Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Differentiated thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the thyroid gland, which is located at the base of the neck. This type of cancer is called differentiated because it arises from thyroid cells that have already started to differentiate or become specialised. There are two main types of differentiated thyroid disease: papillary thyroid cancer and follicular thyroid cancer.
However, papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type, accounting for approximately 80% of all thyroid cancers. Follicular thyroid cancer is less common, accounting for approximately 10% of all thyroid cancers. The exact cause of thyroid cancer is not fully understood. However, it is believed that genetic mutations and exposure to radiation may increase the risk of developing this type of cancer. Symptoms of thyroid cancer could include a lump or swelling in the neck, breathing, hoarseness, and difficulty in swallowing. However, in many cases, there may be no symptoms present.
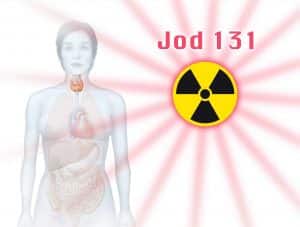
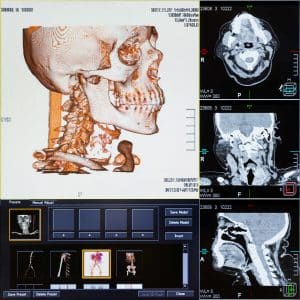
Diagnosis of thyroid cancer usually includes blood tests and imaging tests such as CT scan, MRI and ultrasound. A biopsy can also be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment for differentiated thyroid cancer typically involves surgery to remove the thyroid gland, followed by radioactive iodine therapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells. External beam radiation therapy or chemotherapy may also be used in some cases.
The prognosis for thyroid cancer is generally good, with a five-year survival rate of approximately 98%. However, the prognosis may depend on several factors, including the stage of cancer, the age of the patient, and the presence of any other medical conditions.
Regular follow-up appointments are important for patients with differentiated thyroid cancer to monitor for recurrence and ensure their thyroid hormone levels are within normal range. In some cases, long-term hormone replacement therapy may be necessary to replace the hormones no longer produced by the thyroid gland.
You are here:
home » differentiated thyroid cancer