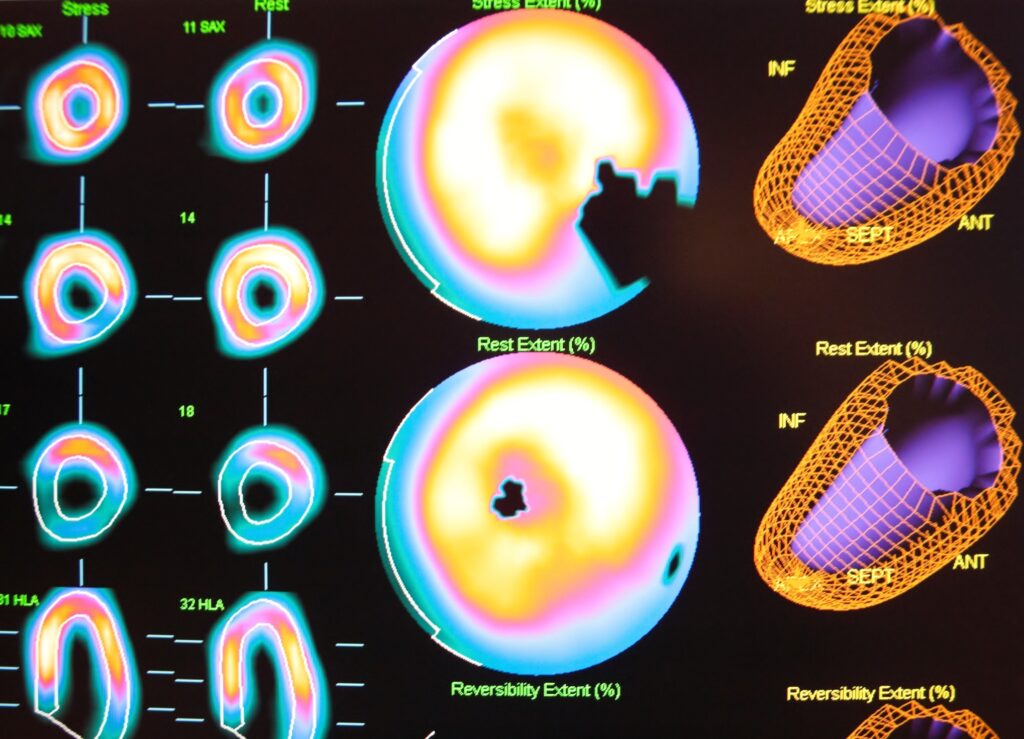
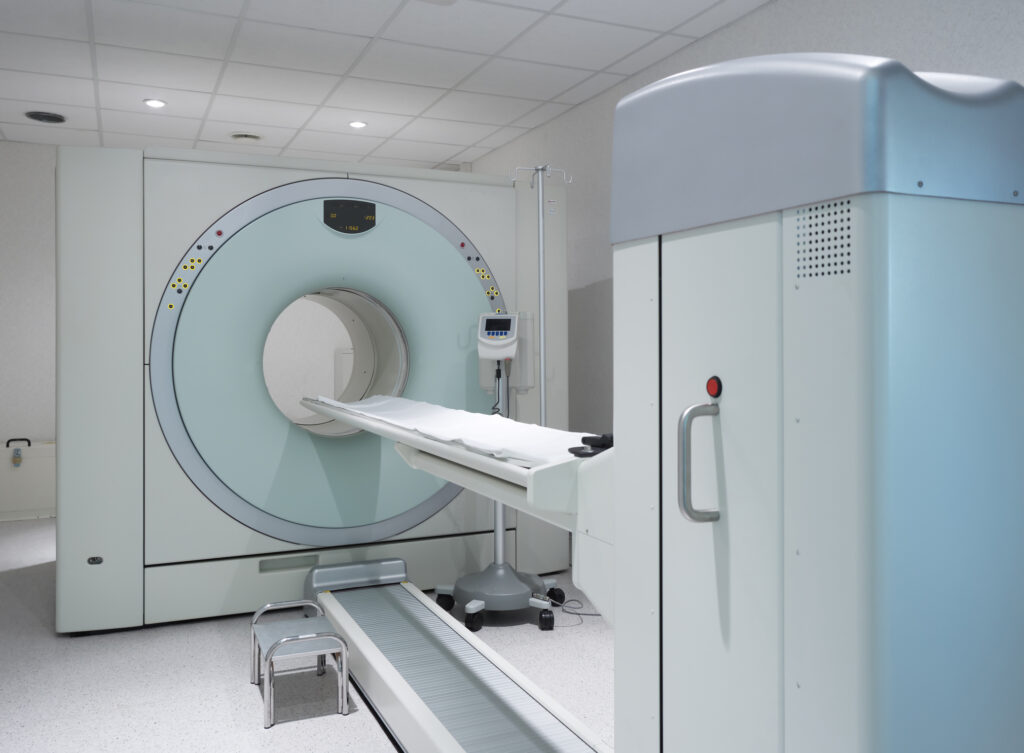
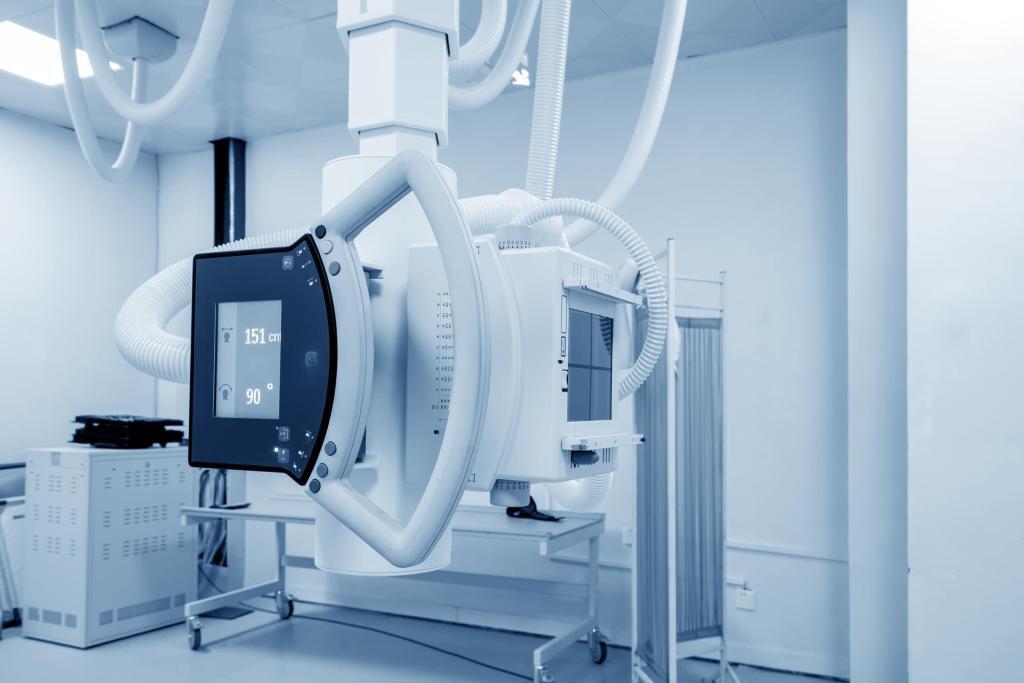
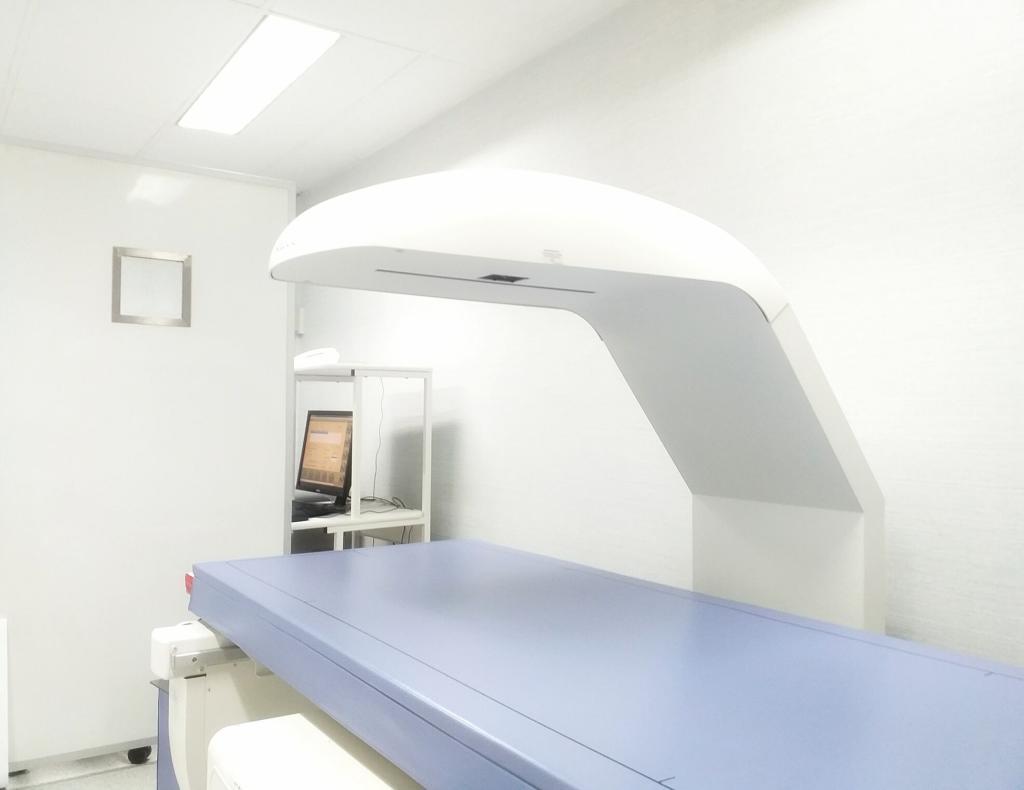
Imaging Techniques Used to Diagnose and Stage Blastoma Tumours
Blastoma tumours require advanced imaging techniques like MRI, CT, PET, and ultrasound for accurate diagnosis and staging.
Advances in Medical Imaging Technology: Unlocking the Mysteries of the Human Body
Advances in medical imaging technology have significantly improved diagnostic accuracy, enabling earlier detection and more personalised treatments.
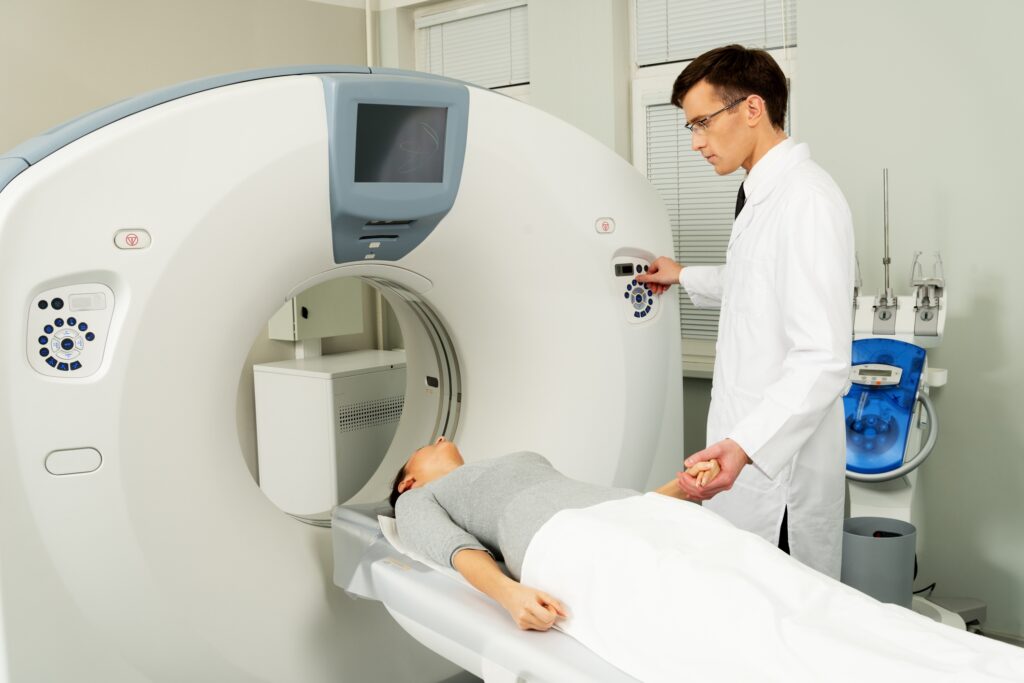
Mobile CT Scanners: Transforming Diagnostics for Any Location
Mobile CT scanners are revolutionising healthcare by providing rapid, accessible diagnostics in remote, emergency, and disaster settings worldwide.
Medical Imaging: What You Need to Know About the Technology Behind the Diagnosis
Discover how medical imaging for diagnosis has transformed healthcare with advanced technologies like MRI and CT scans.
What Science Says About Facial Features and Everyday Confidence
Learn about the role of facial confidence in interpersonal dynamics and how it affects our perception and communication. Image for illustration only. Person depicted is a model.
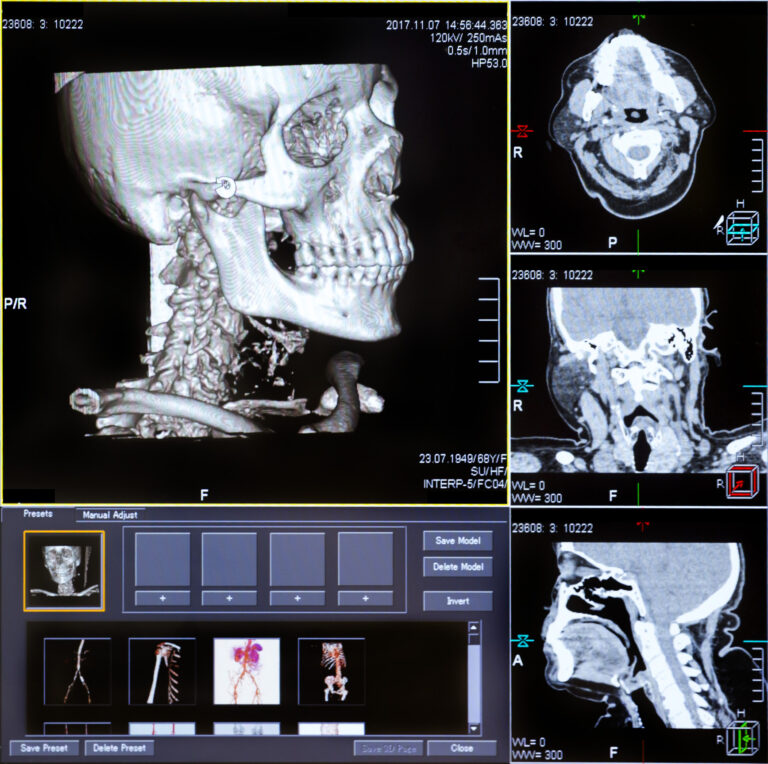
Sharper Images, Safer Scans: The Cutting Edge of Diagnostic Imaging Physics
Uncover the vital role of Diagnostic Imaging Physics in modern medicine with insights into imaging technologies and patient safety.