Alpha Particle Therapy
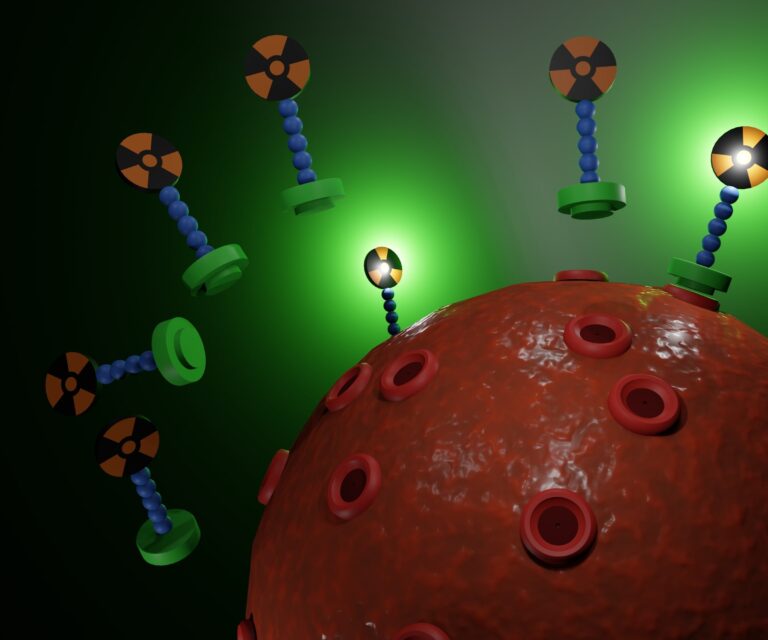
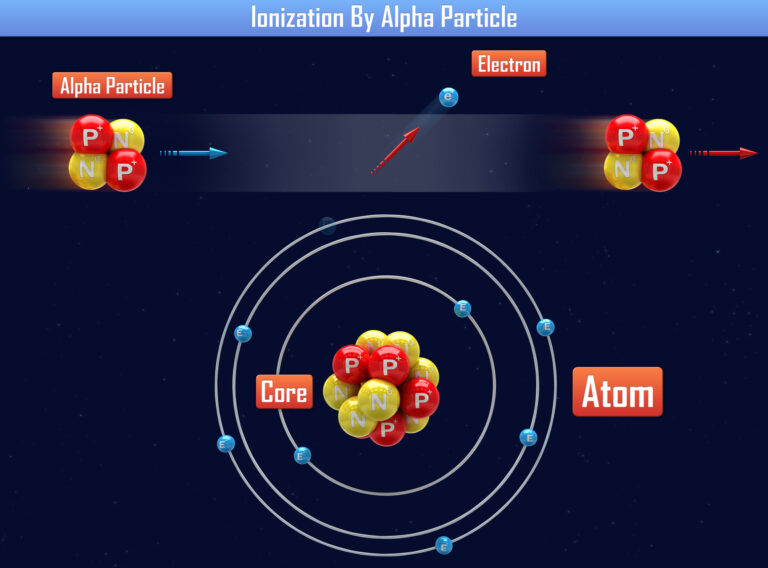
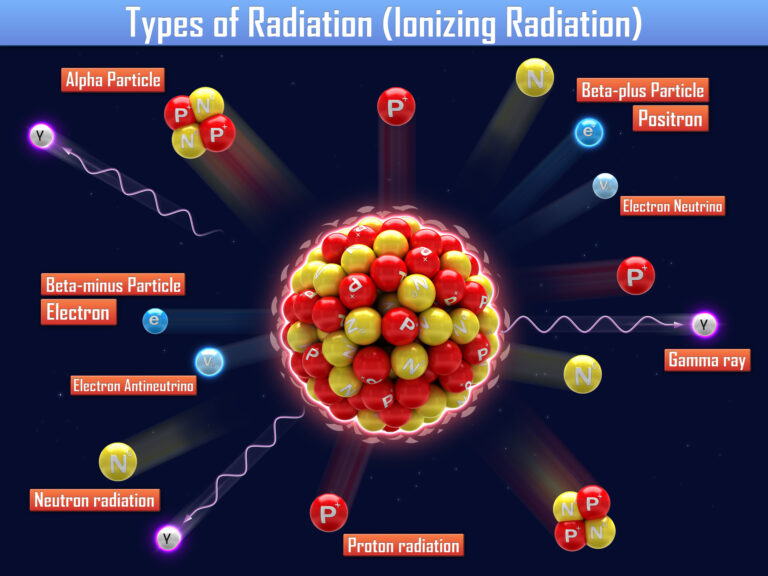
Alpha particle therapy, also known as alpha radiotherapy or alpha-emitter therapy, represents a pioneering approach in the field of cancer treatment. This form of therapy utilises alpha particles — highly energetic helium nuclei — to target and destroy cancerous cells with high precision. The distinct physical properties of alpha particles, particularly their substantial mass and charge, enable them to deliver a concentrated dose of radiation over a very short range, typically a few cell diameters. This allows for maximal damage to tumour cells while minimising the impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
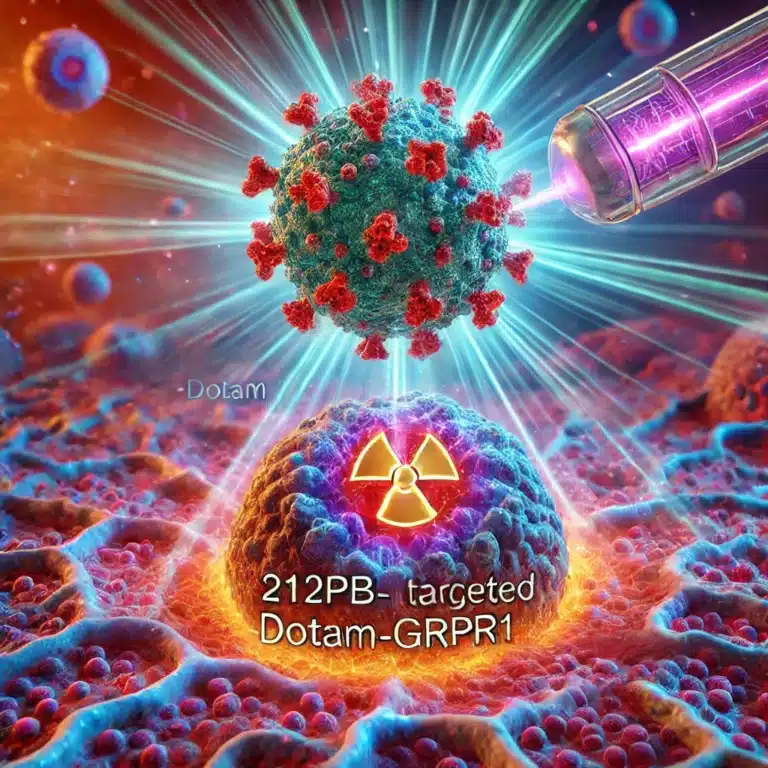
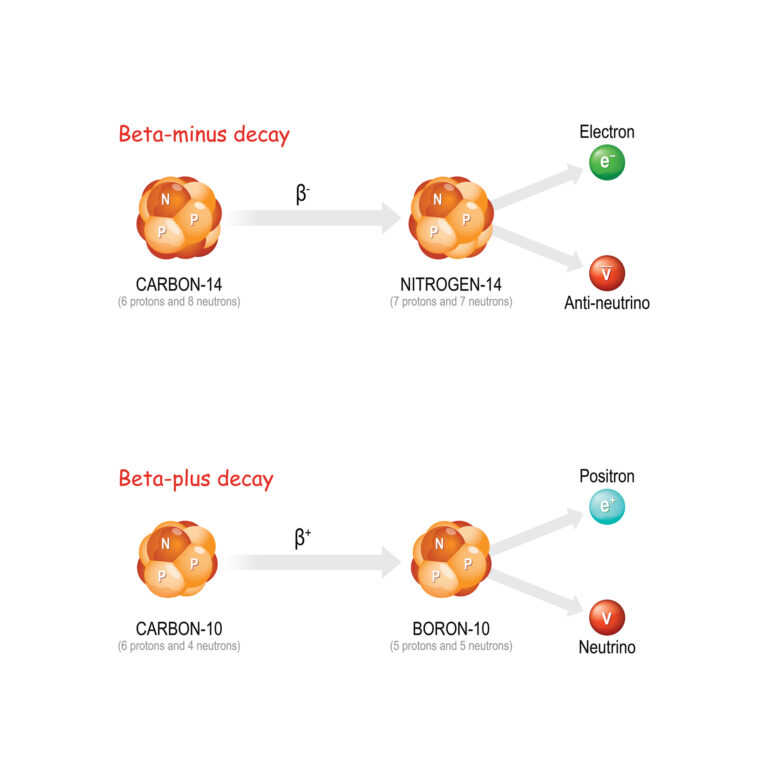
The concept of alpha particle therapy is grounded in the principle of targeted cancer treatment. Alpha-emitting isotopes are linked to molecules that specifically target cancer cells, such as antibodies or ligands that bind to tumour-specific antigens. Once these isotopes are internalised by the cancer cells, the emitted alpha particles cause double-stranded breaks in the cells’ DNA, inducing apoptosis or cellular death. This mechanism is particularly effective against aggressive and micrometastatic cancers that are resistant to conventional therapies.
One of the notable alpha-emitting isotopes used in clinical applications is Radium-223. Approved for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer that has spread to bones, Radium-223 demonstrates a capacity to extend patient survival while also providing palliative benefits. The therapy is well-regarded for its ability to target bone metastases with high precision due to radium’s bone-seeking properties.
Even though it has promising therapeutic benefits, alpha particle therapy does face several challenges and limitations. The production of alpha-emitting isotopes is complex and costly, as it often requires a cyclotron or a nuclear reactor. Furthermore, the handling and transportation of these isotopes demand stringent safety protocols to protect medical staff and patients from radiation exposure. Additionally, the short half-life of many alpha emitters necessitates their rapid use after production, posing logistical challenges.
Research and development in alpha particle therapy are continuously evolving, with numerous clinical trials underway to explore its efficacy across a broader spectrum of cancers. The development of new targeting molecules and the discovery of more suitable alpha-emitting isotopes are critical to expanding the applicability of this therapy. Moreover, advancements in molecular biology and cancer genomics are likely to enhance the selectivity and effectiveness of the targeted delivery mechanisms.
In conclusion, alpha particle therapy offers a promising and highly targeted treatment modality for cancer. It has the potential to improve outcomes for patients with advanced and resistant forms of the disease. As research progresses, it promises to become an integral part of cancer therapy, particularly in cases where traditional treatments have failed.
home » Alpha Particle Therapy