Alzheimer’s Disease
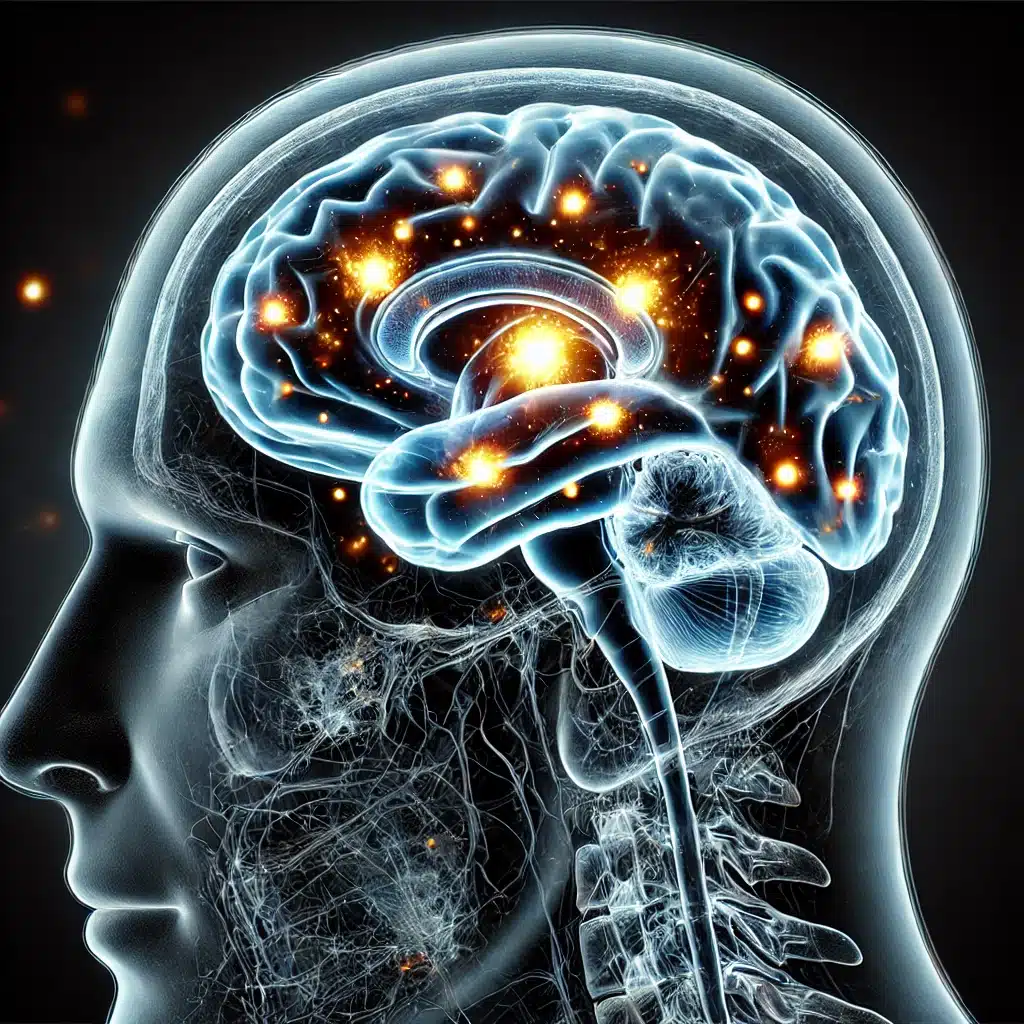
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive brain disorder that slowly diminishes cognitive skills. In the majority of people with Alzheimer’s, symptoms first appear in their 60s, and this is a leading cause of death in the US. Causes of dementia depend on various brain changes, which can lead to vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia and frontotemporal disorders.
In 1906, Alois Alzheimer noticed various changes in the brain tissue of a woman who had died of mental illness. He found several abnormal clumps, now known as amyloid plaques, and tangled bundles of fibres called neurofibrillary (tau, tangles): these are the main features of Alzheimer’s disease. Additional features include loss of connections between neurons in the brain.
The main function of neurons is to transmit information between the brain, muscles and organs in the body. It is thought that changes to the brain occur at least a decade before cognitive problems appear. During the preclinical stage of Alzheimer’s disease, people are mostly symptom-free; however, toxic changes are building up in the brain. These abnormal deposits of protein form amyloid plaques and tau tangles throughout the brain’s network, causing the neurons to lose connectivity with other neurons and subsequently die.
Most neurofibrillary (neural damage) occurs in the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex, which is essential in memory formation. Neuron death also extends to other brain regions, resulting in an overall reduction of brain tissue. Several studies have not identified a specific gene which causes the late onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Nevertheless, possessing one of the forms of the apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene, such as the APOE ε4 gene, does increase a person’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. In order to diagnose Alzheimer’s, the patient will be required to undertake several brain scans, which include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) and, in some cases, a positron emission tomography (PET scan) to rule out any other possible causes for symptoms.
You are here:
home » Alzheimer’s disease