Myocardial Perfusion
Myocardial perfusion refers to blood flow in the heart muscle, also known as the myocardium. The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood to the rest of the body, and it requires a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients to function correctly. Myocardial perfusion ensures that the heart muscle receives an adequate blood supply.
The coronary arteries, which branch off the aorta and encircle the heart, supply blood to the heart muscle. These arteries supply blood to the myocardium during diastole, or the relaxation phase of the heart’s pumping cycle. During diastole, the coronary arteries expand to allow blood to flow into the heart muscle. Myocardial perfusion is critical to the health of the heart. The heart muscle can become damaged without an adequate blood supply, leading to angina, heart attack, and heart failure.
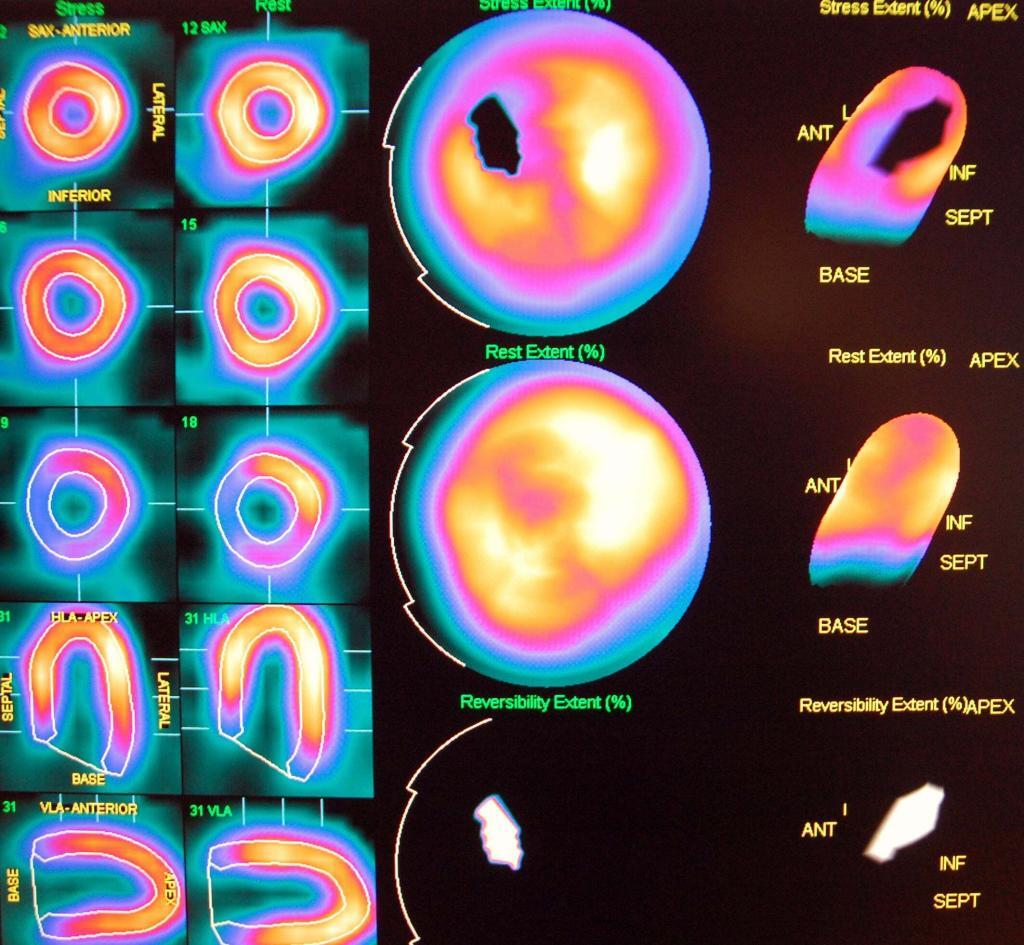
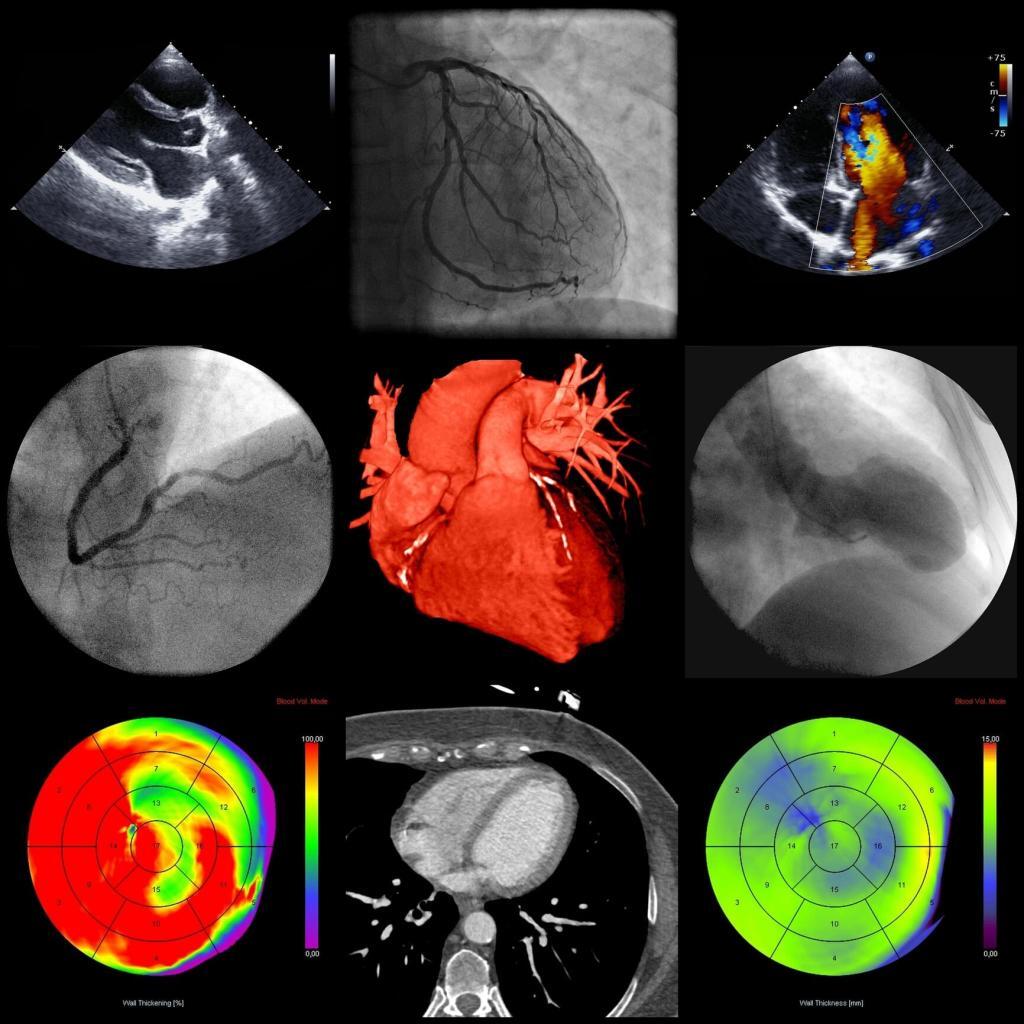
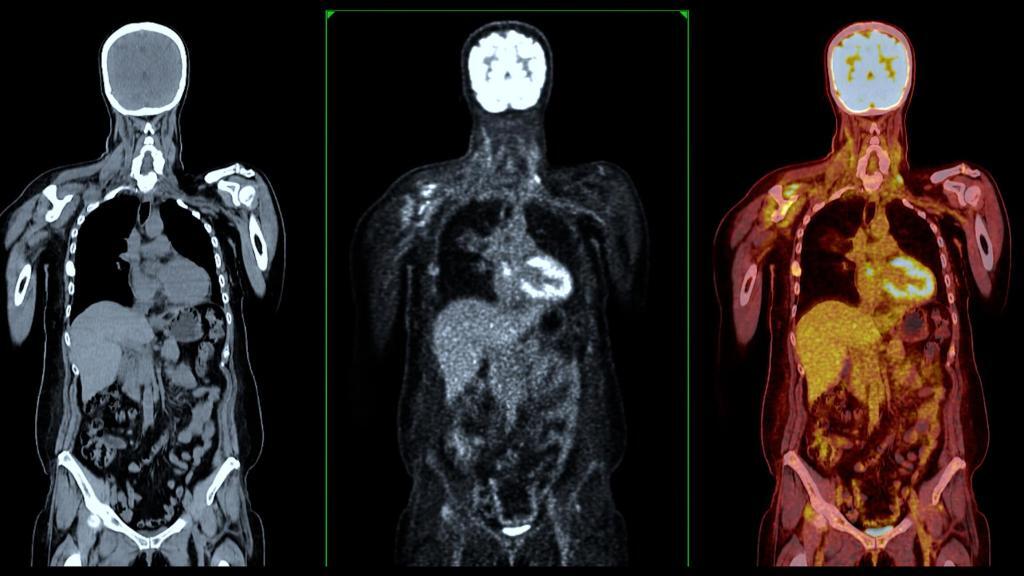
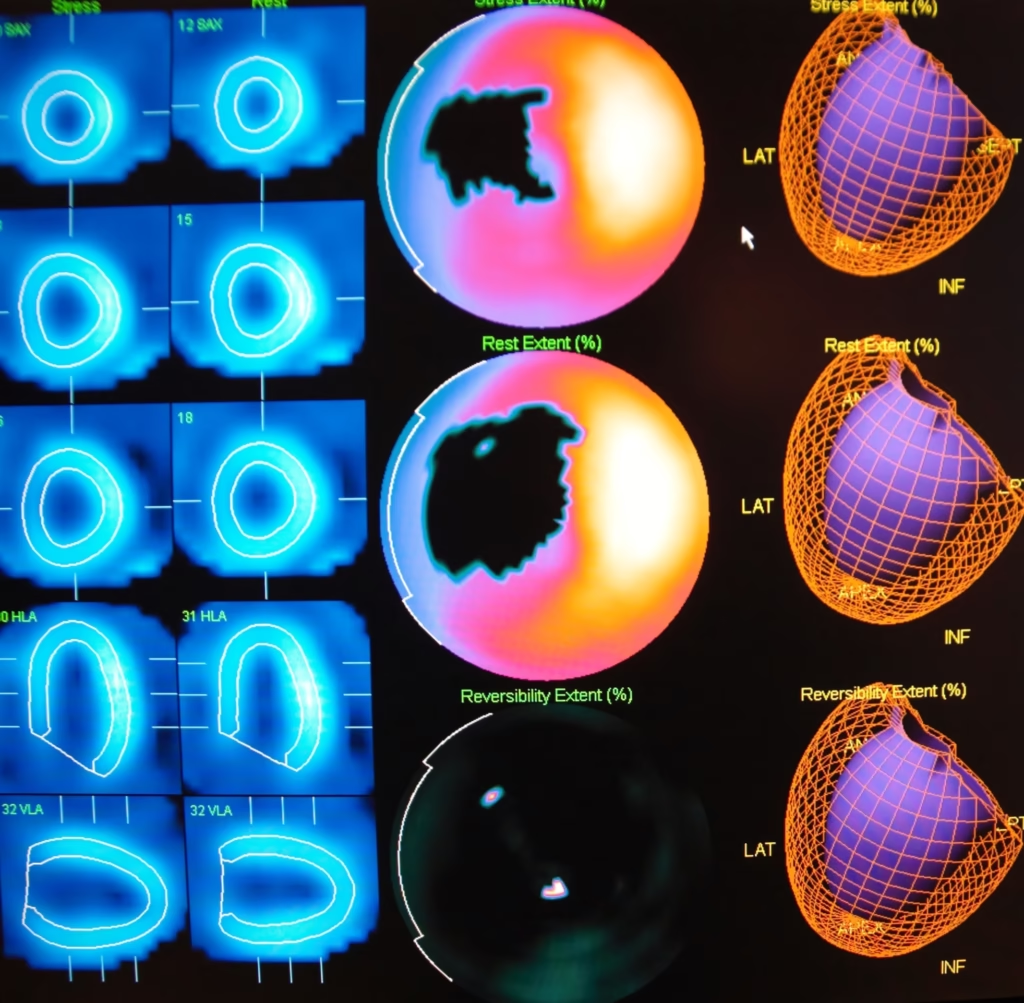
Myocardial perfusion is also crucial for diagnosing heart conditions, as it can provide information about the blood flow to different areas of the heart. Myocardial perfusion can be assessed using a variety of imaging techniques. One common method is myocardial perfusion imaging, which uses a radioactive tracer to visualise blood flow in the heart muscle.
During this test, the tracer is injected into the bloodstream and tracked as it flows through the coronary arteries and into the heart muscle. The tracer emits radiation, which is detected by a special camera to produce images of the heart.
Another method of assessing myocardial perfusion is coronary angiography, which uses a dye injected into the coronary arteries to visualise blood flow. This test may help identify blockages in the coronary arteries, which can cause reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. In addition to diagnostic imaging, treatments are available to improve myocardial perfusion.
One standard treatment is coronary artery bypass graft surgery, which involves rerouting blood flow around a blocked or narrowed coronary artery. Another treatment option is percutaneous coronary intervention, which consists of using a balloon catheter to open up a blocked or narrowed artery and then placing a stent to keep the artery open.
You are here:
home » myocardial perfusion