Computed Tomography
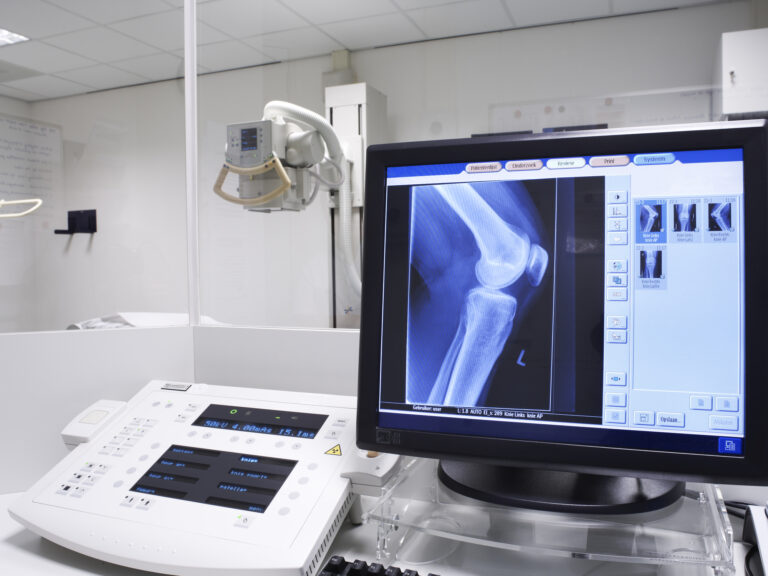
Computed Tomography (CT) was invented by Allan M. Cormack and Godfrey N. Hounsfield in 1972 and is a popular and essential tomographic medical imaging modality. Over the past decade, significant advancements in CT have been due to improvements in speed, radiation dose, slice count, and image quality.
The first CT scans lasted approximately 30 minutes, whereas today, the apex of CT scanners takes just 1-2 seconds to collect images. A pivotal breakthrough concerning radiation dose reductions of 70%- 80% in these modern CT scanners uses techniques based on hybrid Iterative image reconstruction methods. In addition, more dose-efficient CT detector materials with larger dimensions have assisted with lower CT patient radiation dosages without affecting image quality at the same time.
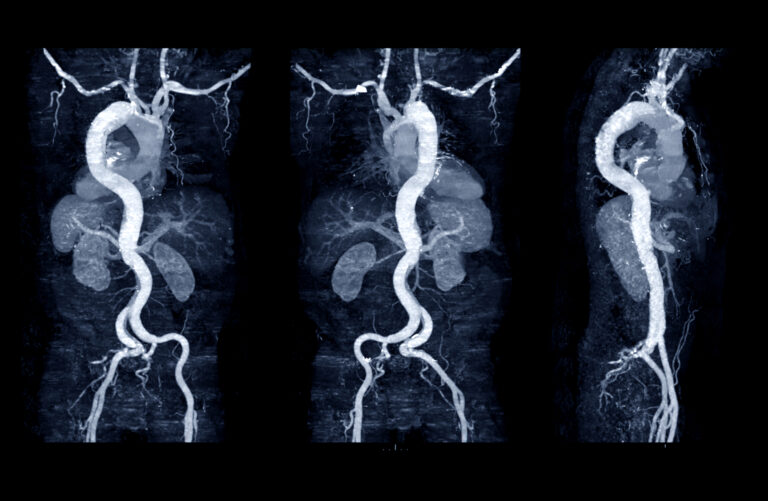
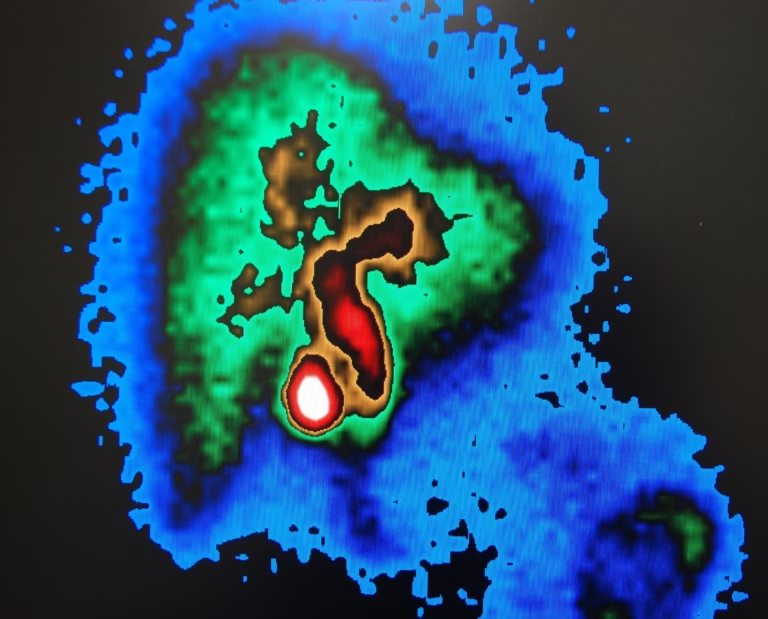
Computed Tomography is used in the clinical setting to perform CT Perfusion imaging to diagnose acute ischaemic stroke. Computed Tomography perfusion of a tumour is used to evaluate the impact of modern cancer therapy regimens.
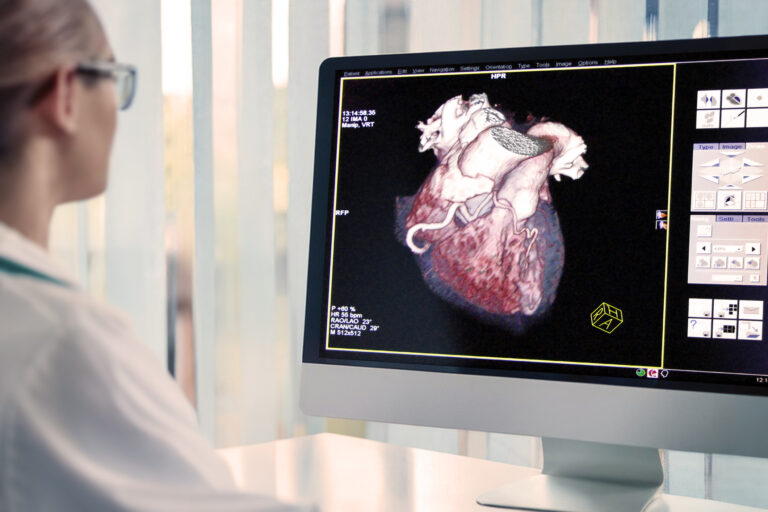
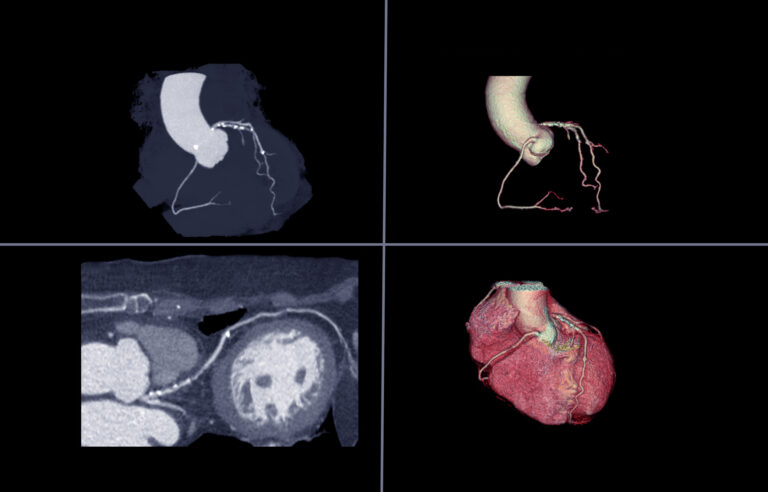
Single-heartbeat CT coronary angiography has shown very high specificity and sensitivity for coronary artery disease. PET/CT for cancer treatment planning allows physicians to have a much more accurate understanding of the extent of a patient’s disease.
Hybrid imaging will enable clinicians to evaluate metabolic and anatomical functions concurrently. These fusion images provide a rapid assessment of response to therapy or myocardial perfusion. Computed Tomography simulation systems include 3-D CT imaging and IMRT.
However, CT simulation has become essential in stereotactic radiosurgery by targeting radiation around sensitive structures.
Furthermore, radiologists are able to have CT data printed in 3-D to assist with surgical planning and implant prototyping.
home » computed tomography